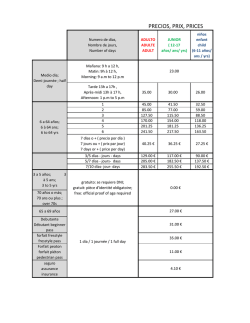
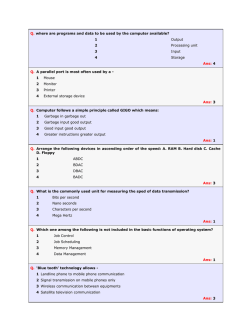
Download PDF File
DISCUSSION_FORUM_FOR_CLERK_INTERVIEW_ IBPS CLERK 4 INTERVIEW PREPARATION DISCUSSION FORUM https://www.facebook.com/groups/clerkinterview2015/ WEBSITE : www.aspiranthub.com 1 .What do u understand by Bank ? 2. What is the difference between RBI and Commercial banks ? 3. What is Repo Rate ? 4. What is Bank Rate ? 5. What is Reverse Repo Rate ? 6. What is CRR ? 7. What is SLR ? 8. What is MSF ? 9. How change in rate will effect Inflation ? 10. What are the types of banking ? 11. How increasing Repo rate or reverse repo rate will gonna effect Inflation ? 12. What is NPA ? 13. What are the types of NPA ? 14. What do you understand by Liability ? 15. What do you understand by Assets ? 16. Why Public sector banks are having more NPAs then Private sector ? 17. Can you explain about Gross NPA and Net NPA ? 18. Who are Business Correspondents ? 19. Is their any difference between Borrower and Customer in banking sector ? 20. Which one will you choose if u want to do banking - Internet or Traditional Banking ? 21. Do you think PMJDY will be useful scheme for banking sector ? 22. What you can tell us about Financial Inclusion ? 23. Why Repo rate is always 1 % Less than MSF ? 24. Could you explain us about Collateral ? 25. Have u ever heard about SARFAESI ACT and DRT , if yes then what are these ? can u explain these terms ? 26. What is LAF ? 27. What is OMO ? 28. What is MSS ? 29. What do you understand by Overdraft ? www.aspiranthub.com 30. Overdraft facility given to Current or Saving or Both type of accounts ?If yes , any specific conditions ? 31. What do you understand by NEFT ? 32. What do you understand by RTGS ? 33. What do you understand by ECS ? 34. What do you understand by CTS ? Which is more better process - Traditional process of clearing cheque or Electronic process and why ? 35. Who is Drawer , Drawee and Payee ? 36. Cheque vs DD ? What are their uses ? 37. What are bank's Tier-1 Capital ? 38. What are bank's Tier-2 Capital ? 39. What do you understand by Risk Weighted Asset ? 40. What is CRAR or CAR ? 1 . What do u understand by Bank ? Ans : Bank is a financial institution which accept deposit n lend to needy persons bt nw a days banks provides various typs of services under one roof lyk insurance mutual fund gold coin remittance forex etc OR - It's a financial institution which accepts money from the public in the form of deposits and d same in lent for purpose of investment 2. What is the difference between RBI and Commercial banks ? Ans : Rbi is the appex banks , banker to banks/govt having sole right to issue currency control credit and money supply commercial banks are fulfledge banks providing banking servicess to individuals n corporate 3. What is Repo Rate ? Ans : Repo rate is the rate at which the central bank of a country lends money to commercial banks in the event of any shortfall of funds. 4. What is Bank Rate ? Ans : Interest rate at which a central bank will advance short term loans to commercial banks. Changes in bank rate are reflected in the prime lending rates offered by commercial banks, which in turn affect investments such as bank deposits, bond issues, mortgages. This term has largely been replaced by newer terms baserate www.aspiranthub.com and prime rate. 5. What is Reverse Repo Rate ? Ans : Reverse repo rate is the rate at which the central bank of a country (RBI in case of India) borrows money from commercial banks within the country. 6. What is CRR ? Ans : Ratio of total ndtl of a bank kept wid Rbi in the form of cash is crr. Right now it is 4%. If increased liquidity decrease nd vice versa. 7. What is SLR ? Ans : Statutory liquidity ratio (SLR) is the Indian government term for reserve requirement that the commercial banks in India require to maintain in the form of gold or government approved securities before providing credit to the customers. OR - min % of bank's NTDL that they must invest in liquid securities ie govt securities and other approved securities 8. What is MSF ? Ans : The rate at which rbi lends to commercial banks for overnight..it is also collateral based lending and 1 % more than repo rate 9. How change in rate will effect Inflation ? Ans : less intrest rate leads to more borrowings leads to more money in market leads to more inflation more intrest rate leads to less borrowing leads to leass money in market same in case of slr and crr more money in market inflation will be more OR - As interest rates changes like inc of CLR srr then the banks have to keep their some amount vth RBI..as interest rates are higher then the money vch thybhave to keep vth the RBI higher so there is less amont with the banks to lend so they increase the lending rates so inflation vl be cntrled OR - change in policy rate like crr,slr will require banks to park more money with rbi or invest more in gsec ,will lead to less money in circulation hance inflation controlled. change in LAF will attract banks to park more money in safe hand of rbi, banks also increase rate of ibtrest on deposits means people will start saving money in banks ,money will b drain www.aspiranthub.com out from markey 10. What are the types of banking ? Ans : In focus - Retail banking, Wholesale banking Rest many names are too - like Parallel banking, social banking , merchant banking, universal banking 11. How increasing Repo rate or reverse repo rate will gonna effect Inflation ? Ans : if repo rate is increased borrowing from rbi will be costlier,also rbi will pay more ibterest on deposits of banks ubder reverse repo. so bank will increase rate of interest on deposits aswell as loan. people will stop obtaining loans as its costlier mean tym they will start saving with bank instead of consuption. inflation controlled OR - If repo rate will increase den loan will bcum costly for banks so dey will lend less money or lend money to public at high rates dis will absorb d liquidity frm market and if d reverse repo will increase bank would lyk to lend deir money to RBI and lend less in d market OR - Repo rate Increased - Bank will took less loan from RBI -- base rate will increase --- Inflation Controlled Reverse Repo rate Increased --- Bank will deposit more money to RBI (( soaking liquidity )) 12. What is NPA ? Ans : non performing asset- ie when loans turn into bad debts or borrowers fail to repay principal + intrest payment..here 90 days overdue criteria is followed..these r further divided into sub-standard assets, doubtful & loss assts 13. What are the types of NPA ? Ans : sub standard- NPA <12 months , doubtfull – NPA >12 months , lost assets- NPA greater than 2 years 14. What do you understand by Liability ? Ans : Liabilities means we have to pay it back like in banking terminology liabilities are deposits 15. What do you understand by Assets ? Ans : Assets are those which we own or which increase our earning capacity 16. Why Public sector banks are having more NPAs then Private sector ? www.aspiranthub.com Ans : Bcoz public sector banks do invest in ventures which r nt dat profitable plus risky lyk priority sector lending in which amt lend mostly turns out as bad debts 1. Due to less autonomy and more political intervention 2. Open to large Public sector lending for investment purpose 3. Providing subsidized loans in reference to Govt which is less in the case of Private sector Some more points : 1)Nexus between Bank officials n borrower. 2)No follow up after lending. 3)Under financing or over financing 4)Sometimes pressure from govt 5)No stricter recovery process. 17. Can you explain about Gross NPA and Net NPA ? Ans : Gross npa: principal+ interest incurred Net npa: only principal 18. Who are Business Correspondents ? Ans : Any intermediary who are authirised by banks to carry out banking activities on behalf of the bank. an nbfc or any individual or any shoap, institution can b authorised for the same 19. Is their any difference between Borrower and Customer in banking sector ? Ans : Customer is a wider term..it includes depositor as well as borrower while borrower is that customer of bank who is only coming for taking loan frm a bank OR yes there is a little difference , a customer of bank can be any person availing of bankibg services whether he has an a/c with the bank or not. also includes borrower. borrower r also custoner for banks who pop ups for borowing purposes OR All borrowers are customers but all customers are not borrowers.... As simple az dis 20. Which one will you choose if u want to do banking - Internet or Traditional Banking ? Ans : I wud use both the services as some work that can only be done by tradition banking and as internet banking is concerned it is the time & cost effective service. So if both the services are used acc to their sectors preference then banking will be more easier. www.aspiranthub.com 21. Do you think PMJDY will be useful scheme for banking sector ? Ans : yes its. as it will fetch more cheaper CASA funds for bank on which they can earn more money. 2ndly they got many new customers without expending much on ads they will keep using banks services and keep paying. OR - Yes it attracts lot of funds by d depositors nd by govt.subsidies,dis helps much to banks as d funds raised nd more money is available for lending thus more profit 22. What you can tell us about Financial Inclusion ? Ans : - FI - Providing banking services to all , but in priority to weaker sections of society so that they can take part in economic growth of country and can be directly benefitted , leading to less corruption practices 23. Why Repo rate is always 1 % Less than MSF ? Ans : Bcz - In MSF , while borrowing overnight Govt securities including SLR is kept while in Repo it is excluding SLR 24. Could you explain us about Collateral ? Ans : It is a physical assets which is to be mortgaged for borrowing purpose such as G-sec,land,machinery 25. Have u ever heard about SARFAESI ACT and DRT , if yes then what are these ? can u explain these terms ? Ans : - DRT came in 1993 on the recommendation of narasimhan committe,1991 . people could file cases here. but with the time DRT mei truckload of cases aane lage. then in 1998 on the recommendation of narsimhan committee II, SARFAESI Act was recommended which came into effect in 2002. under this act, lender can directly take the possession of the assets being mortgaged to recover the loan without going to any civil court. this act applies to loans above 10 lacs only. 26. What is LAF ? Ans : - LAF- Liquidity Adjustment Facility . it is a quantitative tool of RBI's monetary policy by which RBI controls the liquidity/money flow in the market. Under LAF, RBI has two tools :1 Repo Rate 2 reverse repo rate www.aspiranthub.com 27. What is OMO ? Ans : Open mkt operations performed by RBI to control supply of money in economy by sale /purchase of securities 28. What is MSS ? Ans : This schemecame into existence following a MoU between the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Government of India (GoI) with the primary aim of aiding the sterilization operations of the RBI. 29. What do you understand by Overdraft ? Ans : When an individual or company takes out more from an account and the balance drops below the allowed amount by the financial institution. 30. Overdraft facility given to Current or Saving or Both type of accounts ? If yes , any specific conditions ? Ans : Overdraft on both type of account..usually in current account but also available in PMJDY. The number of transactions are however limited in that account so can't be used for business purpose whereas overdraft in current account can be easily used for business transaction.. 31. What do you understand by NEFT ? Ans : NEFT - National Electronic Funds Transfer - It is used for transfering funds electronically from one account to another account Its payment based on DNS ( deferred net settlement )) , in batch processing , took more time than RTGS. Limit -- > Min - no limit , Max - no limit . For Transferring in Nepal A/c - max limit - 50 k 32. What do you understand by RTGS ? Ans : - RTGS - Real Time Gross settlement - It is used for transfering funds electronically from one account to another account, Real time- processing the instructions at the time they r received. "gross settlement"settlement of funds/ transfer occurs individually . thus it is faster than NEFT and mostly preferred by businessman . Min Limit- 2lacs. no max limit 33. What do you understand by ECS ? Ans : Ecs stands electronic clearing service. Used to do transactions that are repetitive or periodic in nature. Consists of 2 :- Ecs credit & ecs debit Ecs credit example--salary dena logo k bank acc mai www.aspiranthub.com Ecs debit --elect. Aur telephone etc bill pay krna 34. What do you understand by CTS ? Which is more better process Traditional process of clearing cheque or Electronic process and why ? Ans : Cheque truncation system is the process of stopying the pyshical movemnt of cheques instead of this there is movement of cheques through electronically by scanng them vth other details..to the receivers bank. It is better than traditional process bcz it takes less time 35. Who is Drawer , Drawee and Payee ? Ans : Drawer s d one who prepares d instrument n drawee who accepts it n payee to whom d payment s to b made OR - Drawer is the person who issues the cheque and drawee is the bank payee is the person on whom cheque is issued 36. Cheque vs DD ? What are their uses ? Ans : The following are the main differences between a cheque and a dd : 1. A cheque is issued by an individual,but a DD is issued by a bank. 2. A cheque is drawn by an a/c holder of a bank, whereas a draft is drawn by 1 branch of a bank on another branch of d same bank. 3. In a cheque, the drawer and the drawee are different persons. But in a draft both the drawer and the drawee are the same bank. 4. A Cheque can be dishonored for want of sufficient balance in the account. Whereas a draft cannot be dishonored. Hence there is certainty of the payment in the case of a demand draft. 5. Payment of a cheque can be stopped by the drawer of the cheque, whereas, the payment of a draft cannot be stopped. 6. A cheque is defined in the Negotiable Instrument Act, 1881, whereas a demand draft has not be precisely defined in the NI Act. 7. A cheque can be made payable either to a bearer or order. But a demand draft is always payable to order of a certain person. 37. What are bank's Tier-1 Capital ? Ans : - It refers to core capital...more important dan tier 2... Can absorb www.aspiranthub.com losses. Consists of paid up capital,,statutory reserves,,disclosed reserves..etc 38. What are bank's Tier-2 Capital ? Ans : C/a subordinate capital,, consists of undisclosed reserves,,long term unsecured loans,,devaluation reserves,,general provisions,subordinate term debt. 39. What do you understand by Risk Weighted Asset ? Ans : Their is always a risk associated wid an underlying asset.. the degree of that risk depends upon the weightage given to it in investment portfolio if we talk about shares.... hence called Risk weighted asset ... like for a building a tangible asset the risk are fire,earthquake etc . 40. What is CRAR or CAR ? Ans : capital adequacy ratio- a basel parameter. it is the ratio of total capital(tier1+tier2) to the risk associated assets. i.e. more the risk weighted assets less will be the CAR and vice-versa. more CAR good for the growth of a bank.. 41. How evaluation of Banks performed ? 42. What are Local area banks ? 43. What is Negotiable Instrument ? 44. What do you understand by Nationalisation of Banks ? In which year nationalisation been done in India 45. What is faceless banking ? 46. What is Offshore banking ? 47. What is the difference between Mobile and Online banking ? 48. What are payment systems ? 49. Why do banks declare dividends ? 50. What do you understand by Merchant Banking ? 51. Why do PSB present dividend cheques to central government ? 52. Do you know Banks are supposed to observe prudential norms. What are these norms ? 53. Now-a-days we are listening a word - "BASEL-III" . Could you just tell what is this BASEL-III and is their any other Basel version ? If yes, then what is the difference ? 54. What is stress testing in banks ? 55. Bank's additional means of earnings is fee based income. What does it mean ? 56. Bank's main source of revenue is interest income. What is it ? www.aspiranthub.com 57. What is the Board for Financial Supervision ? 58. Do you know about IBA . What role does it play ? 59. Five functions of RBI ? 60. What is the difference between EXIM Bank and Commercial banks ? 61. What is Kiosk Banking ? 62. What is Retail Banking ? 63. What are the significance of Bank Deposits ? 64. What is CASA ? 65. Deposit Accounts are classified under two categories. What are those categories ? 66. What is KYC ? 67. What do you know about Current accounts ? Any specific difference between Current and savings accounts ? 68. What is Recurring deposits ? What is the difference between RD and FD . Which is more beneficial for bank and why ? 69. Term - Renewal of Deposits. Could you just give some light on it ? 70. What do you understand by Premature payments ? 71. Which documents are required to open an account ? 72. Who insure bank deposits ? Any norms by insuring body ? 73. What is meant by Accounts of HUF ? 74. Difference b/w retail and wholesale banking ? 75. Do Banks open Pension accounts ? 76. What are Dormant Accounts ? 77. Explain money laundering activities. 78. Why is interest not paid in current accounts ? 79. Can insolvent persons open accounts ? 80. What is TDS on bank interest ? www.aspiranthub.com 41. How evaluation of Banks performed ? Ans : - Through CAMELS Which stands for : C - Capital adequacy A - Asset quality M - Management quality E - Earnings L - Liquidity S - Sensitivity to Market Risk 42. What are Local area banks ? Ans : Banking habit in India is miserable especially if we talk about emerging markets. Villagers and people from small towns feel safe to keep money buried in their backyard but never trust the banks. With a view to promote banking facilities in local area, providing institutional mechanisms for promoting rural savings and to mobilize credit facility for viable economic activities in the rural area Local Area Banks are established there. These LABs are categorized under private sector and included in the second schedule of RBI Act, 1934. Scope : These LABs are restricted to operate maximum in three districts. They will be extending loan facility to agricultural requirements, aggro-trade, aggro-industrial accomplishments, non-husbandry accomplishments etc. These banks will observe the priority sector lending target at 40% of Net Bank Credit as other banks do. Capital : The minimum paid up capital of LABs shall be Rs. 5 cr. However, they are required to increase their capital from Rs. 5 cr to Rs. 25 cr. In next 5-7 years. 43. What is Negotiable Instrument ? Ans : An unconditional promise or order in written to pay a fixed amt of money . Transferable via delivery or endorsement. 44. What do you understand by Nationalisation of Banks ? In which year nationalisation been done in India ? Ans : Wen a country sovereign under take private organisation with interest of common public welfare nd believe by passing an ordinance by parliament which clearly mentioned term nationalisation know as nationalisation of tht industry or organisation. In concern with Banking industry then govt of India done this in year of 1969 with 14 privately owned banks nd again with 6 banks out of which 1 is merged. 45. What is faceless banking ? Ans : - Most of latest banking is done through technology drivenmodels like phone banking, internet banking, mobilebanking etc where the customer does not interact face toface face with any bank official. This form of banking is known as faceless banking. 46. What is Offshore banking ? Ans : Offshore banking - Branch of an Indian bank located at a special www.aspiranthub.com economic area or an area away from the location from the customer in any other nation OR Banking activity out of the country of the a/c holders mainly in those countries where tax is low called tax heaven. 47. What is the difference between Mobile and Online banking ? Ans : Online banking is done over internet which facilitates almost all sevices accept cash deposits like payment & transaction statement, etc whereas mobile banking is limited to transfering fund after registering the number with the bank 48. What are payment systems ? Ans : fund transfer mechanism to transfer mechanism from one bank to another bank is called payment system. for e.g. RTGS, NEFT,ECS,NPCI, N SWIFT etc. OR A system which makes transaction to be effected b/w a payer and a beneficiary. Ex- rtgs, neft etc 49. Why do banks declare dividends ? Ans : Dividend is a part of profit earn by organisations in current year. After profit netting dividend is distributed to its share holder nd govt of india have majority stake in it so tht PSB give dividend to govt of india 50. What do you understand by Merchant Banking ? Ans : It is the combination of Consulting along with Banking services. In simple words directing the customer abt the right investment and doing banking busimess with that is called Merchant banking OR A combo of banking + consultancy services(like,,financial,,legal,,managerial,,marketing ) is k/a merchant banking. 51. Why do PSB present dividend cheques to central government ? Ans : After profit netting dividend is distributed to its share holder nd govt of india have majority stake in it so tht PSB give dividend to govt of india 52. Do you know Banks are supposed to observe prudential norms. What are these norms ? Ans : Prudential Norms for Conversion of Unpaid Interest into 'Funded Interest Term 53. Now-a-days we are listening a word - "BASEL-III" Could you just tell what is this BASEL-III and is their any other Basel www.aspiranthub.com version ? If yes, then what is the difference ? Ans : Basel is city in switzerland n also the headquarter of BIS Bureau of international settelment. main objective of basel is safety ,solvence n soundness of the banking system controlling of redit risk , market risk n operational risk. in 2010 basel 3 guidelinesis released. These guidelines are introduced in response to financial crisis of 2008.India deadline to migrate to basel 3 is 31 march 2019. 54. What is stress testing in banks ? Ans : It is a test performed in a bank to analyse wheather a bank has sufficient capital to overcom d impact of adverse economic condition. it can b done intrnally by bank as a part of ots operation risk or may be done by the supervisory authority as a part of their Regulatory function. OR It is a tool to determine the capacity of commercial banks to safeguard their working from different risks and it is most important part to check the financial soundness of banks 55. Bank's additional means of earnings is fee based income. What does it mean ? Ans : - As banks generate income from Interest from different lending. Now banks started earning from these para banking services. Some example are : A) Transaction charges on remittance of funds B) Locker service C) Letters of credit D) Bankassurance E) Bills business 56. Bank's main source of revenue is interest income. What is it ? Ans : - Difference b/w lending rate and borrowing rate of banks is the real income of banks. OR Overall income = Income earned from interest on loans - Interest paid on savings 57. What is the Board for Financial Supervision ? Ans : BFS was set up in 1994 to oversee the indian financial system, comprising not only commercial bank,state cooperative bank but also all india financial institution and NBFC . BFS has full time vice chairman and 6 other member apart from RBI governar as its chairman. 58. Do you know about IBA . What role does it play ? www.aspiranthub.com Ans : IBA stands for Indian Banking Association Present chairman Mr. TM bashin It is an association of Bankers of India and comprises of 22 banks it works in area of development coordination and strengthening Indian banking system and assist members in implementation of new system and adoption of standards among members Recently it is playing a crucial role in Negotiating Wage Hike for Bankers 59. Five functions of RBI ? Ans : 5 Functions of RBI a ) Banker to bank b ) Banker to central government c ) Currency issuer d ) Forex regulator e ) Monetary policy maker 60. What is the difference between EXIM Bank and Commercial banks ? Ans : A) Exim banks was estd with a purpose to boost export by providing all required assistance like info regarding foreing markets risks associated with, financing project/trade. while commercial banks main job is providing bankin services to individual and corporate B) EXIM BANK - It is an apex bank established mainly for boosting international trade of country, by providing financial assistance through lending loans either by self or with collabaration with commercial banks Commercial Banks - Banks which play a crucial role in Economic sector as they provide banking services to every individual of country C) Banking is accepting the demand deposit with the purpose of lending. This is called commercial bank work bcoz it earn profit. EXIM bank is a development financial bank which is established with the purpose of developments of foreign market finance, information nd training nd risk mitigation of exporters by providing financing. 61. What is Kiosk Banking ? Ans : It is self-service solutions, allowing customers to service themselves with computer based touchscreen and making different sort of transactions. 62. What is Retail Banking ? Ans : Retail banking is when a bank executes transactions directly with www.aspiranthub.com consumers, rather than corporations or other banks. Services offered include savings and transactional accounts, mortgages, personal loans, debit cards, and credit cards. 63. What are the significance of Bank Deposits ? Ans : For bank: essential for passing loans and to generate income and strengthen the economy stability in particular environment 64. What is CASA ? Ans : - current account and saving account.......it refers to demand deposits of a bank 65. Deposit Accounts are classified under two categories. What are those categories ? Ans : 1 DEMAND DEPOSIT 2. TERM DEPOSIT 66. What is KYC? Ans: Know Your Customer launched to stop anti money laundering activities. 67. What do you know about Current accounts ? Any specific difference between Current and savings accounts ? Ans : Current acnt basically businesses men ke lie hote h no. Of withdrawl n deposit pr no restrictions n no interest s provided on deposits. And saving s fr common people whose aim s to save no. Of withdrawls s fixed n interest s provided on deposits 68. What is Recurring deposits ? What is the difference between RD and FD . Which is more beneficial for bank and why ? Ans : RD me ap har month ek fixed amount jama karte h ek fix time k liye...(aaj kal amount varible RD b hoti h) ...FD is better thn RD coz FD me bank ko ke heavy amount initially mil jata h...which is usefull for giving loan... 69. Renewal of Deposits. Could you just give some light on it ? Ans : Its is applied on RAFA...in which u renew the matured amount for a new time period 70. What do you understand by Premature payments ? Ans: Payments which are made before the due date or maturity date. 71. Which documents are required to open an account ? Ans : according to kyc guideline issued by rbi... 1-current photograph 2photo id 3- address proof www.aspiranthub.com OR Photo Id..add proff..photo...introducer well known to bank...peron has to present at the time of opening a acc 72. Who insure bank deposits ? Any norms by insuring body ? Ans : Dicgc(subsidiary of rbi) insures bank deposits each depositor in a bank is insured upto a maximum of Rs.1,00,000 73. What is meant by Accounts of HUF ? Ans : This is the account for hindu undivided fmly.this account is maintained by karta(who is head of family).karta has power to raise loan for family business .he is empowered to do all kind of activities on behalf of family but he cannot enter into patnership business.after karta demise coparcener can take powers of karta 74. Difference b/w retail and wholesale banking ? Ans : Retail banking : its main focus is on individual whereas wholesale banking focus on corporates and big customer , In Retail , size of loan is small and also recovery in retail banking is very difficult whereas in wholesale banking , size of loan are big and recovery can be possible with various DRTs In Retail banking, large network is needed to cater customer base, while in WB its not needed in that large. 75. Do Banks open Pension accounts ? Ans : YES 76. What are Dormant Accounts ? Ans : Those account which are not in use for 2 or more than 2 year are considered as dormant accounts.. 77. Explain money laundering activities. Ans: A set of procedures, laws or regulations designed to stop the practice of generating income through illegal actions. In most cases money launderers hide their actions through a series of steps that make it look like money coming from illegal or unethical sources was earned legitimately. 78. Why is interest not paid in current accounts ? Ans : Because charge lgta h unlimited transcation pr..to interest to vse hi pura ho jata h..& ca is not for saving purpose 79. Can insolvent persons open accounts ? Ans : NO www.aspiranthub.com 80. What is TDS on bank interest ? Ans : Interest earned on bank term deposits is subjected to TDS if the interest amount > stipulated limit announced in the financial year 81. Why the need for stress on Financial Inclusion ? 82. What is no-frills account ? 83. What is atm ? 84. What are different types of ATMs and their difference ? 85. What do you know about SHGs ? 86. What is sub prime mortgage ? 87. What are floating interest rates for housing loans ? 88. How do loans becomes non performing ? 89. Explain the role played by ARC ? 90. What is meant by Credit Score ? 91. What is meant by Priority sector lending ? 92. What is a pre-approved loan ? 93. Consortium Financing ? 94. What is meant by Working Capital needs of a company ? 95. What is EMI and its full form ? 96. Explain CIBIL ? 97. What is a Reverse Mortgage Loan ? 98. What do you understand by this term " mortgage " ? 99. When does a loan becomes sticky ? 100. What is asset liability management ? 101. What is ways and means advaces?? 102. what is loan syndication 103. What is effect of Npa increase for a bank ? 104. Is a guarantor liable on a loan ? 105. teaser rates ? 106. what is sme financing for banks ? 107. what is float money ? 108. what is syndicated lending ? 109. what is credit deposit ratio ? 110. how much of the banks deposits are available to be given as loans ? 111. If a person is not having any a/c how come will he b able to use the credit card? how will he pay back that credited amount? 112. what is basis point ? 113. what is clean balance sheet ? www.aspiranthub.com 114. what is credit default swap ? 115. what is portfolio managmnt ? 116. what is cash flow n fund flow ? 117. what is currency chest and its use ? 118. what is gilt edged securities ? 119. What role has banking played in India's success story? If your branch is not in a good position, what should you do to bring it on the right path? 120. what is decreed account ? 81. Why the need for stress on Financial Inclusion ? Ans : Financial inclusion policy has been brought to target each and every customer and inculcate saving habbit.so that more can be saved and more can be lend which will lead to economic growth.. OR so that economy wud b better thru poor ppl also..aisa na ho paye ki rich ppl hi growth kre aur poor aur poor bne..ise rokne kkl loye financial inclusion OR so that economy wud b better thru poor ppl also..aisa na ho paye ki rich ppl hi growth kre aur poor aur poor bne..ise rokne kkl loye financial inclusion 82. What is no-frills account ? Ans : In Nov 2005,rbi asked banks to open no frill account.No -frill account is low balance or zero based account. OR no frill a/c are those a/c where minimum balance is nt required. may be or may be not opened with zero balance. services are limited means no unnecessary frills OR Accounts with nill or very low balance requirements but devoid of various facilities, so is the name "no frills". Now rbi has directed to convert all no frills into bsbda accounts. OR No frills a/cs means der r no condtns on these acnts..nd these renamed as BSBDA a/cs..to promote d financl inclsn rbi has intrducd dese acounts.. 83. what is atm ? Ans : atm is cash disbursing machine, from where cash can be obtained. also some deposit taking atm accepts www.aspiranthub.com deposits too OR automated teller machine through which we can withdraw cash, check balance and mini statement at any time any day 84. What are different types of ATMs and their difference ? Ans : White label atm n brown label atm brown label atm r of banks n white label atm r of non banking entities brown label atm have logo of bank bt white label dnt have logo of bnk 85. What do you know about SHGs ? Ans : shg means self help group...it is the group of 10-20 poor people come together for any micro business to survive their lives by the help of ngo's and govt. including banks 86. What is sub prime mortgage ? Ans : lending to those who are not economically of sound economic background 87. What are floating interest rates for housing loans ? Ans : floating interest rates vary according to market conditions..bank can vary rate from time to time 88. How do loans becomes non performing ? Ans: Wen the borrower does not repay the principal and interest for 90 days it vl become a NPA OR when loan is not paid by borrower..after 90 days from due date..it is non performing as it is not generating any income for the bank.. 89. Explain the role played by ARC ? Ans : - Asset reconstruction companies that help resolving bank NPA's by purchasing them from bank at low rates.bank have the advantage that they receive some money from fruitless NPA and balance sheet is cleared.. OR asset reconstruction companies buy NPA from banks and try to extract maximum profit(money) out of it.ARC do not pay banks from their pockets but via Security receipts(SR)..SR are issued by ARC and only Qualified foreign investors can buy these SRs...SRs are just like bonds(no interest paid on it).. 90. What is meant by Credit Score ? Ans : Credit score tells about how much a bank can give loan/credit to a www.aspiranthub.com borrower. 91. What is meant by Priority sector lending ? Ans : priority sector lending is lending to those sectors which are very essential for the development of country bt without govt help (subsidies) cant prosper. as per rbi norms all SCBs hv to lend atleast 40% of their total credits to these sectors including foreign banks if sufficient number of branches r operationa in india OR its simply lending to the weaker sections viz agri ..nd other allied activities,,export credit,,home loan ,,edu loan,,every comm bank hv to lend 40% of total cash after excluding crr and slr,and,rrbs ko 60% 92. What is a pre-approved loan ? Ans : A pre approved personal/home/car loan is usually offered by banks to people who have a clean track record of loan repayment history 93. Consortium Financing ? Ans : Financing by multiple banks with one bank acting as a lead bank. All documentation is done by the lead bank. After the loan is sanctioned form creating the charge on assets is to be filed with mca in Form CHG 1 with specifically mentioning it as Consortium Lending OR consortium simply means partnership. when a loan amount is large,generally many banks come togather to lend mutually. this activity is called consortium. one of them generally having the largest share will work as lead bank 94. What is meant by Working Capital needs of a company ? Ans : Short term capital required to conduct d day to day operations of a company lyk purchase of stock ,raw materials etc. 95. What is EMI and its full form ? Ans : EMI stands for equated monthly installments..it is a fixed payment amount made by a borrower to a lender on a specified date of every month. OR EMI - Equated monthly instalment........it's a monthly instalment which is fixed for repayment of any term loan in which part of interest is also included in the instalment... www.aspiranthub.com 96. Explain CIBIL ? Ans : Credit Information Bureau (India) Limited is India’s first Credit Information Company (CIC) founded in August2000. CIBIL collects and maintains records of an individual’s payments pertaining to loans and credit cards. These records are submitted to CIBIL by member banks and credit institutions, on a monthly basis. This information is then used to create Credit information reports (CIR) and credit scores which are provided to credit institutions in order to help evaluate and approve loan applications. CIBIL was created to play a critical role in India’s financial system, helping loan providers manage their business and helping consumers secure credit quicker and on better terms. 97. What is a Reverse Mortgage Loan ? Ans : a scheme launched by nhb for senior citizens where they can get loan against their immovable properties. the major benefit is that they dnt gotta pay the loans back and can use pledged assets either. once they die, the bank will take possession of the assets ,sell it and add the proceeds in the loa a/c. 98. What do you understand by this term " mortgage " ? Ans : A mortgage is an agreement that allows a lender to seize property when a borrower fails to pay....!! OR A mortgage is a way to use one's real property, like land, a house, or a building, as a guarantee for a loan to get money 99. When does a loan becomes sticky ? Ans : when the borrower fails to pay interest on his loans for 90 days den the loans becomes sticky 100. What is asset liability management ? Ans : Asset Liability management has been introduced in banks w.e.f 1 April 1999. It basically deals with ensuring there is no mismatch in assets and liabilities from risk point of view. Banks are required to constitute ALCO -Asset Liability Management Committee headed by CMD or ED for the purpose. OR - management of asset and liabilities for a good return or maximum www.aspiranthub.com overall interest 101. What is ways and means advaces?? Ans : Its a credit facility given by RBI to central and state govts to meet their shortfall of funds OR Government incur expenses daily but receipts are irregular and so at times government faces temporary mismatches in payment and receipts...so to bridge this mismatch RBI gives temporary overdraft to government called ways and means advances(WMA)...time period is of 10 days for both central and state government and rate of interest = repo rate. Now limit is 35000 crore 102. What is loan sydication ? Ans : Loan syndication is a lending process in which a group of lenders provide funds to a single borrower. 103. What is effect of Npa increase for a bank ? Ans : 1)the profitablty of d bank is effectd 2)to the extnt of npa it is creatd as bad debt,hence it does nt genrt ny income or intrst to d bank 3)recyclng of funds is effected(i mean circulatn of mny is effctd). 4)finally the image of d bank also effctd.. 104. Is a guarantor liable on a loan ? Ans : Yes 105. teaser rates ? Ans : Teaser rates means giving home loans primarily on lower rates ..which gets increase acc to market conditions from passage of time. 106. what is sme financing for banks ? Ans : providing credits to small n micro enterprises. comes under PSL OR Financing to small nd medium enterprises..to promote their(sme)growth ...which is imp.. 107. what is float money ? Ans : The amont dt remains wid banks when a cheque comes for collection until the amount finally credited to the beneficiary account. 108. what is syndicated lending ? Ans : also known as consortium financing, when banks comes together and www.aspiranthub.com extend the loan facilities by sharing the loan amt b/w themselves. this helps banks for reducing the risk 109. what is credit deposit ratio ? Ans : Its loan to deposit ratio 110. how much of the banks deposits are available to be given as loans ? Ans : Excluding crr and srr ratio.. On total ndtl. 111. If a person is not having any a/c how come will he be able to use the credit card? how will he pay back that credited amount? Ans : if one obtains a credit card means a revolving a/c is created in his name. there is a mininum amount has to b paid every month on fixed date to continue revolving a/c . hwevr the card holder may pay even the whole amount. and the intrest is charged on remaining amount 112. what is basis point ? Ans :100 basis points = 1% , Its the hundredth part of 1 per cent 113. what is clean balance sheet ? Ans : A statement which shows that company either has no debt or very small debt 114. what is credit default swap ? Ans : It is a tool to transfer and manage credit risk through redistribution of risk 115. what is portfolio managmnt ? Ans : Portfolio Management (PM) guides theinvestor in a method of selecting the bestavailable securities that will provide theexpected rate of return for any givendegree of risk and also to mitigate (reduce)the risks. It is a strategic decision which isaddressed by the top-level managers. OR portfolio management means to carry best(debt free),risk free,multibaggar shares(stocks) of diff. Sectors under single investor .. (explaind in terms of capital market ) 116. what is cash flow n fund flow ? Ans : Cash flow is based on small concept of funds but funds flow is based on the changes in working capital cash folw is based on cash basis and fund folw is based on accural basis cash folw is useful for short term but fund flow is for long term basis OR fund flow shows the changes in working capital,whereas cash flow deals with cash coming frm diff www.aspiranthub.com activities of a buss entrpriese 117. what is currency chest and its use ? Ans : currency chests r authirised branches of banks work as warehouse where currencies are stocked and distributed in that area as per requirement OR To facilitate the distribution of bank notes nd coins rbi has authorised some branches of commercial bank to establiahed currency chest.it's storehouse where bank notes nd coins stocked on d behalf of rbi 118. what is gilt edged securities ? Ans : sometimes government need finance when tax collection is low and need temporary funds..so to get these funds gov issue securities called gilt-edged securities sold by RBI on behalf of government..it is a best option to invest in these securities as there is low risk chances and Gov has high credit ratings(AA) and hence can repay the principal and interest on time for sure. 119. What role has banking played in India's success story? If your branch is not in a good position, what should you do to bring it on the right path? Ans : banking plays a crucial role in development of every country. from individual to corporate via government. its provides credit and other financial services to business in order to make economy prosper. it provide various deposit schemes to common people through which they start saving small amount and hence purchase power parity is increased. it helps govt run its various schemes/ programs/initiative smoothly for the purposes of development & nation building 120. what is decreed account ? Ans : A decreed account is one where a settlement has been reached between a bank and a defaulter, and with the mutual agreement, a consent decree has been obtained either by a civil court or the debt recovery tribunal (DRT). www.aspiranthub.com 121. if a bank doesnt follow priority sector lending toh kya penalties hai ?? 122.Role of gdp in indian economy ?? 123. Problems of rural banking and solutions of it 124. names of negotiable inst. 125. banks me present me jo NPAs h unhe kaise reduce kiya ja sakta h 126. all comm. banks , rrbs, are included in Fin. inclusion then what is the need of payment bank 127 GDR 128 SDR 129 Wats the percentage of loan distribution among priority sector 130 Total n. Of psb,private bank,foreign bnk n rrbs? 131 NDTL 132 what is NRE A/C ,NRO A/C ,FCNR A/C ? 133 kiosk banking example can be ATM ? 134 What is CAD ? 135. What is MUTUAL FUND, DEBENTURES, CHIT FUND ? 136. what is aadhar card and benefits in banking ? 137. what is cpi , wpi ? Explain and give proper difference. 138. Why CPI is a key indicator for inflation ? 139. Can we transfer in abroad via NEFT or RTGS ? If not, then by which service we can do that ? 140. Difference between FCNR A/C and EEFC A/C ??? 141. Why should bank consider debt equity structure of a company before loaning? 142. How important is CASA portfolio for the bank? 143. What is Debit Card ? 144. What is Credit Card ? 145. What is Smart Card ? 146. Basic Difference BTW bal sheet of bank n company ? 147. What is Virtual Banking ? 148. What is Universal Banking ? 149. What do you understand by Underwriting ? 150. What is Settlement ? 151. Repurchase Agreement ? 152. Real Interest Rate ? 153. What is Rate of Return ? 154. What is Priority Sector Advances ? 155. What is Plastic Money ? 156. What is Personal Identification Number (PIN) ? 157. What is MIBOR ? 158. What is LIBOR ? www.aspiranthub.com 159. What is Initial Public Offering (IPO) ? 160. What is Hedge ? 121. if a bank doesnt follow priority sector lending toh kya penalties hai ?? Ans : SECTION II PENALTIES FOR NON-ACHIEVEMENT OF PRIORITY SECTOR LENDING TARGET / SUBTARGETS 1. Domestic scheduled commercial banks – Contribution by banks to Rural Infrastructure Development Fund (RIDF): 9 1.1 Domestic scheduled commercial banks having shortfall in lending to priority sector target (40 per cent of ANBC or credit equivalent amount of Off-Balance Sheet Exposure, whichever is higher) and / or agriculture target (18 per cent of ANBC or credit equivalent amount of OffBalance Sheet Exposure, whichever is higher) shall be allocated amounts for contribution to the Rural Infrastructure Development Fund (RIDF) established with NABARD. The concerned banks will be called upon by NABARD, on receiving demands from various State Governments, to contribute to RIDF. 1.2 The corpus of a particular tranche of RIDF is decided by Government of India every year. Fifty per cent of the corpus shall be allocated among the domestic commercial banks having shortfall in lending to priority sector target of 40 per cent of ANBC or credit equivalent amount of Off-Balance Sheet Exposure, whichever is higher, on a pro-rata basis, and fifty per cent of the corpus shall be allocated among the banks having shortfall in lending to agriculture target of 18 per cent of ANBC or credit equivalent amount of Off-Balance Sheet Exposure, whichever is higher, on a pro-rata basis. The amount of contribution by banks to a particular tranche of RIDF will be decided in the beginning of the financial year. www.aspiranthub.com 1.3 The interest rates on banks’ contribution to 122.Role of gdp in indian economy ? Ans : A country's gdp is the indicator of a country's growth...it tells abt their economic condition..whether it is developed or developing... 123. Problems of rural banking and solutions of it ? Ans : Lack of technology...low participation of villagers... (Mostly the villagers go to moneylenders who offers higher interests...)..agri loan waivers.. 124. names of negotiable instruments ? Ans : Cheque,promissory notes,bank draft,commercial paper,certificate of deposit,treasury bills,railway receipts 125. banks me present me jo NPAs h unhe kaise reduce kiya ja sakta hai ? Ans : precaution is better than cure , can be reduced by lending only after getting colletral, proper documt verification whether the assets being pledged is in the name of customer or nt or if any liabilities towards that assets. 2. proper inquiry whether the loan amount is using for the same purposes for which it has been extainded. to eliminate willful defaulters. 3. stickt enforcement of sarfaisi act or reducing political interferences 4. while making clean loans credit report most be accesed from cibil 126. all comm. banks , rrbs, are included in Fin. inclusion then what is the need of payment bank ? Ans : Bcoz dat banks hv to complete basel norms...but they are lacking funds due to increasing npa.... 127 What is GDR ? Ans : GDRs r financial instruments issued with an objective to raise money from European investors(ie issued in european market) 128 What is SDR ? Ans : SDR is an international reserve asset, created by the IMF in 1969 to supplement its member countries’ official reserves. Its value is based on a basket of four key international currencies, and SDRs can be exchanged for freely usable currencies OR sdr is international reserve fund kept under the custody of imf. it shows www.aspiranthub.com the drawing right of its member states. the value of sdr is determined as the avg value of four major currencies usd, pounds, yen & euro 129 Whats the percentage of loan distribution among priority sector ? Ans : banks with more than 20 branches = 40% ( in which agriculture = 18% advance to weaker secn = 10%) less than 20 branches = 32% 130 Total no. of psb,private bank,foreign bnk n rrbs? Ans : PSB: 27(21+SBI+SB ASSOCIATES) Private:23 Rrbs:56 Foreign:41 Nationalised 19 131 What is NDTL? Ans : NDTL stands for net demand & time liabilities.. these r d liablts of d bank.. Demand liabilities: savings & current deposits.. Time liabilts: fixed & recurring deposits..! OR - Total deposits of the customer with the bank. Ndtl has 2 types of deposits --- demand deposits( which are payable on demand) time deposits ( which are payable on the date of maturity). CASA is demand and RAFA is time deposits. These are the liabilities of the bank 132 what is NRE A/C ,NRO A/C ,FCNR A/C ? Ans : NRO- when a resident becomes Non resident, his domestic rupee a/c gets converted into Non residential ordinary a/c...can be opened as both CASA & RAFA..Pricipal- non repartible, intrest- patriable 133 kiosk banking example can be ATM ? Ans : kiosk means a small store, in case of banking kiosk means an unmaned store where customers can widraw money, deposit money,get their cheque/dd printed, cheque depisit etc. atm can b an example as many atms nwadays accepting cash too 134 What is CAD ? Ans : Current account deficit . its is the difference between the total expenditure and total income of the country. 135. What is MUTUAL FUND, DEBENTURES, CHIT FUND ? www.aspiranthub.com Ans : mutual fund is an investment programme that is made up of a pool of funds collected from many investors for the purpose of investing in securities such as stocks, bonds, money market instruments and similar assets (ie diversified portfolio) and is managed by experts. A type of debt instrument that is not secured by physical assets or collateral. Debentures are backed only by the general creditworthiness and reputation of the issuer..In simple language we can say it's a loan taken from public by corporations and carries fixed return(ie interest) unlike shares Chit Fund is a saving scheme practiced in India. It originated 1000s of years ago. It was started as informal association of traders and households with in communities. It enables poor people to convert small savings into lump sums. Chit fund transaction is an agreement with a specified number of persons that every one of them shall subscribe a certain sum of money over regular fixed intervals, 136. what is aadhar card and benefits in banking ? Ans : Aadhaar is a 12-digit unique identification number issued by the Indian government to every individual resident of India. The Aadhaar project was initiated as an attempt towards having a single, unique identification document or number that would capture all the details, including demographic and biometric information, of every resident Indian individual. It will also serve as the basis for Know Your Customer (KYC) norms used by banks OR the 12-digit adhar card carries biomatric info of the individual it means geting forged info or getting multiple such cards is almost impossible this quality makes it very atractive in bankibg and can be easily accepted under kyc norms as both id proof aswell as adress proof. if the mentioned adress is changed just a self attestation form having current adress will do after puting signture or thumb impression of the customer. also bnks urging evryone to link his existing a/c to adhar so that DBT can be availed 137. what is cpi , wpi ? Explain and give proper difference. www.aspiranthub.com Ans : yes indexes for measuring inflation. cpi measures price rise of goods n services at consumer level where even service charge levied on consumer is included. while wpi measers the same at wholesale level where many taxes or charges levied on consumers r excluded. untill 2014 rbi used wpi bt nw it moved towards cpi OR Wpi s wholesale price index used to measure price chnges in d guds bought by wholesellers from producers while cpi s consumer price index which measures the price chnge in d guds bought by ultimate consumers ....both measure inflation ie price rise 138. Why CPI is a key indicator for inflation ? Ans : cause it gives actual statistics of wat actually consumer bears while making purchases. as in wpi service tax , sale tax etc r excluded which makes a huge difrence b/w consumer price n price at wholesale price level 139. Can we transfer in abroad via NEFT or RTGS ? If not, then by which service we can do that ? Ans : no..we can use wire transfer for such purpose. Wire transfers allow people in different geographic locations to easily transfer money to locales and financial institutions around the globe. For providing the service, banks will collect a fee, sometimes based upon the size of the transfer being made .. 140. Difference between FCNR A/C and EEFC A/C ??? Ans : Exchange Earners' Foreign Currency Account (EEFC) is an account maintained in foreign currency with an Authorised Dealer i.e. a bank dealing in foreign exchange. It is a facility provided to the foreign exchange earners, including exporters, to credit 100 per cent of their foreign exchange earnings to the account, so that the account holders do not have to convert foreign exchange into Rupees and vice versa, thereby minimizing the transaction costs. fcnr opened by NRI EEFC-- All categories of foreign exchange earners, such as individuals, companies, etc. who are resident in India, may open EEFC accounts www.aspiranthub.com 141. Why should bank consider debt equity structure of a company before loaning? Ans : To check its soundness for repayments plus companies act puts limitations on the borrowing of the company linked to equity and reserves so the bank must ensure that the aggregate borrowings must be within the limits. 142. How important is CASA portfolio for the bank? Ans : CASA means current account and saving account. The deposits in these accounts influence the most on banks profitability. The bank gives a very modest rate of interest on saving accounts whereas no interest is paid by the bank on current accounts. Therefore banks are tried hard to deposit more and more money in these accounts by the public so that banks earn spread ie profits by making loans and advances. OR CASA r low cost deposits , thus in order to be competitive, banks should try to garner as much CASA as possible coz by doing so they can control the cost of raising deposits and hence can lend at more competitive rates. 143. What is Debit Card ? Ans : Debit card is a prepaid card.it is a payment gateway through which cutomer can do all transactions if he/she has balance in thier account. 144. What is Credit Card ? Ans : CC is issued by bank/non bank entity through which we can withdraw money frm atm,used at POS for shopping etc ..... also there is overdraft facility 4 customers. 145. What is Smart Card ? Ans : It is an intigrated circuit card(iic)...also known as electric bag...used for transaction purpose....used for shoping......money can load through atm and mobile.... 146. Basic Difference BTW bal sheet of bank n company ? Ans : in banks' b/s assets r loans granted & liabilties r deposits of public and businesses while in case of Co...under assets heads- all fixed & current assets,under liabilties headloans from bank + all other currnt & www.aspiranthub.com fixed liabilties + its own capital 147. What is Virtual Banking ? Ans : to deliver banking services primarily through Internet or other electronic delivery channels is called virtual banking OR internet based banking,,thus eliminating the need to walk to bank premises..eg ATM, Net banking 148. What is Universal Banking ? Ans : all banking services say retail , wholesale, marchant, wealth management etc under one roof . icici bank is said to be the first bank to start universal banking in india 149. What do you understand by Underwriting ? Ans : is an agreement by the underwriter to buy on a fixed date and at a fixed rate, the unsubscribed portion of shares or debentures or other issues. Underwriter gets commission for this agreement. 150. What is Settlement ? Ans : Conclusion of a securities transaction when a customer pays a broker/dealer for securities purchased or delivered, securities sold, and receive from the broker the proceeds of a sale. 151. Repurchase Agreement ? Ans : An arrangement in which a security is sold and later bought back at an agreed price and time. 152. Real Interest Rate ? Ans : nominal interest rate – inflation rate = Real Interest Rate.....An interest rate that has been adjusted to remove the effects of inflation to reflect the real cost of funds to the borrower, and the real yield to the lender. The real interest rate of an investment is calculated as the amount by which the nominal interest rate is higher than the inflation rate. 153. What is Rate of Return ? Ans : (net profit / investment made) * 100 154. What is Priority Sector Advances ? Ans : Lending to certain specified sectors identified as priority sectors by RBI viz MSME, agriculture, SHGs, Rural credit, retail traders..banks hv to lend a certain fixed % of their www.aspiranthub.com lending to these. As per guidlines it's 40% 155. What is Plastic Money ? Ans : These are basically plastic cards that are used for buying goods and services on credit within specified limits and according to term and conditions of the bank. Eg --- debit ,credit and smart card OR - collective term for all types of bank cards viz credit cards, debit cards, smart cards, etc. 156. What is Personal Identification Number (PIN) ? Ans : It is a 4 digit confidential numeric number with the help of it a customer can withdraw money from the ATM's. 157. What is MIBOR ? Ans : MIBOR ie Mumbai Interbank Offer Rate is the interest rate at which bank borrow funds from 1 another in indian interbank market. The MIBOR is calculated everyday by NSE as a weighted average of lending rates of a group of banks. 158. What is LIBOR ? Ans : The LIBOR is the world's most widely used benchmark for short-term interest rates. It's important because it is the rate at which the world's most preferred borrowers are able to borrow money. OR london interbank offered rate is the average interest rate estimated by leading banks in London that they would be paying if they borrow from other banks. 159. What is Initial Public Offering (IPO) ? Ans : when any company issues its shares for the 1st time in stock market to raise capital, its c/d IPO..thereafter it becomes FPO(Further or follow on public offering) 160. What is Hedge ? Ans : It is a strategy used to minimize the risk of a particular investment and at the same time maximize the returns on the investment www.aspiranthub.com 161 bad debts ? 162 what is hawala & money laundering? 163 what is money ? 164. lok adalat ? 165. Line of Credit ? 166. Letter of Credit ? 167. GDP ? 168. GNP ? 169. what is parallel banking? 170. Can a 100 rs note be called as promissory note?and why? 171. On which accounts DICGC provides insurance cover?? 172. Difference between bank and postoffice? 173. Pledge , Hypothecation , Mortgage , Lien ? 174. what is clearing house ? 175. what is participation certificate ?? 176. what r d facilities enjoyed by a schedule bank from RBI/GOI? 177. can non schedule banks also get loans from rbi if there is any emergency?? 178. compulsion to maintain CRR is also with non schedule bank or not ?? 179. wat is difference between Self help groups and microfinance institutions ?? ( activities) 180. Banks maintain crr with RBI...y they have to maintain it...even no interest is given to them on it,.but in federal reserve interest is given to banks ? 181. Types of Money and What is velocity of money. 182 devaluation ?? 183. depreciation??? 184. Inflation vs Depression ? 185. Why RBI conduct open. Market operation? 186. Is a bank-overdraft a liability or an asset to the bank? 187. What is FCCB? 188. Are debentures issued by companies only, not government ?? unline bond which r issued by both companies & govt.... 189. difference between advances and overdraft? 190. Explain Gift card ? 191. Steps taken by RBI to control inflation?? 192. important services by different Indian Banks ? 193. TRADE DEFICIT ? 194. BALANCE OF TRADE ? 195. what is BCSBI (Banking Code and Standard Board of India)? 196. Balance of Payment ? www.aspiranthub.com 197. Islamic banking ? 198. Bharat Bill Payment System..?? 199. IPO vs FPO ? 200. difference between certificate of deposit and fixed deposit ? 161 bad debts ? Ans : Npa known as bad debts or loans given by banks which r not generating prof it for banks OR debt that cannot be collectable 162 what is hawala & money laundering? Ans : Conversion of an illegal money into legal money by process of placement,,layering and integration is called money laundering...hawala is a case of it. 163 what is money ? Ans : its an instrument which can be used instead valueable commodities like gold,silver and a medium for payment of all goods and service OR A thing dat is generally acceptable as means of payment in the settlement of all transactions is money..acts as a medium of exchange OR Four broad functions to serve as money fr a commodity s it shud b a medium of exchange ,measure of value,standard n a store of value 164. lok adalat ? Ans : lok adalat is formed under the provision of legal serice authority act 1987. both banker and borrower come before the judge under one time settelement who after satisfying himself about the genuiness of the case puts his official stamp on the agreement . cases upto rs 20 lacs are handeled here 165. Line of Credit ? Ans : A credit dat can be taken from a bank upto a certain limit ..in which..interest starts charging aftet the actual usage of dat on dat much amount dat is used. If taken 2 lac ,,uses 1 lac,,after 6 months den interest will charge after 6 months on 1 lac only. . 166. Letter of Credit ? Ans : an instrument for assured payments,undertaking of the issuing bank to make payment to beneficiary www.aspiranthub.com against documents stated in letter of credit...parties involved are: applicant/buyer/importer,beneficiary/seller/exporter, issuing bank,advising bank ,nominated/negotiating bank and confirming bank. 167. GDP ? Ans : GDP stands for gross domestic product..domestic --> within your country...so GDP means money value of everything u produce within your country..calculated by three methods-expenditure method,income method and production method 168. GNP ? Ans : GNP=money value of everything produced in India+income from abroad-outgoing money (to abroad). OR Gross national product (GNP) is the market value of all the products and services produced in one year by labour and property supplied by the citizens of a country. UnlikeGross Domestic Product (GDP), which defines production based on the geographical location of production, GNP allocates production based on location of ownership. 169. what is parallel banking? Ans : Parallel banking means carrying bnking activities along with other activities ie nt primarily engaged in bnking activities lyk nbfc dey do not perform complete range of bnking activities 170. Can a 100 rs note be called as promissory note?and why? Ans : According to artical 4 of Negotiable act 1881 promisory notes r define excluding note nd currency OR Nope... Currency and promissory note have same features bt currency is not a PN 171. On which accounts DICGC provides insurance cover?? Ans : The DICGC insures all deposits such as savings, fixed, current, recurring, etc. deposits except the following types of deposits (i) Deposits of foreign Governments; (ii) Deposits of Central/State Governments; (iii) Inter-bank deposits; (iv) Deposits of the State Land Development Banks with the State www.aspiranthub.com co-operative bank; (v) Any amount due on account of and deposit received outside India (vi) Any amount, which has been specifically exempted by the corporation with the previous approval of Reserve Bank of India 172. Difference between bank and postoffice? Ans : in banks we can open current account in post office we can't...in post office the max limit to deposit is 1 lac and in banks no limit...in post office the max time for which we can deposit is 5 while in banks it is 10..the min amount in post office to deposit under time deposit is 200 while in banks it is 1000 under fixed deposit...banks issue Demand draft while post office can't. 173. Pledge , Hypothecation , Mortgage , Lien ? Ans : (1) Pledge is used when the lender (pledgee) takes actual possession of assets (i.e. certificates, goods ). Such securities or goods are movable securities. In this case the pledgee retains the possession of the goods until the pledgor (i.e. borrower) repays the entire debt amount. In case there is default by the borrower, the pledgee has a right to sell the goods in his possession and adjust its proceeds towards the amount due (i.e. principal and interest amount). Some examples of pledge are Gold /Jewellery Loans, Advance against goods,/stock, Advances against National Saving Certif icates etc. (2) Hypothecation is used for creating charge against the security of movable assets, but here the possession of the security remains with the borrower itself. Thus, in case of default by the borrower, the lender (i.e. to whom the goods / security has been hypothecated) will have to first take possession of the security and then sell the same. The best example of this type of arrangement are Car Loans. In this case Car / Vehicle remains with the borrower but the same is hypothecated to the bank / financer. In case the borrower, defaults, banks take possession of the vehicle after giving notice and then sell the same and credit the proceeds to the loan account. Other examples of these www.aspiranthub.com hypothecation are loans against stock and debtors. [Sometimes, borrowers cheat the banker by partly selling goods hypothecated to bank and not keeping the desired amount of stock of goods. In such cases, if bank feels that borrower is trying to cheat, then it can convert hypothecation to pledge i.e. it takes over possession of the goods and keeps the same under lock and key of the bank]. (3) Mortgage : is used for creating charge against immovable property which includes land, buildings or anything that is attached to the earth or permanently fastened to anything attached to the earth (However, it does not include growing crops or grass as they can be easily detached from the earth). The best example when mortage is created is when someone takes a Housing Loan / Home Loan. In this case house is mortgaged in favour of the bank / financer but remains in possession of the borrower, which he uses for himself or even may give on rent . OR - pledge: assets agains which loan is obtained and r kept under banks custody hypo: remains under borower possession mortgage: immoval, remains under the borrwr possession lien: judiciary/ laws r involved 174. what is clearing house ? Ans : Association of banks in a particular locality to settle down payments of cheques..etc by cancellation of equal credit and debits of each bank singly..run by rbi nd sbi..tranfrs funds quickly,,safely and at low cost. OR A facility fr settlement of cheques btw different bnks done periodically 175. what is participation certif icate ?? Ans : They are the instruments dat want to Trade in capital market of a country without being registered by sebi. OR if bank A has to extend credit deposit ratio then it has to either increase deposit ratio or it has to reduce credits. Bank A can reduce its credit by allowing BANK B to participate in its advances .in this case bank A issues participate certif icate to bank B. www.aspiranthub.com 176. what r d facilities enjoyed by a schedule bank from RBI/GOI? Ans : 1)bcms eligible 4 obtaining loans on bank.rate frm rbi 2)get d membership of clearing house 3)get d facility of rediscount of xchange bills frm rbi OR - 1. Insurance of money deposited by there customers.2. If they where in trouble rbi help them as a parent bank.3. Enjoys various facilities lyk part of omo,obtaining long term loan via bank rate etc ..3.can do secondary functions lyk forex exchanges,mutual funds,bankasurance, etc 177. can non schedule banks also get loans from rbi if there is any emergency?? Ans : YES 178. compulsion to maintain CRR is also with non schedule bank or not ?? Ans : Non scheduled bank also maintain CRR at par with schedule banks As they are small banks nd nt hving infrastructure IT so they can't maintain it with RBI nd for this they hv permission to maintain it with commercial bank in current account nd submit return for it fortnightly to RBI 179. wat is difference between Self help groups and microf inance institutions ?? ( activities ) Ans : SHG is a grp of women villagers who collects money among following members to start a micro business....microf ince ins. Are those inst. Which finance micro enterprise(total capital nt more than 25 lakh) to estd/expand their business 180. Banks maintain crr with RBI...y they have to maintain it...even no interest is given to them on it,.but in federal reserve interest is given to banks ? Ans : To secure depositors interest, RBI stipulated a certain percentage of bank NDTL in form of cash only tht is know as CRR. Earlier rbi has given interest on it but aft 2004 it discontinued it . Wen there is run conditions in banks or rumours for banks tht tym bank needs immediate payment of depositors money. Tht tym this CRR give cushion to bank. 181. Types of Money and What is velocity of money. Ans : metallic money --- three type 1 standard money 2 token money 3 subsidiary money www.aspiranthub.com paper money --- 4 type .. 1 representative paper 2 convertible paper 3 inconvertiable paper 4 fiat money acceptability money--- legal tendor money ,, 2 non legal tender money 182 devaluation ?? Ans : reducing the value of currncy of a nation intentionally by its govt in order to promote international trade...was done 3 times in india- 1949, 1966 & 1991 183. depreciation??? Ans : used in 2 context- depreciation of assets(in businesses) and depreciation of currency..depreciation of assets means decrese in its value over its estimated useful life...& depr of currncy means fall in the value of currncy in relation 2 other currencies 184. Inflation vs Depression ? Ans : inflation- continuous increase in the price of a basket of goods and services over a period of time....Depression - i think it's great depression of 1930..that started in 1930 and lasted till late 1930s..in which economies of many nations were totally shattered OR if demand less and supply more deflation and vice-versa 185. Why RBI conduct open. Market operation? Ans : The usual aim of open market operations is to manipulate the short-term interest rate and the supply of base money in an economy, and thus indirectly control the total money supply, in effect expanding money or contracting the money supply. This involves meeting the demand of base money at the target interest rate by buying and selling government securities, or other financial instruments. Monetary targets, such as inflation, interest rates, or exchange rates, are used to guide this implementation 186. Is a bank-overdraft a liability or an asset to the bank? Ans : asset fr bnk n liability fr customer 187. What is FCCB? Ans : Foreign currency convertible bonds...similar to other convertible bonds..only diff is - issued by a company (in its domestic country) in foreign currency...they r an imp tool for MNCs OR A convertable bond dat is issued in a currency other than d issuer's www.aspiranthub.com own. A company may issue an FCCB if it intends to make a large investment in a country using dat foreign currency. 188. Are debentures issued by companies only, not government ?? unline bond which r issued by both companies & govt.... Ans : Yes 189. difference between advances and overdraft? Ans : Advance s loans granted to customers n overdraft s a facility to withdraw more amt Dan u HV in ur accnt 190. Explain Gift card ? Ans : any prepaid card issued by bank ,FIs or marchants, & retail stores that can be used to make purchases OR one of the main point on gift card u hv to give tax.. as like bonus card 191. Steps taken by RBI to control inf lation?? Ans : all monetary policy tools ( LAF( rep +rev repo)+ Reserve ratios(CRR+SLR), OMO, bank rate) 192. important services by different Indian Banks ? Ans : import export transactions payment services loans 193. TRADE DEFICIT ? Ans : a negative balance of trade ie imports- exports 194. BALANCE OF TRADE ? Ans : The difference between a country's imports and its exports. Balance of trade is the largest component of a country's balance of payments. Debit items include imports, foreign aid, domestic spending abroad and domestic investments abroad. Credit items include exports, foreign spending in the domestic economy and foreign investments in the domestic economy. 195. what is BCSBI (Banking Code and Standard Board of India)? Ans : BCSBI is an independent and autonomous institution to monitor and ensure that the Banking Codes and Standards adopted by the banks are adhered to in true spirit while delivering their services. 196. Balance of Payment ? Ans : BOP is the record of all economic transaction between the resident of country and the rest of the world in a particular period. www.aspiranthub.com 197. Islamic banking ? Ans : Banking as per sharia law wherein investment is not done in the business which are harram. Eg liquor gambling pork businesses etc. Islamic banks do not charge interest on loan rather they ask for profit sharing OR it is dat banking systm vich involves principles & rules of SHariah ruling, && dis systm avoids reciept n payments of interest in its transactn,,& cnductng opertns in such a way dat it fullf ils d objectv of islamic economy 198. Bharat Bill Payment System..?? Ans : It is an integrated bill payment system to pay light bill, phone bill, water bill etc. The individuals will pay their bills using modes such as credit cards, debit cards and cash in one window, then the money will go to one escrow account from his account. BBPS then pay each biller from that account . 199. IPO vs FPO ? Ans : ipo is used when an unlisted company in sebi makes offer for sale of its securities to expand business etc .FPO-this offer when already listed company makes a fresh issue of securities to public or offer for sale to public 200. difference between certif icate of deposit and fixed deposit ? Ans : A certificate of deposit is limited in liquidity, with the initial deposit meant to remain in the bank's possession until the end of the term, often six months to a year. Only ten percent of the investment remains liquid and therefore it is available for withdrawal only through payment of a large penalty. Such accounts are designed to mature without interference. A fixed rate deposit often has greater liquidity than a certif icate of deposit, with a thirty percent reserve maintained to service any withdrawal requirements. With three times the reserve of a certif icate of deposit, fixed rate deposits are a strong choice for investors who may be uncertain about their future needs and allow them to access the liquidity of their investment. www.aspiranthub.com 201 what is debt ? 202 hot money 203 Term Money ? 204 Notice Money ? 205 How wil u define risk? 206 Difference betwren line of credit and cash credit ?? 207 Difrnce betwn overnight repo and msf ? 208 Difference between omo and mss?? 209 what is FMC??who controls it?? 210 Adjustable-Rate Mortgages (ARMS) ? 211 Effect of Repo rate cut of 0.25 % in Economy ? 212 What is Authorization ? 213 What do you know about Bank Ombudsman ? 214 Difference between Small Bank and Payment Bank ? 215 What do you understand by Bouncing of a cheque ? 216 Certificate of Deposits (CDs) ? 217 If a person doesn't have proper proof,how will you open an account?? 218 NABARD functions vs RRB Functions ? 219 Diff b/w FDI and FII ??? 220 difference between banking and finance? 221 Participatory notes? 222 Definition of Term "REPO" only ? 223 Y is inflation a debtors enemy n creditors best frnd 224 Den diff BTW capital n money mkt ? 225 what is the difference between credit and investment? 226 Wt do u understand by share capital n its types ? 227 What is Subprime crisis? 228 Wt r d various sources fr raising capital ? 229 NOSTRO vs VOSTRO A/c ? 230 Base Rate vs Bank Rate ? 231 What is e-KYC? What is itz work? 232 Whats the difference between debentures and bonds..? 233 multi branch banking ??is it same as CBS ? 234 What is "Term Repo" ? 235 Under PMJDY, If the present address is different than that of printed on Aadhaar Card, then a self certification of current address is sufficient. What is exactly self certification?? 236 Is there any limit on amount in jan dhan account ?can i convert my www.aspiranthub.com normal saving account into jan dhan account? 237 why bbps hs been proposed to be introduced if payments can be made through online transaction smoothly????? 238 Does PMJDY not violating the KYC guidelines?? 239 What are inflation index bonds & to which inflation index r they linked to- WPI or CPI ?? 240 What is a wire transfer? 201 what is debt ? Ans : A debt is a loan which is given by one person to another. OR - that doesnt belong to a person/firm..ie they owe it to others...in simple language it's a loan 202 hot money Ans : It is flow of funds or capital from one country to another in order to earn a short -term profit on interest rate differences or anticipated exchange rate shifts. These capital flows are called 'hot money' because they can move very quickly in and out of markets. OR money which is unstable in nature & moves into & out of the financial mrkt of a company very quickly...it is so c/d coz of its unstable nature..best eg is of fii 203 Term Money ? Ans : 14 day above loans c/a term loan 204 Notice Money ? Ans : in notice money , money is borrowed or lend for the period b/w 2 days and 14 day s 205 How wil u def ine risk? Ans : deviation of actual return from expected return 206 Difference betwren line of credit and cash credit ?? Ans : Line of credit includes loans and advances wherein interest is charged on lump sum amount. line of credit is generally provided to corporates. Cash credit sets a limit to withdraw the amount from tge the account. Cash credit is provide against security. What ever the amount is withdrawn interest is charged only on that amount not on lumpsum. www.aspiranthub.com OR line of credit ek limit hai jisske uppar credit ka use nahi kiya jaata and cash credit ek credit facility hai jo kisi security k badle diya jaata hai 207 Difrnce betwn overnight repo and msf ? Ans : he major diff is that under repo gsec cant be pledged lying under SLR quota while in msf even slr quota gsec can b pledged. under repo a bank can fetch as much fund frm rbi as it has security to pledge while under msf max upto 2% of their NDTL loans undr repo rate is available upto 90days where as under msf just for ovrnight basis and...repo rate is cheaper than msf 208 Difference between omo and mss?? Ans : dono mae govt security hi bechi jaati hai but mss mae paisa govt k account mae rakha jaata hai jabki omo mae rbi aapne pass rakhti hai 209 what is FMC??who controls it?? Ans : FMC is an independent body. its regulates comodity market. its already a regulatory body. anyway its controlled by ministry of finance, and PM too 210 Adjustable-Rate Mortgages (ARMS) ? Ans : Also known as variable-rate mortgages. The initial interest rate is usually below that of conventional fixed-rate loans. The interest rate may change over the life of the loan as market conditions change. There is typically a maximum (or ceiling) and a minimum (or floor) defined in the loan agreement. If interest rates rise, so does the loan payment. If interest rates fall, the loan payment may as well. 211 Effect of Repo rate cut of 0.25 % in Economy ? Ans : interest rate kam honge jisse ki log jada loan lenge and kharch karenge jisse business ka expension hoga OR - business will grow as borowing rates will be decresed by banks soon. retail customers will also get benefited as loans on home car etc will fall dwn. investment will be incresed thas y sensex incresed 650points www.aspiranthub.com 212 What is Authorization ? Ans : aapne badle kisi ko decision lene k power ko tranfer karne ko Authorization OR authorising somone to carry out sm activities. 213 What do you know about Bank Ombudsman ? Ans : The Banking Ombudsman Scheme enable an expeditious to bank customers for resolution of complaints relating to certain services rendered by banks. The Banking Ombudsman Scheme is introduced under Section 35 A of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 by RBI with effect from 1995. there are 15 place where stable it .. . 214 Difference between Small Bank and Payment Bank ? Ans : Small banks acepts all types of deposits like casa, fd rd..... Where as payment bank acept only casa deposite Small banks give loans to for small area of operation..... Payment bank cant give loans.. They invest in govt. Security... Sells mutual funds, insurance products 215 What do you understand by Bouncing of a cheque ? Ans : it means the chq is of amount which is not present in a/c at the time when chq present for payment OR jb a/c me sufficient money ni hota cheque ko pas krne k liye to cheque bounce ho gati hai OR bouncing of cheque is also called dishonor of cheque - according to negotiable instrument 1881 sec 138 it is crime ----- bouncing of cheque only - don't have sufficient balance ************ result- jail up to 2 year or monetry fine upto double the amount written on cheque... or both 216 Certif icate of Deposits (CDs) ? Ans : issued by all scheduled commercial bank(expect -rrbs, labs)min-7days , max-1year **** amount min -1 lakh max- its multiple *****when CDs issue financial institution - min 1 year max -3 year ** amount same 217 If a person doesn't have proper proof,how will you open an account?? Ans : he/she can open small acnt by submiting a photograph and sign in d presence of bank officer for 1 year(validity is further extended if d customer wil submit all d reqd documents)..... these acnts hv also sm www.aspiranthub.com operational restrictions 218 NABARD functions vs RRB Functions ? Ans : abard is a development bank in the field of agrii & rural. it regulates n refinance rrbs and all types cooperative banks except urban or primary cooperatives which r directly regltd by rbi. whereas rrbs are Scheduled commercial banks cattering to small n marginal farmers labourers n small incom family. main objective is to provide farmers fequate n tymly credits 219 Diff b/w FDI and FII ??? Ans : Fii are the foreign firm investing money in share /eqity market of india after taking permission from sebi OR forigner jab 10% se jada invest karenge toe fdi warna fii fdi long term investment plan k tahat aata hai but fii short term plan k tehat OR - FDI- A foreign invests acquire the controlling stake of the country..ie acquires a part of ownership..it has control over its management...FII- Foreign co only invests in shares of Co and has no controlling stake...FDI cant be taken back easily by such Cos..but FII can easily disinvest at anytime they want 220 difference between banking and finance? Ans : finance is a much wider term that includes resource allocation, their management & investment ,while banking is limited to accepting deposits & lending. . OR Bank is the financial institution which takes deposite ,gives loan,cheque clearing,tranfer money,invest or safegaurd the money of customer.....and finance is the branch of economics with resource allocation and resource mangmt....finace is related to money and the makt. . 221 Participatory notes? Ans : These are financial instruments used by investors or hedge funds that are not registered with the Securities and Exchange Board of India to invest in Indian securities. Indian-based brokerages buy India-based securities and then issue participatory notes to foreign investors. 222 Definition of Term "REPO" only ? Ans : re purchase option : bank security rbi ko bechti hai and wachan deti www.aspiranthub.com ahi ki dubara kharidegi 223 Y is inf lation a debtors enemy n creditors best frnd Ans : ja inf lation hoga toe price badh jaayega means same ammount ka market value ghat chuka hoga toe jo paisa le raha hai ussko wo ammount mehnge rate pae milega but jo de raha hai usska fayada hai kyuki ussko toe high intrest mil raha hai usspae 224 Den diff BTW capital n money mkt ? Ans : capital mrkt- deal in long term instruments, money mrkt- its for short term instruments OR capital market is regulated ba SEBI whre as money market is regulated by RBI. in capital market for long term lending and borrowing is done whereas in money market short term lending and borrowing is done. 225 what is the difference between credit and investment? Ans : credit mae aap kisi ko loan dete hai but investment mae aap kisi field mae invest karte hai jismae se kitna return aayega usska koi garantee nahi rehta jo ki credit mae rehta hai 226 Wt do u understand by share capital n its types ? Ans : share means part of smthing when it comes in business it means part of ownership that r sold to smone else making him partly owner n utilitising the fund raised in business. that share is traded in secondary market from one person to anothr. OR capital that is raised by issuing shares is share capital...its 2 main types- equity share cap & preferential share cap 227 What is Subprime crisis? Ans : when a person has not d capacity to repay the loan instead of dis bank gives loan to him(in the lure of getting high rate of intrsrt) is called sub prime lending and dis generates d sub prime crisis lyk in past euro zone,LIBOR crisis hapnd OR When bank gives loan to low creditworthy customers is called sub prime lending.. Thus crisis is due to sub prime lending is called sub prime crisis.. 228 Wt r d various sources fr raising capital ? Ans : capital market, debt market...borowing from banks of FIs. www.aspiranthub.com for govt: disinvestment, manupulating rbi to propel banks to invest more in slr. imposing taxes, making sourcefull investment tax empted. for common people: overtime OR - shares , debentures & bonds r 3 main ways of raising capita l 229 NOSTRO vs VOSTRO A/c ? Ans : nostro- our a/c with you , vostro- ur a/c with us...***********.NOSTRO Account: A NOSTRO account is maintained by an Indian bank in the foreign countries. ************VOSTRO Account: a vostro a/c is maintained by a foreign bank in India with their corresponding bank. OR nostro- our account with you.. vostro- your account with us. 230 Base Rate vs Bank Rate ? Ans : base rate- min rate below which banks cant lend to borrowers...bank rate- it's a monetary policy tool , rate at which RBI lends to bank for long term 231 What is e-KYC? What is itz work? Ans : acc 2 rbi guidelines for e-kyc u should hv 12 digit aadhar no.... u hv to submit just ur aadhar no. to bank 4 ekyc service... after dis uidai wil transfer all ur ident ity(lyk photograph,name ,gender,age etc) 2 ur bank electonically. 232 Whats the difference between debentures and bonds..? Ans : debenture : issued only by corporates , high return, high risk , bonds: by goi or PSE , comparetivly less return bt less or no risk OR bonds are more secured than debentures...in bankruptcy case bondholders are paid first and than debenture holders. Interest in debentures r more than bobds 233 multi branch banking ??is it same as CBS ? Ans : ll the transaction is done in any branch bank in multi branch Whereas CBS is fully computerised banking in which all the branchs of the bank is connected to core server so data is directly assessed. i think both r same . OR multi branch banking means banking servies provided by various branches of the particular bank 234 What is "Term Repo" ? www.aspiranthub.com Ans : A practice in which a bank or other financial institution buys securities with the proviso that the seller repurchases the same securities foran agreedupon price on a certain day more than one day after the establishment of the agreement. Investors and financ ial institutions do thisin order to raise shortterm capital. A term repo differs from other types of repo because the term is more than one day. 235 Under PMJDY, If the present address is different than that of printed on Aadhaar Card, then a self certif ication of current address is sufficient. What is exactly self certif ication?? Ans : self certif ication means... mentioning that my address has been changed to xyz which is different from that mentioned on adhar card. and certifying it by self by puting signature or thumb impression 236 Is there any limit on amount in jan dhan account ?can i convert my normal saving account into jan dhan account? Ans : yes there is a limit in JDA.yes u can convert normal saving account into jan dhan account 237 why bbps hs been proposed to be introduced if payments can be made through online transaction smoothly????? Ans : cause online facilities r nt easily available to everyone. before the launching of pmjdy only 60% people hv access to bank outta wich only 20% hv acces to internet banking. bbps will work as a unif ied plateform for all from where utility bils or recurring bills can be paid. OR ll definitely save time n money as it wud avoid duplications plus uniformity ll b ensure thru single bill n ll curb frauds too certain extent 238 Does PMJDY not violating the KYC guidelines?? Ans : nope. kyc is also done here. anyway kyc norms has just been simplif ied..e.g adhar will serve as both adress aswell as id proof. even if address is diffrent self certif ication will do etc. 239 What are inflation index bonds & to which inf lation index r they linked www.aspiranthub.com to- WPI or CPI ?? Ans : bonds that adjusted as per inf lation ie their rates r kept higher than the inf lation rate. . earlier they were linked to WPI..now CPI 240 What is a wire transfer? Ans : means to tranfser money b/w 2 countries 241 Why PSBs give 4% Interest rate while Private Sector bank 7-8%???? 242 .does bank charge penalty on premature withdrawal of FD? 243 what is fiscal policy ? 244 wht is ICRA nd ONICRA? 245 Difference between Mutual Funds and Hedge funds? 246 Why RBI is known as controller of credit? 247 Any reason for keeping Reverse Repo Rate 1% less than Repo Rate?? 248 In the total reserves of the RBI, how much % should be maintained in the form of gold? 249 wt is disinvestment? 250 What are G-Secs ? 251 Diff bet Liquidity & Solvency? 252 Difference b/w tier 1 and tier 2 capital? 253 Difference between open cheque and bearer cheque? 254 Explain how ARC Work ? 255 What were the Basel-2 norms? explain in simple language 256 Who is a Qualified Foreign Investor? 257 what is hard and soft money? 258 Can a blind person open an account. If yes does he need witness. Can cheques atm be issued to him ? 259 what is external commercial borrowing? Explain. 260 Net Asset Value ? 261 Pass Book ? 262 Post-Dated Cheque ? Why it is useful ? 263 explain the difference btw authorised capital ,issued capital and paid up capital 264 Underlying Security ? 265 what is welfare banking? Who introduced it in india? 266 Difference between Micro finance and micro credit? 267 Are BSBDA and Small Accounts same??? 268 what is refinance?? www.aspiranthub.com 269 Difference between Fixed and Variable Expenses? 270 Why a person should prefer a bank rather than a post-office for keeping deposits? 271 special crossing cheques bearing , "SBI a/c payee " how it will honour ?? 272 explain d layering stage(of money laundering) in easy language ? 273 Explain kishan credit card ? 274 why bancassurance is done by banks ? 275 what is prime lending rate ? 276 ATM : automated teller machine what is automated ? 277 CORE and CBS ? 278 Convertible Bond ? 279 ECS vs ACH ? 280 Arbitrage ? 241 Why PSBs give 4% Interest rate while Private Sector bank 7-8%???? Ans : private banks first to seize the opportunity and differentiate themselves by offering higher rate of interest. Public sector banks enjoys a large network of branches, huge customer base and relatively high CASA.... OR Private sector banks are still less attractive then PSB in India. The requirements to open account in private sector are also strict. So private sector bank offers more attractive intrest rate(generally 6-7%) then PSB to make its customer base stronger. OR To attract more customer so it can get more deposit it leads to more loans leads to more profit 242 .does bank charge penalty on premature withdrawal of FD? Ans : Yes,1% or sometimes they dont charge.depends on the bank. 243 what is fiscal policy ? Ans : fiscal policy means govt. adjust its spending level & tax rates to moniter and inf luence a nations economy OR - fiscal policy means budgetory policy considering revenue n expenditure to bring stability in economy 244 wht is ICRA nd ONICRA? Ans : Credit rating agencies , hq—gurgaon 245 Difference between Mutual Funds and Hedge funds? Ans : Mutual funds are low risk fund with low prof it while hedge funds are www.aspiranthub.com high risk funds to aim high profit . OR - only diff z dat in hedge fund investment z much more higher,,dats y its formed by high net worth individual only... OR mutual fund--any investor can invest , eq-100 rs min required in sbi Hedge fund-only high net worth individual (ambani types k liye) 1 crore is min investment 246 Why RBI is known as controller of credit? Ans : coz it controls d creation of credit in d economy by regulating bnk rate ,repo rate ,crr,etc. according to d need of economy by increasing it in deflationary trend n reducing it inf lationary trend 247 Any reason for keeping Reverse Repo Rate 1% less than Repo Rate?? Ans : no there is no reason it is the rule of rbi..(2010) 248 In the total reserves of the RBI, how much % should be maintained in the form of gold? Ans : 115 cr gold and 85cr foreign currency total 200 cr 249 wt is disinvestment? Ans : selling of govt. stake in public enterprises to private sector with a view to contain deficit 250 What are G-Secs ? Ans : g-sec means easly convert into cash like bond ,treasury bill 251 Diff bet Liquidity & Solvency? Ans : Solvency refers to an enterprise's capacity to meet its long-term financial commitments but Liquidity refers to an enterprise’s ability to pay short-term obligations. 252 Difference b/w tier 1 and tier 2 capital? Ans : tier1 capital z considered the core capital of an organisation as it easily can converted into cash like equity capital....tier2 capital is less liquid taked more tym to convert into cash like property as mortgage near to bank OR - Tier 1 core capital like equity and reserves and surpluses and tier2 supplimentary capital like undisclosef reseve and general loss reserves 253 Difference between open cheque and bearer cheque? Ans : bearer cheque z a type of open cheque where payee can incashed the amount at counter..and in case of www.aspiranthub.com bearer cheque any person who presents it at counter get the cash OR Open cheque can be endorsed to anyone but there is no need of endorsement in bearer cheque anyone can encash it 254 Explain how ARC Work ? Ans : asset reconstruction company buy npa from bank and sell to other and make profit. . OR Bank sell their bad debt or npa to arc.. they charge their commsion on this, futher arc try to fetch more profit from these npa, they have to register under rbi, arcil is one of them, they issue security receipts and qualif ied institutions buyer wil buy thm like this process goin on.. 255 What were the Basel-2 norms? explain in simple language Ans : Basel 2 are reformed verson of basel 1. ek chij jo dono me common ki minimum capital adquacy 8% 2nd chij ki bank ek better risk management technique use kre jaise ki avi bda loan dene se phle credit rating check krti hai. aur 3rd ki bank jo v risk assesment ya risk exposure technique use krti hai wo central bank ko jarur se disclose kre. OR basel 2 does nt have any explicit regulation on the debt that bank could take and focused more on individual f inancial institution and ignore systematic risk (entire banking system may be collapse : like 2007 crisi). to ensure that bank does nt take excessive debt and dont rely much on short term funds, Basel 3 was preposed. 256 Who is a Qualif ied Foreign Investor? Ans : 1)scheduled commercial bank 2)insurance company 3) FII 257 what is hard and soft money? Ans : hard mny means physical money like currency n coins and soft money means cash balances in our accounts OR - Hard money/currency---- it is a freely convertible currency that is not expected to depreciate in value relative to other currencies. It is of highly industrialised nations. Eg - $,£,€ and ¥ etc. Soft money/currency--- it is a currency that is expected to drop in value relative to other currencies. www.aspiranthub.com It is of weaker economies. 258 Can a blind person open an account. If yes does he need witness. Can cheques atm be issued to him ? Ans : Yes..sa and term depo accounts can b opened..wid sig nd thumb impression in the opening form which should be witnessed by a respectable person .. No chequebook can be issued. OR You need to remember that a blind person is fully competent to enter into a contract like any other person. However, due to his physical disability, there can be a situation where he contests subsequently that the facts were misrepresented to him and-thereby try to avoid the contract. Therefore, signature or thumb impression of the blind person should be attested by an independent witness to the effect that all terms and conditions were properly explained to the blind person in his presence. Moreover, cash deposit and withdrawal by blind person should be handled by the officer of the bank. Cheque book can be issued only if the blind person can sign consistently. 259 what is external commercial borrowing? Explain. Ans : Corporates getting f inance from foreign countries OR - Borrowing money from foreign countries for business. 260 Net Asset Value ? Ans : current market value of all the assests minus current liabilities divided by no. of units 261 Pass Book ? Ans : passbook is a statement which is recorded the customer deposit value and withdraw value OR Passbook is customer document which records all the ledger transactions of his bank account 262 Post-Dated Cheque ? Why it is useful ? Ans : Cheque having a date of future. Means that cheque will become valid after that particular date of future. OR it provides security to the issuer if work is nt accomplished in future he cn cancel it 263 explain the difference btw authorised capital ,issued capital and paid up capita l www.aspiranthub.com Ans : authorised which d co. s authorise to issue to d public by registrar of companies ,issued d amt of capital ie actually issued to d public fr subscription it may happen d co do not issues d entire authorised capital fr subscription n paid up capital s amt of share capital actually paid by d shareholders cos it may b a case dat shareholders do not pay d entire amt together OR Authorised means max capital which can be issued . It is mentioned in memorandum or article of association Issued : that part of authorised cap which is issued to share holders Paidup : that part of issued capital which is paid by shareholders 264 Underlying Security ? Ans : The security subject to being purchased or sold upon exercise of the option contract. 265 what is welfare banking? Who introduced it in india? Ans : welfare banking refers to provide financial support of needy ppl in lower income group or economically backgroung ppl. 266 Difference between Micro finance and micro credit? Ans : Microf inance is a much broader concept than microcredit and refers to loans, savings, insurance, money transfers, and other financial products targeted at poor and low-income people. Microcredit refers more specif ically to making small loans available to poor people, especially those traditionally excluded from financial services, through programmes designed specif ically to meet their particular needs and circumstances OR Micro credit is part of microf inance js a provision to provide financial services to poor ppl, micro credit is extension of micro loans to unemployed , poor who r not considered S bankable, they lack collatral, employment and even they also lack in verif iable credit history, so they are not eligible for even a traditional loan Originated in bangladesh and now in imdian banking also. . 267 Are BSBDA and Small Accounts same??? Ans : Bsbda are kyc compliant accounts, Small accounts are kyc relaxed www.aspiranthub.com accounts 268 what is refinance?? Ans : nabard rrb ko finance kare or rrb public ko to ise hi ref inance bolte h OR refinancing means to rplace existing debt or loan with a new debt or loan with different conditions of payment often done to take reduce risk 269 Difference between Fixed and Variable Expenses? Ans : fixed_expenses r fixd in nature lyk godown rent a/c ,, dey will remain same irrespective of quantity produced where as variable_expenses will accur only if uh produce lyk cost of raw material nd Labour etc. OR fixed expenses a those whose amt s fixed in nature irrespective of d production or usage lyk rent of building etc n variable r those which vary with production or usage lyk cost of raw materials etc . 270 Why a person should prefer a bank rather than a post-office for keeping deposits? Ans :Due to the services related to net banking, mob banking n more customer oriented approach 271 special crossing cheques bearing , "SBI a/c payee " how it will honour ?? Ans : In account of the beneficiary only if sbi presents it. OR Crossing the cheque means the amount have to be credit in the account of beneficial. It can not be encashed on counter.. It is safest mode for cheque. . OR Only sbi m ke a/c me hi transfer hoga amt 272 explain d layering stage(of money laundering) in easy language? Ans : Money laundering involves three stages: placement, layering and integration. Placement involves physically placing illegally obtained money into the financial system or the economy. Layering means separating the illegally obtained money from its source through a series of financial transactions that makes it diff icult to trace the origin. Integration means converting the illicit funds into a seemingly legitimate form. Integration may include the purchase of businesses, automobiles, real estate and other assets. 273 Explain kishan credit card ? www.aspiranthub.com Ans : Credit card issued to farmers to meet their agricultural needs for seeds, instruments n fertilizers OR It is a combined intiative of goi, rbi and nabard. Main aim to easily provide credit to farmers without paper work or less paper work. 274 why bancassurance is done by banks ? Ans : To provide insurance and banking under one roof so that customer dont have to go in search for insurance co. Also to earn profit and customer satisfaction 275 what is prime lending rate ? Ans : A rate on which bank lends to its credit worthy customer / prime customer also called benchmark prime lending rate . This is old concept now it is replaced by base rate 276 ATM : automated teller machine what is automated ? Ans : Cash counting and vending primarily Apart from that the functions of a bank teller whuch a machine performs OR An automated maxhine means it wil perform bankers operations automatically, like balance info, couting of cash, deduction money from account.. etc.. 277 CORE and CBS ? Ans : Centralised online real time exchange 278 Convertible Bond ? Ans : That bond which are converted in to equity shares 279 ECS vs ACH ? Ans : Ecs electronic clearing service.. . frequent payments are cleared Automated clearing house is a mediator to clear interbank payments e. g rbi in case of nef t OR Ecs is for repeated and periodicle transactions in which bank is responsible for clearing payment on a certain date.. Ach is mediator for interbank payments.. 280 Arbitrage ? Ans : The simultaneous purchase and sale of an asset in order to profit from a difference in the price. It is a trade that profits by exploiting price differences of identical or similar f inancial instruments, on different markets or in different forms OR simultaneous buying n selling of securities used as a tool to avoid risk www.aspiranthub.com due to chnge in interest rates OR buying security from 1 market at lesser price and selling it in another mrkt at high price . Arbitrage strategy is based on taking advantage of price differences in diff mrkts.. www.aspiranthub.com
© Copyright 2026