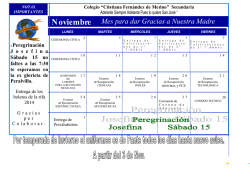
Descargar Libro de Resúmenes
28th International Congress of Condition Monitoring and Diagnostic Engineering X Congreso Regional de Ensayos No Destructivos y Estructurales BOOK OF ABSTRACTS LIBRO DE RESÚMENES 01-04.12.2015 Centro Atómico Constituyentes, Comisión Nacional de Energía Atómica (CNEA) Av. Gral. Paz 1499 San Martín, Provincia de Buenos Aires Argentina COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina Resúmenes del 28° Congreso Internacional de Gestión de Ingeniería en el Monitoreo y Diagnóstico de Condiciones y del 10° Congreso Regional de Ensayos No Destructivos y Estructurales Book of abstracts of the 28th International Congress of Condition Monitoring and Diagnostic Engineering and the 10 Regional Conference on Non Destructive and Structural Testing th 18º Encuentro del Comité Sectorial MERCOSUR CSM 24 de Ensayos No Destructivos Meeting of the MERCOSUR NDT Standards Committee Reunión del Comité Panamericano de END Pan American NDT Federation Meeting 01-04.12. 2015 Buenos Aires – Argentina 3 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE 28º COMADEM + X CORENDE 2015 Libro de resúmenes y programa del 28º International Congress of Condition Monitoring and Diagnostic Engineering Management (COMADEM 2015) y el 10º Congreso Regional de Ensayos No Destructivos y Estructurales (X CORENDE) Buenos Aires, 01 al 04 de diciembre de 2015 Asociación Argentina de Ensayos No Destructivos y Estructurales (AAENDE) Coordinado por Marta Clelia Ruch Primera Edición – Buenos Aires, 2015 ISBN 978-987-23957-6-6 CDD 620 4 Buenos Aires, Argentina COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina PROLOGO Este libro recoge los trabajos presentados en el 28° Congreso Internacional de Gestión de Ingeniería en el Monitoreo y Diagnóstico de Condiciones (COMADEM 2015) y el 10º Congreso Regional de Ensayos No Destructivos y Estructurales (X CORENDE) organizado por la Asociación Argentina de Ensayos No Destructivos y Estructurales (AAENDE), JPS Argentina y COMADEM International, con el auspicio y colaboración de instituciones, empresas y entidades académicas. Este encuentro busca aunar esfuerzos y reunir a todos los interesados en la temática a nivel mundial, con el objetivo de fomentar el intercambio cultural. La COMADEM es la oportunidad para ponerse en contacto con las tecnologías que continuamente mejoran y realzan la calidad, confiabilidad, seguridad, mantenibilidad y desempeño de los activos (tanto físicos como humanos) de forma tan amplia como sea posible y obteniendo los máximos beneficios con un mínimo riesgo. Mientras que el CORENDE se propone como un foro de discusión, donde se intercambien y discutan ideas acerca de las mejoras en el uso de las tecnologías en la evaluación de componentes, sistemas y estructuras, en todas las etapas, desde la investigación hasta la producción y comercialización. Los trabajos de la COMADEM 2015 y el X CORENDE que se incluyen en este volumen, presentan una panorámica del estado del arte de los desarrollos y aplicaciones más recientes en ambos campos del conocimiento. Se ha dividido en 6 sesiones, que recorren las siguientes temáticas: Monitoreo de la Condición, Ensayos No Destructivos, Análisis de Vibraciones, Gestión de Activos, Análisis de Proceso y Rodamientos. Además de presentar los artículos, es un honor para este congreso presentar las siguientes Conferencias Plenarias: The CAREM Project Lic. Osvaldo Calzetta Larrieu – CNEA, Argentina Condition Monitoring and Diagnosis of Modern Dynamic Complex Systems using Criticality Aspect of Key Performance Indicators Prof. Aditya Parida – Luleå University of Technology, Sweden Modern envelope analysis for bearing diagnostics Prof. Robert Randall – University of New South Wales, Australia Early Preventive Actions for Space Mission Success Ing. Edgardo Roggero – CONAE, Argentina Conference on NII – Non Intrusive Inspection Francisco Carlos Rodrigues Marques - Petrobras, Brasil Transformation from Maintenance to Asset Management Ing. Ricardo Pauro – UTN, Argentina INVAP: from nuclear technology to aerospace technology Dr. Vicente D. Campenni – INVAP, Argentina Reliability Matters, of course! but how ‘reliable’ is Reliability? Prof. B.K.N. Rao – COMADEM Internacional, UK Y la presentación de OLYMPUS: Detecting stress corrosion cracking with eddy current array technology Emilie Peloquin – Houston, Texas, USA Como es habitual, en el marco de este evento, se reúne el Comité que trabaja para el desarrollo de normativas de Ensayos No Destructivos comunes, para todo el ámbito del MERCOSUR. En este caso es el 18º Encuentro del Comité Sectorial MERCOSUR CSM 24 de Ensayos No Destructivos. En esta oportunidad, tenemos el placer de organizar la Reunión de las Asociaciones de Ensayos No Destructivos de la Región Panamericana, que se dan cita para tratar todas las temáticas que contribuyan a promover la actividad en nuestra región. Ofrecemos nuestro sincero agradecimiento a todos los que colaboraron con la realización de esta Conferencia, a las entidades patrocinadoras del COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE, y particularmente a los participantes que nos acompañan y lo hacen posible. Buenos Aires, Noviembre de 2015 Comité Organizador 5 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina FOREWORDS This volume compiles all the abstracts that were presented to the 28º International Congress of Condition Monitoring and Diagnostic Engineering Management (COMADEM 2015) and the 10th Regional Non-Destructive & Structural Testing Congress (X CORENDE) organized by the Argentine Society of Structural and Non Destructive Testing (AAENDE after its name in Spanish), JPS Argentina and COMADEM International, with the sponsorship and collaboration of several firms and academic institutions. The Congress intends to invite and integrate people involved in this study area in an open forum to encourage and facilitate exchange of information and experiences from all regions of the world. COMADEM is the opportunity to get in touch with technologies that continuously improve and enhance the quality, reliability, safety, availability, maintainability and performance of all assets (both physical and human) for as long as possible and to derive maximum benefits with minimum risk. CORENDE is a forum to discuss the improvements in the technologies used in the evaluation of components, systems and structures: non-destructive testing, personnel certification, standards, welding inspection, maintenance and structural testing. The COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE papers in this volume present a panorama of the state-of-the art of the most recent R/D and applications in both fields. It has been divided in 6 sessions covering the following subjects: Condition Monitoring, Non-Destructive Testing, Vibration Analysis, Asset Management, Process Analysis and Bearings. Besides the contributed papers, it is an honor to present the following Plenary Conferences: The CAREM Project Lic. Osvaldo Calzetta Larrieu – CNEA, Argentina Condition Monitoring and Diagnosis of Modern Dynamic Complex Systems using Criticality Aspect of Key Performance Indicators Prof. Aditya Parida – Luleå University of Technology, Sweden Modern envelope analysis for bearing diagnostics Prof. Robert Randall – University of New South Wales, Australia Early Preventive Actions for Space Mission Success Eng. Edgardo Roggero – CONAE, Argentina Conference on NII – Non Intrusive Inspection Francisco Carlos Rodrigues Marques – Petrobras, Brasil Transformation from Maintenance to Asset Management Eng. Ricardo Pauro – UTN, Argentina INVAP: from nuclear technology to aerospace technology Dr. Vicente D. Campenni – INVAP, Argentina Reliability Matters, of course! but how ‘reliable’ is Reliability? Prof. B.K.N. Rao – COMADEM Internacional, UK And the OLYMPUS special presentation: Detecting stress corrosion cracking with eddy current array technology Emilie Peloquin – Houston, Texas, USA As usual, within this event, the MERCOSUR NDT Standards Committee will meet for the 18º time for the development of NDT common standards in the region. In this opportunity, we are glad to hold also the Pan American NDT Federation Meeting, where the associations gather to discuss different subjects in order to promote the activity in our region. We gratefully acknowledge the gentle cooperation of all those who worked with us for this Conference, COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE’s sponsors and last but not least, the participants, who made this conference possible. Buenos Aires, November 2015 Organizing Committee 6 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina COMITÉS / COMMITTEES Presidentes/Congress Chairs Ing. César G. Belinco, AAENDE-CNEA, Argentina Prof. B.K.N. Rao, COMADEM International Comité de Dirección /Congress Co-Chairs Ing. Jorge A. Amsler, AAENDE-CAEFE, Argentina Ing. Jorge P. Amsler, AAENDE-BRUKE, Argentina Lic. Natalia Surraco, AAENDE, Argentina Mg. Ricardo Echevarría, AAENDE-UNCOMA, Argentina Ing. Héctor Espejo, AAENDE, Argentina Ing. Carlos Farina, AAENDE-UTN-Delta, Argentina Ing. Alejandro García, AAENDE-CNEA, Argentina Ing. Mariano Mofsovich, JPS, Argentina Ing. Marcelo Noble, AAENDE-OSHMA, Argentina Ing. Fernando Nuñez, AAENDE-TENARIS, Argentina Prof. Aditya Parida, PhD, Lulea University of Technology, Sweden Dra. Marta Ruch, AAENDE-CNEA, Argentina Ing. Claudio Vozar, AAENDE-TENARIS, Argentina Comité Científico/ Scientific Committee Coord: Dra. Marta C. Ruch, AAENDE-CNEA, Argentina Dr. Jose Brizuela, CONICET-CNEA, Argentina Dr. Gopinath Chattopadhyay, University of Queensland, Australia Ing. Carlos Coppié, JPS, Argentina Prof. Daniel DeSouza Jr., Fluminense Federal University, Brazil Dra. Elsa Hogert, CNEA, Argentina Dr. Kenneth Holmberg, VTT Technical Research Centre, Finland Dr Erkki Jantunen, VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland, Finland Prof. Rakesh Mishra, PhD, University of Huddersfield, Huddersfield, UK Prof. Aditya Parida, PhD, Luleå University of Technology, Sweden Ing. Ricardo Pauro, UTN, Argentina Ing. Mauricio Torretta, JPS, Argentina Prof. Karsten Schmidt, Frankfurt University of Applied Sciences, Germany Prof. Dr. Fengshou Gu, University of Huddersfield, UK Apoyos institucionales/ Technical Event Partners Committee of Equipment Fault Diagnosis of Chinese Society for Vibration Engineering (CSVE) Committee of Plant Diagnosis Engineering of China Association of Plant Engineering (CAPE) Committee of Plant and Maintenance Engineering of Chinese Mechanical Engineering Society (CMES) Prognostics Health Management (PHM) Machinery Failure Prevention Technology Society based in USA (MFPT) International Tribology Council based in UK (ITC) Condition Monitoring Society of India (CMSI) 7 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE CHAIRS Prof. B.K.N. Rao, COMADEM International Ing. Carlos Farina, AAENDE-UTN-Delta, Argentina Ing. Héctor Espejo, AAENDE, Argentina Ing. Mariano Mofsovich, JPS, Argentina Prof. Aditya Parida, PhD, Luleå University of Technology, Sweden Ing. Jorge A. Amsler, AAENDE-CAEFE, Argentina Prof. Rakesh Mishra, PhD, University of Huddersfield, UK Ing. Jorge P. Amsler, AAENDE-BRUKE, Argentina Ing. Francisco Carlos Rodrigues Marques, Petrobras, Brasil Mg. Ricardo Echevarría, AAENDE-UNCOMA, Argentina Ing. Alejandro García, AAENDE-CNEA, Argentina Prof. Robert Randall, University of New South Wales, Australia Prof. Daniel DeSouza Jr., Fluminense Federal University, Brazil Prof. Dr. Fengshou Gu, University of Huddersfield, UK Ing. César G. Belinco, AAENDE-CNEA, Argentina Prof. Zi Yanyang, PhD, Xi’an Jiantong University, China Dra. Marta C. Ruch, AAENDE-CNEA, Argentina 8 Buenos Aires, Argentina COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina PROGRAMA Lunes 30-Nov Martes 01-Dic 9.00-18.00hs Encuentro del Comité de Normativa MERCOSUR END Coordinación: IRAM Miércoles 02-Dic Jueves 03-Dic Viernes 04-Dic 9.00hs Apertura de registro de participantes 10.00-13.00 hs Reunión del Comité Panamericano de END Coordinación: ABENDI 9.00-10.00hs Plenaria Conference on NII – Non Intrusive Inspection Francisco Carlos Rodrigues Marques – Petrobras, Brasil 9.00-10.00hs Plenaria Modern envelope analysis for bearing diagnostics Prof. Robert Randall – Universidad de New South Wales, Australia 10.00-10.30hs Intervalo de café 10.30-12.10hs Sesión técnica 2 Auditorio: Monitoreo de la condición (traducción simultánea) Aula A: Análisis de vibraciones / Aula B: CORENDE / Aula C: Gestión 10.30-12.10hs Sesión técnica 4 Auditorio: Monitoreo de la condición (traducción simultánea) Aula B: CORENDE 10.00hs Apertura de registro de participantes 10.00-11.00hs Plenaria Transformation from Maintenance to Asset Management Ing. Ricardo Pauro UTN, Argentina 11.00-12.00hs Sesión técnica 6 Auditorio: Monitoreo de la condición (traducción simultánea) Aula B: CORENDE 12.10-13.10hs Almuerzo en el Salón de Exposición Apertura de las sesiones Palabras de bienvenida 14.00-15.00hs Plenaria The CAREM Project Lic. Osvaldo Calzetta Larrieu – CNEA, Argentina 15.00-16.00hs Sesión técnica 1 Auditorio: Monitoreo de la condición (traducción simultánea) Aula A: Análisis de vibraciones / Aula B: CORENDE / Aula C: Gestión de activos 16.00-16.30hs Intervalo de café (Apertura EXPO) 16.30-17.30hs Sesión técnica 1 Auditorio: Monitoreo de la condición (traducción simultánea) Aula A: Análisis de vibraciones / Aula B: CORENDE / Aula C: Gestión de activos 17.35-18.00hs Ceremonia de apertura 13.10-14.10hs 13.10-13.50hs Presentación OLYMPUS Detecting stress corrosion cracking with eddy current array technology Emilie Peloquin 14.10-15.10hs Sesión técnica 3 Auditorio: Monitoreo de la condición (traducción simultánea) Aula A: Rodamientos / Aula B: CORENDE / Aula C: Análsis de proceso 13.50-14.50hs Plenaria INVAP: from nuclear technology to aerospace technology Dr. Vicente D. Campenni – INVAP, Argentina Plenaria Early Preventive Actions for Space Mission Success Ing. Edgardo Roggero – CONAE, Argentina 15.10-15.40hs Intervalo de café 15.40-17.10hs Sesión técnica 3 Auditorio: Monitoreo de la condición (traducción simultánea) Aula A: Rodamientos / Aula B: CORENDE / Aula C: Análsis de proceso 13.00-14.00hs Plenaria Reliability Matters, of course! but how ‘reliable’ is Reliability? Prof. B.K.N. Rao – COMADEM Internacional, Reino Unido 14.00-14.30hs Ceremonia de cierre 14.30-15.30hs Visita técnica al CAC (Centro Atómico Constituyentes) 15.20-17.00hs Sesión técnica 5 Auditorio: Monitoreo de la condición (traducción simultánea) Aula B: CORENDE 17hs / 17.10hs Fin de sesiones del día 18.00-19.00hs Plenaria Condition Monitoring and Diagnosis of Modern Dynamic Complex Systems using Criticality Aspect of Key Performance Indicators Prof. Aditya Parida Universidad de Luleå, Suecia 19.00-20.30hs Cocktail de bienvenida 20.00hs Cena de camaradería Presentación COMADEM 2016 9 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina PROGRAM Monday 30-Nov Tuesday 01-Dic 9.00-18.00hs Wednesday 02-Dec Thursday 03-Dec Friday 04-Dec 9.00hs Opening of Conference Registration & Reception Desk Meeting of the MERCOSUR NDT Standards Committee 10.00-13.00 hs Coordination: IRAM Pan American NDT Federation Meeting Coordination: ABENDI 9.00-10.00hs Plenary Session Conference on NII – Non Intrusive Inspection Francisco Carlos Rodrigues Marques – Petrobras, Brasil 9.00-10.00hs Plenary Session Modern envelope analysis for bearing diagnostics Prof. Robert Randall – University of New South Wales, Australia 10.00-10.30hs Coffee Break 10.30-12.10hs Technical Session 2 Auditorium: Condition monitoring (simultaneous translation) Room A: Vibration analysis / Room B: CORENDE (NDT) / Room C: Asset Management 10.30-12.10hs Technical Session 4 Auditorium: Condition monitoring (simultaneous translation) Room B: CORENDE (NDT) 10.00hs Opening of Conference Registration & Reception Desk 10.00-11.00hs Plenary Session Transformation from Maintenance to Asset Management Ing. Ricardo Pauro UTN, Argentina 11.00-12.00hs Technical Session 6 Auditorium: Condition monitoring (simultaneous translation) Room B: CORENDE (NDT) 12.10-13.10hs Lunch at the Exhibition Hall Opening Session Welcome and keynote speech 14.00-15.00hs Plenary Session The CAREM Project Lic. Osvaldo Calzetta Larrieu – CNEA, Argentina 15.00-16.00hs Technical Session 1 Auditorium: Condition monitoring (simultaneous translation) Room A: Vibration analysis / Room B: CORENDE (NDT) / Room C: Asset Management 16.00-16.30hs Coffee Break (EXPO Opening) 16.30-17.30hs Technical Session 1 Auditorium: Condition monitoring (simultaneous translation) Room A: Vibration analysis / Room B: CORENDE (NDT) / Room C: Asset Management 17.35-18.00hs Opening Ceremony 13.10-14.10hs Plenary Session INVAP: from nuclear technology to aerospace technology Dr. Vicente D. Campenni – INVAP, Argentina 13.10-13.50hs OLYMPUS Presentation Detecting stress corrosion cracking with eddy current array technology Emilie Peloquin 14.10-15.10hs Technical Session 3 Auditorium: Condition monitoring (simultaneous translation) Room A: Bearings / Room B: CORENDE (NDT) / Room C: Process analysis 13.50-14.50hs Plenary Session Early Preventive Actions for Space Mission Success Ing. Edgardo Roggero – CONAE, Argentina 15.10-15.40hs Coffee Break 15.40-17.10hs Technical Session 3 Auditorium: Condition monitoring (simultaneous translation) Room A: Bearings / Room B: CORENDE (NDT) / Room C: Process analysis 15.20-17.00hs Technical Session 5 Auditorium: Condition monitoring (simultaneous translation) Room B: CORENDE (NDT) 17hs / 17.10hs Adjourn 18.00-19.00hs Plenary Session Condition Monitoring and Diagnosis of Modern Dynamic Complex Systems using Criticality Aspect of Key Performance Indicators Prof. Aditya Parida – Luleå University of Technology, Sweden 19.00-20.30hs Welcome Cocktail 10 20.00hs Gala Dinner Presentation of COMADEM 2016 13.00-14.00hs Plenary Session Reliability Matters, of course! but how ‘reliable’ is Reliability? Prof. B.K.N. Rao – COMADEM Internacional, UK 14.00-14.30hs Closing Ceremony 14.30-15.30hs Technical Visit of CAC (Constituyentes Atomic Center) COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina 01.12.2015 CRONOGRAMA SESIÓN TÉCNICA 1 / SCHEDULE TECHNICAL SESSION 1 15.00-15.20 hs 15.20-15.40 hs 15.40-16.00 hs Auditorio/Auditorium Monitoreo de la condición Condition Monitoring Chair: Prof. B.K.N. Rao, COMADEM International Aula/Room A Análisis de vibraciones Vibration Analysis Chair: Ing. Mariano Mofsovich, JPS, Argentina Aula/Room B CORENDE (NDT) Chair: Ing. Carlos Farina, AAENDE-UTN-Delta, Argentina Aula/Room C Gestión de Activos Asset Management Chair: Ing. Héctor Espejo, AAENDE, Argentina Towards condition assessment: Dragline condition monitoring by analysis of motor current and voltage signals (1) SOUTH AFRICA Fault-implantable vibration signal model for fault diagnosis of sun gear in planetary gearboxes (11) UK Introducción al comportamiento de nanopartículas magnetizables en la detección y estudio de discontinuidades microestructurales (10) ARGENTINA Just-in Time and Dynamic Maintenance (JIT-Maint) for Turbine, Generator, Gearbox and Sawmills: Case Stories (8) SWEDEN Enhancing the quality of data from a wheel profile measurement system: a proposed approach (5) SWEDEN A novel criterion for the selection of resonance bands in Complex Shifted Morlet Wavelet based demodulation of defective rolling element bearings vibration response (75) BELGIUM/ GREECE Sistema rápido de inspección de ejes ferroviarios (20) ARGENTINA Optimal corrective maintenance of manufacturing series systems (9) CANADA Investigating Optimal Parameters of Abrassive Water Jet Cutting Process: Engineering Robust Design Based Approach (130) NORWAY Grinding chatter detection based on built-in encoder (79) CHINA Inspección de tubos realizados en plásticos reforzados con fibra de vidrio (21) ARGENTINA Managing the value of maintenance comprehensively in a business network context (22) FINLAND Intervalo de café/Coffee Break Application Acoustic Emission Techniques in Helicopter Main Gearbox Bearing Defect Identification (87) UK Calificación y certificación de personal en Ensayos No destructivos. Comparación entre sistema ISO 9712 y sistema SNT TC 1A (ASNT) (50) ARGENTINA Requalification of offshore assets (124) NORWAY 16.30-16.50 hs Design and implementation of deep neural network based multi-parameter monitoring and diagnostic system for CNC machine tool (15) CHINA 16.50-17.10 hs Fault diagnosis of stay bolt looseness for the dismountable disk-and-drum rotor of aero-engine (19) CHINA Study on active control of rotor unbalanced vibration based on variable frequency dynamic vibration absorber (93) CHINA Análisis de la Emisión Acústica producida en el taladrado de compuestos multicapas (74) ARGENTINA Brake tests to evaluate the human behaviour at different brake pedal characteristics (96) GERMANY/UK 17.10-17.30 hs Mechanical fault detection for motor-gear driving system using motor current signal spectrum analysis (14) LIBYA Perfilómetro compacto basado en triangulación láser activa con luz estructurada (126) ARGENTINA 11 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina 02.12.2015 CRONOGRAMA SESIÓN TÉCNICA 2 / SCHEDULE TECHNICAL SESSION 2 10.30-10.50 hs Auditorio/Auditorium Monitoreo de la condición Condition Monitoring Chair: Prof. Aditya Parida, PhD, Luleå University of Technology, Sweden Aula/Room A Análisis de vibraciones Vibration Analysis Chair: Prof. Zi Yanyang, PhD, Xi’an Jiantong University, China Predictive maintenance system in TermoNorte turbo-generators (27) BRAZIL A research on the dynamic characteristics of gas pulsation in reducer of reciprocating compressor piping system (100) CHINA Escaneo láser con luz estructurada. Aplicación a la inspección de componentes ferroviarios (123) ARGENTINA Service-oriented approach of an eMaintenance Cloud (114) SWEDEN Predictive fault system in internal combustion engines (28) BRAZIL A fault diagnosis method based on spectral kurtosis and three-order cumulation (105) CHINA Evaluación y monitoreo estructural de edificio industrial con vibraciones debidas a máquinas utilizando técnicas dinámicas no destructivas (4) ARGENTINA Multivariate Reliability Assessment Study for Support Ring of Reciprocating Compressor Based on Multidimensional information (116) CHINA A novel method for intelligent fault diagnosis of machinery based on unsupervised feature learning (32) CHINA Vibration analysis of a twenty mill roll grinding machine with a spalling defect on the tip (113) CHINA Análisis de vibraciones de casos de roce parcial y holgura mecánica en máquinas críticas, utilizando medición multicanal (35) ARGENTINA 10.50-11.10 hs 11.10-11.30 hs 11.30-11.50 hs 11.50-12.10 hs 12 Aula/Room B CORENDE (NDT) Chair: Ing. Jorge A. Amsler, AAENDE-CAEFE, Argentina “Implementation of non-destructive techniques for the monitoring of rebar corrosion of concretes developed for nuclear applicationss (33) ARGENTINA” Mediciones especiales en la Central Nuclear Atucha II (49) ARGENTINA Convex Hull-based Support Vector MachineRule Extraction and Applicationin Hot-dip Galvanizing (34) CHINA Validación de modelo de barras combustibles a partir de ensayos hidrodinámicos en el Circuito Experimental de Baja Presión (99) ARGENTINA Aula/Room C Gestión de Activos Asset Management Chair: Prof. Rakesh Mishra, PhD, University of Huddersfield, UK COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina 02.12.2015 CRONOGRAMA SESIÓN TÉCNICA 3 / SCHEDULE TECHNICAL SESSION 3 14.10-14.30 hs. 14.30-14.50 hs 14.50-15.10 hs Auditorio/Auditorium Monitoreo de la condición Condition Monitoring Chair: Ing. Francisco Carlos Rodrigues Marques, Petrobras, Brasil Aula/Room A Rodamientos Bearings Chair: Prof. Robert Randall, University of New South Wales, Australia Aula/Room B CORENDE (NDT) Chair: Mg. Ricardo Echevarría, AAENDE-UNCOMA, Argentina Aula/Room C Análisis de proceso Process Analysis Chair: Ing. Alejandro García, AAENDE-CNEA, Argentina Damage Detection of Composite Material Wind Turbine Blades (37) CHINA Ship-borne Satellite Antenna Bearing Fault Diagnosis using Enhanced Empirical Wavelet Transform via Data-driven Adaptive Fourier Spectrum Segment (29) CHINA Optimización en el monitoreo de la condición del sistema primario del reactor de investigación RA-6: Tanque de decaimiento (118) ARGENTINA A novel transformation of non-stationary signals to periodic signals. Part 1 theoretical foundation (23) POLAND Adaptive Step-size Algorithm for Equivariant Adaptive Separation via Independence (38) CHINA Bearing fault diagnosis based on discriminative K-SVD for dictionary learning (39) CHINA Optimización en el monitoreo de la condición del sistema primario del reactor de investigación RA-6: Bomba primario (119) ARGENTINA A novel transformation of non-stationary signals to periodic signals. Part 2 application to rotary machinery diagnostic (24) POLAND Fault recognition of marine diesel engines via cyclic polar map method (43) CHINA Dynamic modeling and vibration simulation for double-row tapered roller bearings with localized surface defects (41) CHINA Evaluación estructural de recipientes a presión mediante magnetometría y Small Punch Test (13) ARGENTINA Numerical study of Nonlinear S0 mode Lamb waves for the detection of material nonlinearity (52) CHINA Intervalo de café/Coffee Break 15.40-16.00 hs 16.00-16.20 hs 16.20-16.50 hs 16.50-17.10 hs Condition monitoring system for parallel hydraulic pumps in non-stationary operation (45) CANADA Condition monitoring of bearings in parallel operating belt drive systems (44) CANADA Modelado térmico y termografía de probetas Charpy ensayadas en altas temperaturas por corriente eléctrica (18) ARGENTINA A fault diagnosis method for electro-mechanical and hydraulic integrated system via graphic recognition (81) CHINA Acoustic Emission Monitoring of Scratch Processes for Metals (48) CHINA A classification method via sparse representation for rolling bearing fault recognition (94) CHINA Estudio de la condición de las brocas de taladrado mediante Emisión Acústica y Redes Neuronales (60) ARGENTINA Compressive sensing: a new insight to signal processing for condition monitoring and fault diagnosis (95) CHINA Rapid inspection technique for contact wire based on ultrasonic guided wave (55) CHINA Fault prognosis for bearings based on morphological fractal dimension and ELM (106) CHINA Medición de espesores en cañerías de acero al carbono aisladas en servicio por medio de Radiografía Digital (136) ARGENTINA An improved Locality Preserving Projection method for fault diagnosis (104) CHINA A robust fault detection method of rolling bearings using modulation signal bispectrum analysis (131) UK Tidal turbine drive train life assessment (137) UK 13 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina 03.12.2015 CRONOGRAMA SESIÓN TÉCNICA 4 / SCHEDULE TECHNICAL SESSION 4 Auditorio/Auditorium Monitoreo de la condición Condition Monitoring Chair: Prof. Daniel DeSouza Jr., Fluminense Federal University, Brazil Life testing of a fatigue resistant steel component with a Weibull model as the sampling distribution (59) BRAZIL Evaluación de las condiciones de servicio de puentes peatonales (61) ARGENTINA Optimal Vaneless Diffuser Design For A High-End Centrifugal Compressor (76) UK Evaluación de la integridad estructural de la unión entre la conexión o “Bota de Condensado” y el cuerpo de un recipiente contenedor de presión, mediante el método de elementos finitos, bajo los lineamientos del Código ASME Sección VIII División 2 “Diseño por Análisis” (64) ARGENTINA 11.10-11.30 hs Effect of solar heat flux and thermal loading on the flow distribution within the riser pipes of a closed-loop solar thermo-syphon hot water system (77) UK Análisis de Ruido Magnético Barkhausen en acero AISI 304 (65) ARGENTINA 11.30-11.50 hs Condition Monitoring System of Mine Air Compressors Based on ZigBee (92) CHINA La simulación numérica como herramienta de evaluación de recipientes a presión (68) ARGENTINA 10.30-10.50 hs 10.50-11.10 hs 11.50-12.10 hs 14 Aula/Room B CORENDE (NDT) Chair: Dra. Marta C. Ruch, CNEA- AAENDE, Argentina Caracterización de recubrimientos obtenidos a partir de film líquidos por interferometría de baja coherencia (69) ARGENTINA COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina 03.12.2015 CRONOGRAMA SESIÓN TÉCNICA 5 / SCHEDULE TECHNICAL SESSION 5 Auditorio/Auditorium Monitoreo de la condición Condition Monitoring Chair: Prof. Dr. Fengshou Gu, University of Huddersfield, UK Aula/Room B CORENDE (NDT) Chair: Ing. César G. Belinco, AAENDE-CNEA, Argentina Qualitative condition monitoring of a conveyor unit using a state observer (97) UK Calificación ambiental de componentes de seguridad de centrales nucleares de potencia (101) ARGENTINA Flow Diagnostics in Centrifugal Pumps by Motor Current Signature Analysis (102) INDIA/UK Estudio de la emisión acústica producida por la falla de la adherencia de insertos metálicos en un panel de fibra de carbono (109) ARGENTINA 16.00-16.20 hs Modelling and measurements of dynamic ring gear strains at 1st stage of main gearboxes in wind turbines (110) GERMANY Mediciones de comportamiento estructural en condiciones complejas (57) ARGENTINA 16.20-16.40 hs A wear fault diagnosis method of reciprocating compressor connecting rod (117) CHINA Monitoreo de la condición: su fortaleza reside en que sea realizado por personal confiable (91) ARGENTINA 16.40-17.00 hs Online Detection System of Inter-turn Stator Winding Fault by Negative Sequence in Induction Motors (127) JAPAN Detección por imágenes del daño incipiente por corrosión sobre superficies metálicas (85) ARGENTINA 15.20-15.40 hs 15.40-16.00 hs 15 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina 04.12.2015 CRONOGRAMA SESIÓN TÉCNICA 6 / SCHEDULE TECHNICAL SESSION 6 Auditorio/Auditorium Monitoreo de la condición Condition Monitoring Chair: Ing. Jorge P. Amsler, AAENDE-BRUKE, Argentina 11.00-11.20 hs Effects of Blade Trailing Edge Angle on the Performance of a Centrifugal Pump Impeller (128) INDIA Análisis comparativo en la determinación de ferrita delta para aceros inoxidables austeníticos (90) ARGENTINA 11.20-11.40 hs Study of the influence factors on the accuracy of sound field reconstruction based on the interpolated time-domain equivalent source method (26) CHINA Análisis de la integridad estructural en uniones soldadas de aceros estructurales con riesgo a la fisuración en frío en el metal de soldadura (107) ARGENTINA Observer-based Fault Detection and Diagnosis for Mechanical Transmission Systems with Sensorless Variable Speed Drives (132) UK Desarrollo e implementación de un dispositivo de inspección ultrasónica para la medición del desgaste en tubos de calandria de la Central Nuclear Embalse (138) ARGENTINA 11.40-12.00 hs 16 Aula/Room B CORENDE (NDT) Chair: Dra. Marta C. Ruch, AAENDE-CNEA, Argentina COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina CONFERENCIAS PLENARIAS/ PLENARY SESSIONS The CAREM Project Lic. Osvaldo Calzetta Larrieu – CNEA, Argentina (01.12.2015 14hs) Condition Monitoring and Diagnosis of Modern Dynamic Complex Systems using Criticality Aspect of Key Performance Indicators Prof. Aditya Parida – Luleå University of Technology, Sweden (01.12.2015 18hs) Conference on NII – Non Intrusive Inspection Francisco Carlos Rodrigues Marques – Petrobras, Brasil (02.12.2015 9hs) INVAP: from nuclear technology to aerospace technology Dr. Vicente D. Campenni – INVAP, Argentina (02.12.2015 13.10hs) Modern envelope analysis for bearing diagnostics Prof. Robert Randall – University of New South Wales, Australia (03.12.2015 9hs) Early Preventive Actions for Space Mission Success Ing. Edgardo Roggero – CONAE, Argentina (03.12.2015 13.50hs) Transformation from Maintenance to Asset Management Ing. Ricardo Pauro – UTN, Argentina (04.12.2015 10hs) Reliability Matters, of course! but how ‘reliable’ is Reliability? Prof. B.K.N. Rao – COMADEM Internacional, UK (04.12.2015 13hs) 17 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina STANDS AAENDE www.aaende.org.ar Stand: 14 ARO S.A. www.aroline.com.ar Stands: 11-12 BRUKE S.A. www.brukesa.com Stand: 3 CNEA/INSTITUTO SABATO www.cnea.gov.ar Stand: 4 JPS ARGENTINA www.jpsargentina.com Stands: 5-6-7 NUCLEOELÉCTRICA ARGENTINA S.A. www.na-sa.com.ar Stand: 8 OSHMA SRL www.oshma.com.ar Stands: 9-10 SPALA – NDT S.A. [email protected] Stand: 15 UTN FACULTAD REGIONAL DELTA www.frd.utn.edu.ar Stand: 2 18 28th International Congress of Condition Monitoring and Diagnostic Engineering (COMADEM 2015) X Congreso Regional de Ensayos No Destructivos y Estructurales Resúmenes de trabajos Abstracts Buenos Aires Argentina COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Resúmenes de trabajos Buenos Aires, Argentina INDICE / INDEX Sesiones Plenarias / Plenary Sessions 03 - 07 - 12 - 17 - 73 - Conference on NII – Non Intrusive Inspection...............................................................................................................pág 24 Transformation from Maintenance to Asset Management.............................................................................................pág 24 Reliability Matters, of course! but how ‘reliable’ is Reliability?......................................................................................pág 25 Modern envelope analysis for bearing diagnostics.........................................................................................................pág 25 Condition Monitoring and Diagnosis of Modern Dynamic Complex Systems using Criticality Aspect of Key Performance Indicators.........................................................................................................................................................................pág 26 98 - INVAP: from nuclear technology to aerospace technology............................................................................................pág 26 121 - Early Preventive Actions for Space Mission Success......................................................................................................pág 26 134 - The CAREM Project ........................................................................................................................................................ pág 27 Sesión: Monitoreo de la condición / Session: Condition Monitoring 1 - 5- 14 - 15 - Towards condition assessment: Dragline condition monitoring by analysis of motor current and voltage signals......pág 28 Enhancing the quality of data from a wheel profile measurement system: a proposed approach................................pág 28 Mechanical fault detection for motor-gear driving system using motor current signal spectrum analysis..................pág 28 Design and implementation of deep neural network based multi-parameter monitoring and diagnostic system for CNC machine tool....................................................................................................................................................................pág 29 19 - Fault diagnosis of stay bolt looseness for the dismountable disk-and-drum rotor of aero-engine...............................pág 30 26 - Study of the influence factors on the accuracy of sound field reconstruction based on the interpolated time-domain equivalent source method...............................................................................................................................................pág 30 27 - Predictive maintenance system in TermoNorte turbo-generators................................................................................. pág 31 28 - Predictive fault system in internal combustion engines................................................................................................. pág 31 32 - A novel method for intelligent fault diagnosis of machinery based on unsupervised feature learning.........................pág 32 33 - Implementation of non-destructive techniques for the monitoring of rebar corrosion of concretes developed for nuclear applications......................................................................................................................................................................pág 32 34 - Convex Hull-based Support Vector MachineRule Extraction and Applicationin Hot-dip Galvanizing............................pág 33 37 - Damage Detection of Composite Material Wind Turbine Blades...................................................................................pág 33 38 - Adaptive Step-size Algorithm for Equivariant Adaptive Separation via Independence..................................................pág 34 43 - Fault recognition of marine diesel engines via cyclic polar map method......................................................................pág 34 45 - Condition monitoring system for parallel hydraulic pumps in non-stationary operation..............................................pág 35 48 - Acoustic Emission Monitoring of Scratch Processes for Metals....................................................................................pág 35 55 - Rapid inspection technique for contact wire based on ultrasonic guided wave............................................................pág 36 59 - Life testing of a fatigue resistant steel component with a Weibull model as the sampling distribution.......................pág 36 76 - Optimal Vaneless Diffuser Design For A High-End Centrifugal Compressor.................................................................. pág 37 77 - Effect of solar heat flux and thermal loading on the flow distribution within the riser pipes of a closed-loop solar thermo-syphon hot water system................................................................................................................................... pág 37 92 - Condition Monitoring System of Mine Air Compressors Based on ZigBee....................................................................pág 38 97 - Qualitative condition monitoring of a conveyor unit using a state observer.................................................................pág 38 102 - Flow Diagnostics in Centrifugal Pumps by Motor Current Signature Analysis...............................................................pág 39 110 - Modelling and measurements of dynamic ring gear strains at 1st stage of main gearboxes in wind turbines..............pág 39 117 - A wear fault diagnosis method of reciprocating compressor connecting rod...............................................................pág 40 127 - Online Detection System of Inter-turn Stator Winding Fault by Negative Sequence in Induction Motors...................pág 40 128 - Effects of Blade Trailing Edge Angle on the Performance of a Centrifugal Pump Impeller............................................ pág 41 130 - Investigating Optimal Parameters of Abrassive Water Jet Cutting Process: Engineering Robust Design Based Approach....pág 41 132 - Observer-based Fault Detection and Diagnosis for Mechanical Transmission Systems with Sensorless Variable Speed Drives...............................................................................................................................................................................pág 42 21 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Abstracts Buenos Aires, Argentina INDICE / INDEX Sesión: Análisis de Vibraciones / Session: Vibration Analysis 11 - Fault-implantable vibration signal model for fault diagnosis of sun gear in planetary gearboxes.................................pág 43 75 - A novel criterion for the selection of resonance bands in Complex Shifted Morlet Wavelet based demodulation of defective rolling element bearings vibration response..................................................................................................pág 43 79 - Grinding chatter detection based on built-in encoder....................................................................................................pág 44 87 - Application Acoustic Emission Techniques in Helicopter Main Gearbox Bearing Defect Identification........................pág 44 93 - Study on active control of rotor unbalanced vibration based on variable frequency dynamic vibration absorber.......pág 45 100 - A research on the dynamic characteristics of gas pulsation in reducer of reciprocating compressor piping system..pág 45 105 - A fault diagnosis method based on spectral kurtosis and three-order cumulation.......................................................pág 46 113 - Vibration analysis of a twenty mill roll grinding machine with a spalling defect on the tip...........................................pág 46 Sesión: Ensayos No Destructivos / Session: Non-Destructive Testing 4 - Evaluación y monitoreo estructural de edificio industrial con vibraciones debidas a máquinas utilizando técnicas dinámicas no destructivas..........................................................................................................................................................pág 47 10 - Introducción al comportamiento de nanopartículas magnetizables en la detección y estudio de discontinuidades microestructurales..........................................................................................................................................................pág 47 13 - Evaluación estructural de recipientes a presión mediante magnetometría y Small Punch Test....................................pág 48 18 - Modelado térmico y termografía de probetas Charpy ensayadas en altas temperaturas por corriente eléctrica .......pág 48 20 - Sistema rápido de inspección de ejes ferroviarios.........................................................................................................pág 49 21 - Inspección de tubos realizados en plásticos reforzados con fibra de vidrio..................................................................pág 49 35 - Análisis de vibraciones de casos de roce parcial y holgura mecánica en máquinas críticas, utilizando medición multicanal.....pág 50 49 - Mediciones especiales en la Central Nuclear Atucha II..................................................................................................pág 50 50 - Calificación y certificación de personal en Ensayos No destructivos. Comparación entre sistema ISO 9712 y sistema SNT TC 1A (ASNT).................................................................................................................................................................... pág 51 57 - Mediciones de comportamiento estructural en condiciones complejas........................................................................ pág 51 60 - Estudio de la condición de las brocas de taladrado mediante Emisión Acústica y Redes Neuronales..........................pág 52 61 - Evaluación de las condiciones de servicio de puentes peatonales................................................................................pág 52 64 - Evaluación de la integridad estructural de la unión entre la conexión o “Bota de Condensado” y el cuerpo de un recipiente contenedor de presión, mediante el método de elementos finitos, bajo los lineamientos del Código ASME Sección VIII División 2 “Diseño por Análisis”..................................................................................................................pág 53 65 - Análisis de Ruido Magnético Barkhausen en acero AISI 304..........................................................................................pág 53 68 - La simulación numérica como herramienta de evaluación de recipientes a presión....................................................pág 54 69 - Caracterización de recubrimientos obtenidos a partir de film líquidos por interferometría de baja coheencia...........pág 54 74 - Análisis de la Emisión Acústica producida en el taladrado de compuestos multicapas................................................pág 55 85 - Detección por imágenes del daño incipiente por corrosión sobre superficies metálicas.............................................pág 55 90 - Análisis comparativo en la determinación de ferrita delta para aceros inoxidables austeníticos................................pág 56 91 - Monitoreo de la condición: su fortaleza reside en que sea realizado por personal confiable.......................................pág 56 99 - Validación de modelo de barras combustibles a partir de ensayos hidrodinámicos en el Circuito Experimental de Baja Presión............................................................................................................................................................................. pág 57 101 - Calificación ambiental de componentes de seguridad de centrales nucleares de potencia......................................... pág 57 107 - Análisis de la integridad estructural en uniones soldadas de aceros estructurales con riesgo a la fisuración en frío en el metal de soldadura..........................................................................................................................................................pág 58 109 - Estudio de la emisión acústica producida por la falla de la adherencia de insertos metálicos en un panel de fibra de carbono........pág 58 118 - Optimización en el monitoreo de la condición del sistema primario del reactor de investigación RA-6: Tanque de decaimiento....pág 59 119 - Optimización en el monitoreo de la condición del sistema primario del reactor de investigación RA-6: Bomba primario... pág 59 123 - Escaneo láser con luz estructurada. Aplicación a la inspección de componentes ferroviarios.....................................pág 60 126 - Perfilómetro compacto basado en triangulación láser activa con luz estructurada......................................................pág 60 22 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Resúmenes de trabajos Buenos Aires, Argentina INDICE / INDEX 136 - Medición de espesores en cañerías de acero al carbono aisladas en servicio por medio de Radiografía Digital.........pág 60 138 - Desarrollo e implementación de un dispositivo de inspección ultrasónica para la medición del desgaste en tubos de calandria de la Central Nuclear Embalse................................................................................................................................. pág 61 Sesión: Gestión de Activos / Session: Asset Management 8 - Just-in Time and Dynamic Maintenance (JIT-Maint) for Turbine, Generator, Gearbox and Sawmills: Case Stories.......pág 62 9 - Optimal corrective maintenance of manufacturing series systems...............................................................................pág 62 22 - Managing the value of maintenance comprehensively in a business network context.................................................pág 62 96 - Brake tests to evaluate the human behaviour at different brake pedal characteristics.................................................pág 63 114 - Service-oriented approach of an eMaintenance Cloud..................................................................................................pág 63 116 - Multivariate Reliability Assessment Study for Support Ring of Reciprocating Compressor Based on Multidimensional information.........pág 64 124 - Requalification of offshore assets...................................................................................................................................pág 64 Sesión: Análisis de Proceso / Session: Process Analysis 23 - A novel transformation of non-stationary signals to periodic signals. Part 1 theoretical foundation............................pág 65 24 - A novel transformation of non-stationary signals to periodic signals. Part 2 application to rotary machinery diagnostic...........pág 65 52 - Numerical study of Nonlinear S0 mode Lamb waves for the detection of material nonlinearity..................................pág 66 81 - A fault diagnosis method for electro-mechanical and hydraulic integrated system via graphic recognition................pág 66 95 - Compressive sensing: a new insight to signal processing for condition monitoring and fault diagnosis...................... pág 67 104 - An improved Locality Preserving Projection method for fault diagnosis....................................................................... pág 67 137 - Tidal turbine drive train life assessment.........................................................................................................................pág 68 Sesión: Rodamientos / Session: Bearings 29 - Ship-borne Satellite Antenna Bearing Fault Diagnosis using Enhanced Empirical Wavelet Transform via Data-driven Adaptive Fourier Spectrum Segment..............................................................................................................................pág 69 39 - Bearing fault diagnosis based on discriminative K-SVD for dictionary learning............................................................pág 69 41- Dynamic modeling and vibration simulation for double-row tapered roller bearings with localized surface defects.......pág 70 44 - Condition monitoring of bearings in parallel operating belt drive systems...................................................................pág 70 94 - A classification method via sparse representation for rolling bearing fault recognition............................................... pág 71 106 - Fault prognosis for bearings based on morphological fractal dimension and ELM........................................................ pág 71 131 - A robust fault detection method of rolling bearings using modulation signal bispectrum analysis.............................. pág 72 Sesión Comercial/Commercial Session 47- Detecting stress corrosion cracking with eddy current array technology..................................................................... pág 73 23 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Abstracts Buenos Aires, Argentina SESIONES PLENARIAS / PLENARY SESSIONS 03 - Non Intrusive Inspection (NII) Marques – Francisco Carlos Rodrigues Consultant – Rua Evaristo da Veiga, 35, sala 1514, Rio de Janeiro, 20031-040, Brasil. ABSTRACT NII is a methodology that establishes a strict criteria for its application, based on prior knowledge of the historic integrity through inspection of a particular equipment. The main objective of this methodology is to access the status of internal integrity of a equipment without the need to open it, and therefore without interrupting its operation. The use of this methodology by the major oil companies began in the 90s of last century. The multi-client project HOIS - Harwell Offshore Inspection (R & D) Services, which consists of 43 member companies, has developed in early 2000 a guide of good practices that have been incorporated as a standard (DNV-RP-G103). The method’s viability depends mainly on the massive use of advanced technologies of non-destructive testing and the monitoring of the degradation processes of the equipments. This methodology offers a wide range’s advantages, both technical and economic. The opportunity to inspect the equipment without interrupting operation, generally involves considerable savings for industrial production processes, particularly with regard to loss of earnings. Added to this there is considerable gain in safety and reliability in the results of the evaluation of integrity of the equipment, as the NII involves the use of best engineering practices and advanced technologies of nondestructive testing and monitoring . Another important aspect is the ability to assess the internal integrity of equipment that does not allow physical access to the inside. In Brazil the legal standards for pressure equipment require internal inspections for all. NII solve this limitation, it is one of the main uses of this methodology in Brazil. At this conference the main assumptions of the DNV RPG guide 103 will be presented, as well as examples of major technical and economic advantages that its use provides to the process integrity management of industrial assets. The legal aspects of its use and the Brazilian and international experience in this area will also be presented. Keywords: Plant integrity; fault diagnostic, inpsection, monitoring. * Corresponding author. e-mail: [email protected] 07- Transformation from Maintenance to Asset Management Ricardo Pauro Centro de Investigación en Gestión de Activos Físicos UTN Buenos Aires ,Espronceda 2776 Buenos Aires Capital Federal, Argentina ABSTRACT This paper presents the results of cases performed to diagnose, audit and establish the deployment plan to bridge the gap from a “classical maintenance management” to a “modern asset management.” Currently we would be in the age of information or knowledge [2] and is believed to human activity mutate into service work. These changes are also enrolled in the new rearrangement of the factors of global power that began with the end of the cold war. Moreover, man builds and operates more complex machines but, paradoxically, is the main cause of failure. Why?. Basically because the human mistake designs, operation or maintenance. Asset management and maintenance has generated one of the most important changes in the managerial field especially companies whose products or services rely heavily on the assets they own. Within the model of comprehensive asset management, organizations must have a vision and a comprehensive approach that links all interrelated activities in the field of business operation. During this presentation we will show the findings of studies in various industries: Food and beverage, Facilty (corporate buildings),Manufacture Mining ,Petrochemistry, Automotive, Energy. Keywords: Asset Management; Classical Maintenance. * Corresponding author. e-mail: [email protected] 24 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Resúmenes de trabajos Buenos Aires, Argentina 12 - Reliability Matters, of course! but how ‘reliable’ is Reliability? B.K.N. Rao COMADEM International, UK ABSTRACT Everyone’s final objective in life is to attain perfection that leads to eternal freedom, happiness and immortality. This is only possible when we (and all our assets) are defects free, failure free, ignorance free and reliable at all times. Great civilizations existed in the past and their survival and sustained prosperity was closely linked to ‘reliable culture’. The oldest and most reliable language Sanskrith uses the adjective words Apth/shaswath to define ‘Reliability’. Apth means absolute trust, absolute dependence, absolute confidence and pride throughout one’s life. Shaswath means life-long. ‘Reliability’ is multi-dimensional, human centred and culture-based. Modern ‘Real-life’ is far from it; due to various reasons humans are prone to make bad decisions resulting in many unreliable products/services. Plenty of literature exists narrating many types of catastrophic failures. We are living in an increasingly uncertain, unreliable and dangerous world. Judging our politicians, scientists, engineers, managers and ‘leaders’ as trustworthy/reliable decision makers who really cares for the welfare of the society and the environment is causing a lot of public concern. If they are reliable and trustworthy then why their decision making is flawed? Why so many ‘scientifically robust’ theories are still flawed? Why catastrophic failures are still taking place? Why we are still making mistakes? Why most of us are not really happy? How to deal with multiplicities and uncertainties in a robust manner? How to incorporate ‘Black Swan Events’ under the field of Reliability? Also, Reliability is always associated with ‘life-cycle’ of physical assets. This begs the question what is ‘life’ and ‘cycle’? Philosophers, scientists, engineers and end-users define ‘Life’ in various ways. ‘Life’ generally refers to all living assets. ‘Cycle’ is associated with living assets and are bound by time & repetitiveness. How to define ‘life-cycle’ when we are dealing with ‘lifeless’ assets? How to predict the ‘life-cycle’ (reliability) of a new product or system with which we have no previous knowledge and experience? Overall Reliability of Complex Systems are absolutely dependent upon Humans who created and employ them. How much do we really know & understand the Complex Systems & the innate human behaviour who create and operate them? Reliability matters, of course; but how ‘reliable’ is reliability? This presentation briefly discuss some of these issues and highlights the importance of Human Centred Reliability (HCR). 17- Modern envelope analysis for bearing diagnostics Robert Randall a * a School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, University of New South Wales, Sydney 2052, Australia ABSTRACT Envelope analysis, sometimes known as the “high frequency resonance technique” (HFRT) is by far the most successful method for rolling element bearing diagnostics. It was first developed in the 1970s, using analogue processing to extract the envelope and frequency analyse it. The most efficient way of obtaining the (squared) envelope of an optimally band-pass filtered signal now uses the so-called “Hilbert” process, by inverse transforming a reduced bandwidth 1-sided frequency spectrum. The benefits include the fact that the bandpass filtration is by an ideal filter, able to exclude large discrete frequency components immediately adjacent to the filtered band, and that the signal is automatically down-sampled, without aliasing, to a rate corresponding to the range of the modulating frequencies, and that the squared envelope is superior to the envelope. Moreover, the “Hilbert” envelope hugs the signal optimally, without the requirement to decide on a time constant for the RC smoothing, which limits the rate of decay of the envelope. The paper compares the Hilbert technique with some new alternatives, including wavelet analysis, the proprietary “PeakVue” method, and the Teager Kaiser Energy Operator (TKEO), which is shown to be simply the squared envelope of the derivative of a time signal. Keywords: Bearing diagnostics; envelope analysis; Hilbert method; PeakVue method; Teager Kaiser Energy Operator (TKEO) * Corresponding author. Tel.: +61-4-2222-8214; fax: +61-2-9663-1222; e-mail: [email protected] 25 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Abstracts Buenos Aires, Argentina 73 - Condition Monitoring and Diagnosis of Modern Dynamic Complex Systems using Criticality aspect of Key Performance Indicators Aditya Parida Division of Operation and maintenance Engineering, Luleå University of Technology, 971 87 Luleå, Sweden ABSTRACT Proactive condition monitoring, diagnosis and prognosis of modern complex engineering systems is becoming an increasingly challenging issue. This is mainly attributed to the dynamic global scenario and the ever increasing stakeholders conflicting interests. One of the most important missing links that is often given a low priority while assessing the health of a complex dynamic system is the key criticality of the system in question. This paper discusses some of the challenging issues facing the Asset Management personnel and highlights the importance of incorporating criticality aspect of the key performance indicator in the diagnosis and prognosis of all modern complex systems. Keywords: Asset Management; Condition Monitoting, Key Performance Indicators, diagnosis, prognosis * Corresponding author. e-mail: [email protected] 98 - INVAP: from nuclear technology to aerospace technology Vicente D. Campenni a a INVAP, Av. Cmte. Luis Piedrabuena 4950, Rio Negro, Bariloche, 8403CPV, Argentina ABSTRACT INVAP is an enterprise dedicated to designing and building complex technological systems. We have been in this business for over thirty five years at home, and more than twenty five years, on the international market. From its inception in the field of nuclear technology, INVAP matured its capability in knowledge management which led us to undertaking the application of this know-how to other fields. This, added to the strategic and intelligent use of purchasing power on the part of the Argentine Government, in turn, has led us to be able to undertake our truly diversified technological projects in a wide range of fields. At the beginning we took on nuclear projects such as, but not only, reactors and nuclear medical centers. Over time, we went into the business of earth observation satellites, radar systems, terrestrial and satellite communications and UAV. This presentation follows the overall road travelled by INVAP, and in particular our past ten years which saw the better part of our growth, within the environment of the Argentine Government’s policy for the support of scientific and technological advancement for the socioeconomic development of the country. Keywords: INVAP, technology , reactors, satellites, radar, UAV. * Corresponding author. Carlos Amaya: e-mail: [email protected] 121 - Early Preventive Actions for Space Mission Success Edgardo Roggero a, Leonel Garategaray a and Lucas Benitezb a CONAE, Paseo Colon 751, Ciudad de Buenos Aires (1063), Argentina b VENG SA, Paseo Colon 751, Ciudad de Buenos Aires (1063), Argentina ABSTRACT Space Projects have become a necessity by providing access to critical resources for scientific, civil, military and commercial sectors alike. Therefore a failure of a satellite can have catastrophic consequences to all stakeholders; therefore 26 Resúmenes de trabajos COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina any effort to prevent it contributes to “making the product better” adding value to the space system and minimizing the catastrophic consequences. Mission Success is the natural consequence of an uncompromising commitment to safety, teamwork, and integrity; mainly materialized through a set of preventive actions that are performed during each satellite project phase. In order to contribute to the Space Mission Success, this paper is focused in some critical preventive actions that have to be done early in the project lifecycle. It intent to provide, based in past experiences, a wide view of these critical actions like the understanding about the risk that a specific space project is having due to the relationship between its cost and schedule as a function of its mission complexity, or the effect of using specific margins, models or environmental test philosophies in the Space Missions Success. Finally a set of recommendations shall be presented in order to clarify some of the major risks involved in early phase decisions. 134 - The CAREM Project Osvaldo Calzetta Larrieu a a CNEA, Avenida del Libertador 8250, CABA, 1429, Argentina ABSTRACT The National Atomic Energy Commission of Argentina (CNEA) is constructing the first nuclear power plant completely designed in the country, which prototype is known as “CAREM25”. Low and mid power CAREM plants are based on a kind of reactor of which construction, operation and maintenance present a simpler and safer concept in relation with the PWR currently under construction and operation around the world. CAREM25 prototype is being built in a site placed in the Province of Buenos Aires, near Atucha I and II NPPs. It will generate about 27 MWe, which will be able to supply a population of 60.000 inhabitants. Among its possible benefits, it can be highlighted both its capacity of supplying isolated regions or industrial poles with high electric demand as well as its capability of being complemented with a sea water desalinization plant. CAREM25 counts with simple and innovative design solutions which increment and optimize the safety standards. Among its distinctive characteristics it can be pointed out: • Primary circuit, control rods and steam generation circuit integration inside a single self - pressurized pressure vessel • Core cooling by natural convection • Inherent safety scheme based on passive systems • Hydraulically driven control rod mechanisms Integration of the primary circuit, the control rods mechanisms and the steam generators in the same pressure vessel present several advantages, such as the significant reduction of pipes and other connections outside the vessel. This minimizes the possibility of occurrence of accidents such as LOCA, commonly associated with piping damage. The reactor pressure vessel surveillance and inspection plans prevent the potential releases of radioactive materials. CAREM NPP design considers a wide support to guarantee safety, with passive systems that reduce the failure margin and provide more reliability. Keywords: Power generation facilities; fault detection/diagnosis. * Corresponding author. Tel.:+ 541147041429; fax:+541147041474 e-mail: [email protected] 27 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Abstracts Buenos Aires, Argentina SESIÓN: MONITOREO DE LA CONDICIÓN / SESSION: CONDITION MONITORING 01 - Towards condition assessment: Online condition monitoring of a dragline by analysis of motor current and voltage signals Bheki Duma, Joe Amadi-Echendu Department of Engineering and Technology Management, Graduate School of Technology Management, University of Pretoria, South Africa ABSTRACT Draglines are deployed in opencast mining operations due to their high productivity and relatively low operating cost. In most of the mining regions in the world, the average dragline fleet age is approximately 35years and there is an increasing expectation from the operators to increase the productivity and the operating life span while reducing operational cost. This paper describes a study into online condition monitoring of draglines deployed in open cast mining operations. The data used arises from one mining operation. Monitoring the Ward-Leonard system loop currents and voltages provides information for condition assessment of draglines. Dragline maintenance actions must balance a range of issues from technical and operational integrity, ecological footprint, to meeting growing demand, against financial constraints. Keywords: Condition Assessment; Dragline Maintenance; Motor signature analysis. 05 - Method for ensuring the quality of data from a wheel profile measurement system Matthias Asplund * a, Jing Lin a, and Matti Rantatalo a a Luleå University of Technology, Luleå SE-97187, Sweden ABSTRACT This paper presents a method for ensuring the quality of data from an automatic condition monitoring system for railway rolling stock wheels, in order to assure the right data quality for further use of the data. Also presented in the paper are the challenges of monitoring the condition of rolling stock in an unregulated market where there is only one infrastructure owner and there are many operators on the track. It is especially in a setup where there is shared responsibility for the wheel-rail system that good knowledge of the wheel-rail interaction plays a significant role, preventing sub-optimisation of either the wheel or the rail and maintaining a long service life of the assets. The quality assurance method presented is used to ensure a higher reliability of the data analysis and to propose thresholds for the reproducibility and repeatability of the measurement system. Through using the method, one will receive an indication as to when a correction action is needed to maintain the predefined data quality. A case study on field data shows how the method behaves. This paper ends with a discussion of the strengths of this valid method and how it can be improved. Keywords: Data quality; Railway; Condition monitoring; Wheel profiles; Reproducibility and repeatability * Corresponding author. Tel.: +46 920-49 10 62 e-mail: [email protected] 14 - Mechanical Fault Detection for Motor-Gear Driving System Using Motor Current Signal Spectrum Analysis * Mohamed Rgeai 1 a , Mohamed Elhaj 2 a, Salem Al Arbi 3 a, and Otman Maklouf 1 b 28 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Resúmenes de trabajos Buenos Aires, Argentina The College of Electronic Technology 1, Al-Jarba Street, Tripoli ,Libya a 7th of April University 2, Zawia, Libya a Center of Radiation Measurements and Training 3, Gasser ben Ghachir, Tripoli, Libya b The Engineering Academy1, Tajoura. Libya ABSTRACT This paper presents a study of detecting mechanical faults in helical gearbox driven by 11Kw induction motor using motor current signature analysis (MCSA). This technique is a non-intrusive approach which takes the advantage of using the electrical motor as an efficient, transducer to sense the mechanical abnormality in helical gearbox. The motor senses mesh stiffness, mechanical load, speed variations and reflected on its performance. Using MCSA to extract down-stream mechanical abnormality in gearboxes is very sophisticated and a complex procedure of interaction between the electrical and mechanical processes involved in an electro-mechanical system operation, as result a mathematical model has been developed in this work to gain an insight understanding of the dynamic behavior of helical gearbox under operation, and to simulate numerically the behaviour of the system under normal and abnormal conditions. The key aspects of the model include the effects of gear eccentricity and gear local faults. Spectral analysis was used to utilize the detection of mechanical faults in a helical gearbox. Both, simulated and experimental current spectrum show identical results in detecting faults in the gearbox. The spectrum is dominated by the 50Hz component and sidebands that correlate with the shaft rotational frequencies (RF) and gear meshing frequency (GMF). Moreover, the amplitude of these sidebands become higher and there are more sidebands when a local fault is introduced to the gear. These detection features have been confirmed experimentally in an 11Kw induction motor-gear system. Although the measured current spectrum is noisy, the difference between the faulty and the healthy spectra can be seen easily at feature frequencies. This study has thus demonstrated that MSCA can be used for fault detection of downstream machines. Keywords: Fault detection and diagnosis; rotating devices; signal processing. * Corresponding author. Mohamed Rgeai. Tel.: +218924235948; fax: +218 21 360 1555; email: [email protected] 15 - Design and implementation of deep neural network based multi-parameter monitoring and diagnostic system for CNC machine tool Luyang Jing a, Taiyong Wang a-b *, Peng Wang a and Dongxiang Chen a a Key laboratory of mechanism theory and equipment design of ministry of education, Tianjin University, Tianjin300072, China b Tianjin engineering research center of NC technology, Tianjin300072, China ABSTRACT Computerized numerical control (CNC) machine tool is one of the most widely used equipments in industrial application. An effective diagnosis system for it can provide multifarious benefits. However, with a complex and stochastic system integrated by mechanic, electric and hydraulic, it is more tedious and difficult to monitor, diagnose and repair faults of CNC machine tool. In order to solve this problem, a multi-parameter monitoring system which can detect the multi-subsystems of CNC machine tool is required and correspondingly a higher complexity pattern recognition method is needed. DNN has been proved to be a very effective method to implement functions of higher complexity, which meets the complicated nature of fault diagnosis problem and the requirements of multi-parameters diagnosis system. In this paper, a deep neural network (DNN) based multi-parameter monitoring and diagnostic system for CNC machine tool is built. The system is consisted of multi-parameter monitoring system and remote fault diagnosis system. The multi-parameter monitoring system achieves a real-time monitoring for CNC machine tools, and the remote fault diagnosis system provides DNN based diagnosis methods to analyze multi-parameter data uploaded from monitoring system. The system can offer real-time state information of CNC machine tools and reduce downtime of machines. Keywords: Fault diagnosis; deep neural networks; monitoring system; CNC machine tool * Corresponding author. Tel.: +86-022-87402033; fax: +86-022-27404536; e-mail: [email protected] 29 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Abstracts Buenos Aires, Argentina 19 - Fault Diagnosis of Stay Bolt Relaxation for The Dismountable Disk-and-Drum Rotor of engine Xiaoli Zhang a-b, Baojian Wang a, Guoying Li a and Xuefeng Chen a * a Xi’an Jiaotong University, State Key Laboratory for Manufacturing Systems Engineering, Xi’an 710049, China b Chang’an University, School of Engineering Machinery, Xi’an 710064, China ABSTRACT The dismountable disk-and-drum rotor refers to the rotor constituted by separate discs or several segments of non-removable rotor, which are pressed into a unitary structure by dismountable stay bolts in sufficient preload. Since the structure of the particular rotor is no longer a continuous holistic rotor, the assembly tightness and the preload distribution uniformity of the stay bolts along the circumferential discs are the major factors affecting the vibration characteristics of the dismountable disk-and-drum rotor. Therefore, dynamic response signals are measured and analyzed in different bolt preloads from looseness to tightness in an engine. A deteriorated dismountable disk-and-drum rotor is used to test the effectiveness of the proposed method and identified as an fault type of bolt relaxation, leading to abnormal engine vibration and cracks on the bolt holes. Keywords: Fault Diagnosis; Stay Bolt; Dismountable Disk-and-Drum Rotor. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +86-29-8339-5053; fax: +86-29-8339-5053; e-mail: [email protected] 26 - Study of the influence factors on the accuracy of sound field reconstruction based on the interpolated time-domain equivalent source method C.K Wang a *, J Chen a a State Key Laboratory of Mechanical System and Viberation, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, P R China ABSTRACT Interpolated time-domain equivalent source method (ITDESM) is developed by introducing the interpolation algorithms to time-domain ESM formulation. This study aims to obtain several influence factors increasing the accuracy of the sound field reconstruction by ITDESM, e.g., the hologram position, the equivalent source plane, the grid spacing and the measurement error, etc. According to the simulation results, which is acquired by using monopole sound source and Tikhonov regularization, some conclusions are drawn that short measurement distances, a short-distance equivalent source plane and small grid spacing could help improve the accuracy of the sound field reconstruction. These instructions can not only increase the flexibility in the use of ITDESM, but also expand the scope of the ITDESM application. Meanwhile, the results prove that ITDESM could be an effective tool for condition monitoring and fault diagnosis on machinery. Keywords: Interpolated time-domain equivalent source method; sound field reconstruction; Tikhonov regularization. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +86-21-3420-6664; e-mail: [email protected] 30 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Resúmenes de trabajos Buenos Aires, Argentina 27 - Predictive maintenance system in TermoNorte turbo-generators Erik Leandro Bonaldi a *, Levy Ely de Lacerda de Oliveira a, Germano Lambert-Torres a, Alexandre Pellicel b, Gonçalo Cássio b, Marco Aurélio A. Lopes b, Luiz Eduardo Borges da Silva c a Gnarus Institute, Itajuba, MG, 37500-052, Brazil b Termo Norte Energy, Porto Velho, RO 78.912-190 Brazil c Itajuba Federal University, Itajuba, MG, 37500-503, Brazil ABSTRACT The generating capacity of electric power systems represents a crucial point in the operation of the system. The economic implications of this operation are enormous and the guarantee that the component responsible for such an operation, the turbo-generator, operate correctly must be maintained at any cost. What typically occurs is that the period of continuous work of the generators feeding electrical loads, submits this equipment to stresses that can cause failures and loss of their generating capacity, resulting in uncertainty about its real nominal capacity. Therefore, a careful and rigorous assessment of this operational capacity reduction produces: a substantial increase in the reliability of the equipment, a visible reduction of costs with planned corrective maintenance and the possibility to avoid unscheduled downtimes. This paper presents a real predictive maintenance system and its performance, installed at Termo Norte power plant. This paper describes the installed system, the theoretical foundation of the analysis and presents real measurements and analysis. Keywords: Electrical signature analysis; fault diagnosis; predictive maintenance; predictive maintenance; turbo-generators. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +55-35-99865893; fax: +55-35- 3622-0132; e-mail: [email protected] 28 - Predictive fault system in internal combustion engines Phillip Mendonça a, Erik Leandro Bonaldi b, Levy Ely de Lacerda de Oliveira b, Germano Lambert-Torres b *, Luiz Eduardo Borges da Silva c, Camila Paes Salomon b-c, and Wilson Cesar Santanab c a SUAPE II Energy, Cabo de Santo Agostinho, PE, 54590-000, Brazil b Gnarus Institute, Itajuba, MG, 37500-052, Brazil c Itajuba Federal University, Itajuba, MG, 37500-503, Brazil ABSTRACT The culture of excellence in the area of maintenance combined with the needs of production cost reduction and increased productivity makes the reliability of electric power generation process becomes increasingly important, making room for the emergence of new maintenance techniques, especially predictive techniques that use continuous monitoring equipment systems. Predictive maintenance is the technique that establishes the planned corrective maintenance based on the changing monitored parameters. These monitored parameters may come from continuous condition monitoring system, which are more effective. Within this context, the most ancient and widespread technique is the vibration analysis. However, a relatively new technique and, until so little used, is the electrical signature analysis of generators. This paper presents the development of a predictive system for diagnosing internal combustion engines faults as well excitation and coupling through the electrical signature analysis of voltage and current signals of the generator. The main goal of this system is to obtain the signature of the electrical signals to identify the magnitude and frequency of each individual component allowing the identification of different faults in the generator group. The paper presents some measurements acquired directly through the installation of the developed system in SUAPE II thermal power plant. Keywords: Electrical signature analysis; fault diagnosis; machine availability; predictive maintenance; internal combustion engines. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +55-35-99860378; fax: +55-35- 3622-0132; e-mail: [email protected] 31 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Abstracts Buenos Aires, Argentina 32 - A novel method for intelligent fault diagnosis of machinery based on unsupervised feature learning Yaguo Lei *, Feng Jia, Naipeng Li and Jing Lin State Key Laboratory for Manufacturing Systems Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, No. 28 Xianning West Road, Xi’an 710049, China ABSTRACT Intelligent fault diagnosis of machinery has attracted lots of attention due to its ability in effectively analyzing massive monitoring signals and providing accurate diagnosis results. In intelligent diagnosis methods, however, the fault features are manually designed depending on prior knowledge about the characteristics of machinery signals and diagnostic expertise, which is a time-consuming and labour-consuming work. It is interesting to use unsupervised feature learning techniques to directly and adaptively learn fault features from the vibration signals and reduce the need for prior knowledge. Therefore, a novel method is proposed for intelligent fault diagnosis of machinery in this study. In the method, sparse filtering, an unsupervised feature learning technique, is applied to learn sparse representations from the vibration signals of machinery and extract robust features with little prior knowledge. Then softmax regression is employed to identify the health conditions based on these features. The proposed method is validated by a dataset from planetary gearboxes which involves seven health conditions. The results show that the proposed method obtains fairly high diagnosis accuracies compared with the method based on the features designed for gearboxes like FM0, sideband index, sideband level factor, etc. Keywords: Unsupervised feature learning; Intelligent fault diagnosis; Sparse filtering; Softmax regression. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +86-29-8339-5041; fax: +86-29-8339-5041; e-mail: [email protected] 33 - Implementation of non-destructive techniques for the monitoring of rebars corrosion of reinforced concretes developed for nuclear applications Damián Vazquez a-b * and Gustavo Duffó a-b-c a Comisión Nacional de Energía Atómica, Gerencia de Materiales, Departamento Corrosión, División Corrosión Aplicada. Av. Gral. Paz 1499, San Martín (1650), Argentina. b Universidad Nacional de San Martín, Instituto de Tecnología Jorge Sabato. Av. Gral. Paz 1499, San Martín (1650), Buenos Aires, Argentina. c Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET). Av. Gral. Paz 1499, San Martín (1650), Argentina ABSTRACT There are many mechanisms associated to the degradation of reinforced concrete and, among them; the corrosion of the reinforcing bars is the most frequently degradation mechanism found. It is worth mentioning that the annual worldwide cost of maintaining and repairing of reinforced concrete structures is approximately eight thousand million dollars. So, the monitoring of the corrosion state of a reinforcing concrete structure is mandatory for economical (among others) reasons. In the present work, the rebar corrosion was studied by mean of different parameters such as: corrosion potential, corrosion rate, electrical resistivity, oxygen availability and temperature of the concrete and environment. The measurements were carried out by non-destructive electrochemical techniques, implemented with corrosion sensors embedded in the concrete. The sensor design involves an appropriate electrodes system. Besides, some of these parameters were measured directly from the structure by mean of a commercial instrument, which allows the confinement of the electrochemical signals in a selected zone. Two different reinforced concretes, designed for nuclear applications and whose durability must be higher than three hundred years, where compared from the rebar corrosion point of view. The work was carried out on prototypes, but focuses in the implementation of these techniques in real structures. Keywords: Reinforced concrete corrosion; durability of reinforced concrete; nuclear materials. * Corresponding author. Damián Vazquez; Tel.: +54-11-6772-7236; fax: +54-11-67727388; e-mail: [email protected] 32 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Resúmenes de trabajos Buenos Aires, Argentina 34 - Convex Hull-based Support Vector MachineRule Extraction and Applicationin Hot-dip Galvanizing Jian-guoWang a, Bin Yang a*, Wen-xingZhang a, BoQin a and Wen-jingLiu a a Mechanical Engineering School, Inner Mongolia University of Science & Technology, Baotou, 014010, China ABSTRACT Support vector machine is a new machine learning method, and has a lot of specialadvantages.However, similarly to the artificial neuronal networks case, it is a black box model. This opacityproperty prevents them from being used in many real-life applications where both accuracy and comprehensibility arerequired.In order to overcome the problem,a new rule extraction algorithm based on convex hull is proposed in this paper. First, all the vectors were clustered to be some clusters on the decision hyper-plane; then, extracted the convex hull for every cluster; finally, the region of each convex hull covered were transferred to each interval-type rule.The idea of rules mining based on support vector machine is introduced to the monitoring of the actual strip hot-dip galvanizing. The zinc coating weight is used as the investigated subject. The sample datasets are trained by the proposed method, and the quantitative relationship can be obtained in the form of knowledge rules among input variables (such as the parameters of raw materials and control parameters of production) and output ones (the quality parameters), with which the production control parameters can be set and updated easily.Experiment results showed that the proposed method is efficient. Keywords: Support Vector Machine; Black Box Model; Rules Extraction;Convex Hull; Hot-dip Galvanizing; Quality Monitoring. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +86-150-4496-7398; fax: +86-472-595-1574; e-mail: [email protected] 37 - Damage Detection of Composite Material Wind Turbine Blades Xiaojun Zhu a, Xuefeng Chen a * and Zhi Zhai a a The State Key Laboratory for Manufacturing Systems Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, 710049,P.R. China ABSTRACT For the problem that composites wind turbine blades always occurre damage, a composite microscopic damage analysis model based on a microscopic failure criterion is proposed. The unidirectional composite laminated plates with periodic microstructures are modelled by the generalized method of cells (GMC). A microscopic failure criterion based Huang model, where the failure mode of fiber and matrix are characterized respectively microscopically, is also introduced. Static loading experiments are carried on composite wind turbine blades with two different states (damaged and undamaged). The influence of the damage on the strain of the wind turbine blades is monitored by the fiber bragg grating. The strain curves get through the failure experiment of the typical unidirectional laminate are used to verify the effectiveness of the algorithm proposed. The experimental results show that the carrying capacity of the composite wind turbine blades will reduce when it is damaged, and their strain curves can be used to monitor the health statement of wind turbine blades. The proposed model can predict the mechanical properties and breaking strength values of unidirectional composite plates very well. Keywords: Composites Wind Turbine Blades; Generalized Method of Cells; Strain Fiber Bragg Grating;Damage Detection. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +86 29 82663689; fax: +86 29 82663689; e-mail: [email protected] 33 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Abstracts Buenos Aires, Argentina 38 - Adaptive Step-size Algorithm for Equivariant Adaptive Separation via Independence Lu Jiantao, Cheng Wei *, Zi Yanyang, He Zhengjia State Key Laboratory for Manufacturing System Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, 710049, China ABSTRACT The traditional blind source separation (BSS) algorithms with fixed step size have the disadvantage that cannot well balance the convergence rate and the steady-state error. A novel adaptive step-size algorithm for equivariant adaptive separation via independence (EASI) is proposed to solve this problem, which can speed up the convergence rate, and reduce the steady-state error of the adaptive BSS algorithm. Firstly, a separation indicator that indicates the separation degree is obtained by analyzing the convergence condition of the EASI algorithm, and the indicator is applied to improve the step size. Secondly, to weaken the error effects of the data at the initial stage, a forget factor is applied to online update the separation indicator. Finally, a nonlinear monotone increasing function is proposed, which implements the one-to-one mapping between the separation indicator and the step size. Compared with the fixed step-size natural gradient algorithm, the fixed step-size EASI algorithm, the exponential decay step-size algorithm and the adaptive step-size algorithm with weighted orthogonalization, the proposed algorithm has faster convergence rate, smaller steady-state error and better robustness. This research can benefit for the vibration & acoustical source separation and identification, and provide pure source information for machinery condition monitoring and fault diagnosis. Keywords: Blind source separation; EASI; Separation indicator; Adaptive step-size; Online algorithm. * Corresponding author. e-mail: [email protected] 43 - Fault recognition of marine diesel engines via cyclic polar map method Mingquan Zhang a , Yanyang Zi a *, Jinglong Chen a, Yu Wang a and Yiqing Li a a State Key Laboratory for Manufacturing and Systems Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, PR China ABSTRACT Determining the reliability of a diesel engine with efficient and robust fault diagnosis techniques is important to ensure that the engine stays in optimal operating condition and minimize the probability of failure. However, most current techniques for this purpose rely on the specification of threshold levels and heuristic knowledge to assign states as nonfaulty or faulty, making them difficult to be widely adopted in practice. This article introduces a cyclic polar map (CPM) method to diagnose the abnormal combustion using the information contained in the instantaneous crankshaft speed variations. A new time domain evaluating indicator, related to the power contribution of each cylinder, is proposed to generate polar map (PM). The CPM, as the expression form of cycle-to-cycle variation in PM, is used to show the non-uniformities in operation. Moreover, this method only processes the data during one engine cycle, which makes it more suitable for real-time diagnosis. To validate its effectiveness, three typical experimental studies on a 16-cylinder marine diesel engine at three different loads of 25%, 50% and 75% are discussed in this paper. The results show that distortion degree of CPM can well reflect the fault deterioration trend and the fault cylinder position. Keywords: Fault recognition; Marine diesel engine; Instantaneous crankshaft speed; cyclic polar map method. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +86 29 82667963; fax: +86 29 82663689; e-mail: [email protected] 34 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Resúmenes de trabajos Buenos Aires, Argentina 45 - Condition monitoring system for parallel hydraulic pumps in non-stationary operation Alexander Rose a, Dustin Helm a, and Markus Timusk a * a Bharti School of Engineering Laurentian University, 935 Ramsey Lake Road, Sudbury ON, P3E2C6, Canada ABSTRACT There is a current demand to advance condition monitoring research for non-stationary systems as a significant proportion of industrial equipment is required to function under variable speeds and loads. This work advances the development of a fault detection system to for such equipment. The proposed system compares the pressure and vibration signals of two identical gear pumps subjected to synchronized duty cycles. The premise is a developing fault will cause a change in the residual between signal features while in stationary and non-stationary operation. Pump components (thrust plates and gear teeth) at several progressions of deterioration were interchanged within a single pump and were examined under various duty cycles. This paper evaluates the proposed fault detection methodology and the results of this approach are discussed with respect to the advantages and drawbacks over conventional systems. This study validates that this technique provides sufficient information to detect faults in parallel hydraulic pumps under non-stationary operation. Keywords: Condition monitoring; hydraulic pump; gear pump; fault detection; non-stationary operation * Corresponding author. Markus Timusk. Tel.: 1-705-675-1151 ext:2243 e-mail: [email protected] 48 - Acoustic Emission Monitoring of Scratch Processes for Metals Wenbin Zhou, Yongyong He * and Xinchun Lu State Key Laboratory of Tribology, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 10084, China ABSTRACT Acoustic Emission (AE) has become a successful tool for extracting the features of material damages. It could also be used to monitor the tribological process which might be helpful to avoid the damage and improve the remained life of system. In this paper, scratch tests were conducted at the surfaces of well-polished metals (copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), and tungsten (W)) with a diamond indenter. Meanwhile, AE responses were sampled to investigate the relationship between AE and scratch processes. From the results, different scratch features were found which were related to the plastic deformation, tear and crack. By analyzing the AE results, it can be concluded that AE is sensitive to the damages during the scratch process. The AE signal of Cu was the continuous waveform and generated due to the plastic deformation, while the AE signal of W was the burst-type signal and generated due to the crack. The detected AE signal of Mo was composed of continuous waveform and bursts, which were owing to the tearing deformation and the crack, respectively. Keywords: Acoustic emission; Scratch; Plastic deformation; Crack. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +86-010-62787932; fax: +86-010-62787932; e-mail: [email protected] 35 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Abstracts Buenos Aires, Argentina 55 - Rapid inspection technique for contact wire based on ultrasonic guided wave Yong Chang a , Yanyang Zi a * , Yu Wang a and Zhe Yang a a State Key Laboratory for Manufacturing and Systems Engineering, School of Mechanical Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, PR China ABSTRACT Performance of contact wire is very important for power collection in railways, thus effective inspection techniques of contact wire are necessary to ensure railway service quality and security. As a new non-destructive testing (NDT) method, ultrasonic guided wave has the advantage of being more sensitive and faster than previous ultrasonic technique. In this paper, guided wave technique is employed to detect the defects of contact wire. Generally, dispersion curve is the prerequisite of guided wave inspection. However, due to the complex cross-section shape of contact wire, the conventional methods such as analytic method and finite element method have difficulty in calculating the dispersion curves. Thus, a special calculation method named semi-analytical finite element (SAFE) was studied to obtain the dispersion curves of contact wire. In order to make use of guided wave propagation for detecting defects of contact wire, the actuator and sensor placement was optimized through minimizing Bayes risk. According to the dispersion curves and the optimization results, several tests were carried out for detecting artificial defects at different positions of contact wire. The experimental results show that the minimum crack depth of guided wave can be detected is 0.5mm and the location error is less than 10%. Keywords: Non-destructive testing; Contact wire inspection; Ultrasonic guided wave; Semi-analytical finite element ;Bayes risk. * Corresponding author. Tel: +86 029 82663689; E-mail: [email protected]. 59 - Life testing of a fatigue resistant steel component with a Weibull model as the sampling distribution Daniel De Souza a *, Daniele Fonseca a a Fluminense Federal University, R. Jorn. Henrique Cordeiro 310/1602, Bloco 1, 22631-450 Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil ABSTRACT In some occasions the amount of time we have available for testing could be considerably less than the expected lifetime of a component or part. To overcome such a problem, we could rely on the accelerated life-testing alternative. One feasible way to transform test results acquired under accelerated conditions to normal using conditions could be through the application of the “Maxwell Distribution Law,” as we recently did in a paper using an Inverse Weibull model as the sampling distribution. In this paper we will be able to test the fatigue resistant steel component at normal using condition. Since this test at normal using condition will take a long time to be finished, we will also test this steel part at a specific accelerated condition to determine an accelerator factor. This accelerated factor could be used in further tests of this steel component to transform the results obtained under its specific acceleration condition to normal using condition. We will apply a combined approach of a sequential life testing and an accelerated life testing to this steel part or component. We will be using as the underlying sampling distribution the three-parameter Weibull model. An example will illustrate the application of this procedure. Keywords: Sequential Life Testing, Accelerated Life Testing, Underlying Three-Parameter Weibull Model, Maxwell Distribution Law. * Corresponding author. Tel: ++55-21-24952294; e-mail:[email protected] 36 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Resúmenes de trabajos Buenos Aires, Argentina 76 - Optimal Vaneless Diffuser Design For A High-End Centrifugal Compressor Noukhez Ahmed a, Taimoor Asim a * , Rakesh Mishra a, Subenuka Sivagnanasundaram d and Paul Eynon e a b c University of Huddersfield, Queensgate, Huddersfield, HD1 3DH, UK d e Cummins Turbo Technologies, St Andrew’s Road, Huddersfield, HD1 6RA, UK ABSTRACT Turbochargers are widely used in the automotive industry to reduce engine emissions and to increase the power. Centrifugal compressors are an integral part of turbochargers. Centrifugal compressors comprises primarily of inducer, impeller, diffuser and volute. The diffuser has an important role in the isentropic efficiency of the compressor. Over the past few decades, researchers have been trying to increase the total-to-total compressor stage efficiency by altering the diffuser’s geometries. Many different methods have been adopted for this purpose, like pinching the diffuser walls, tilting the diffuser walls etc. Pinching increases the outer width of the diffuser while tilting provides an increased radial length. In the present study, both these methods have been used simultaneously. The primary benefit of doing so is to make the turbocharger compressor stage more compact in design, which is the current requirement of the automotive market. In order to investigate the effect of pinching and tilting of diffuser walls, a Computational Fluid Dynamics based solver has been used to predict the flow phenomena within the compressor, especially in the vaneless diffuser. Design of Experiments, using Taguchi’s method, has been incorporated in this study to statistically define the scope of the numerical work, and to obtain the optimal configuration of pinching and tilting that leads to maximum total-to-total compressor stage efficiency. The results depict that the compressor stage efficiency increases up to a tilt angle of 6.25º, after which it starts to decrease. Furthermore, the stage efficiency increases with increase of diffuser outlet width i.e., pinching the diffuser passage, however, this increasing trend has been observed up to an outlet width ratio of 1.23, after which the stage efficiency starts to decrease. Hence, the optimal diffuser model, based on the combined tilting and pinching results obtained, which leads to the maximum total-to-total compressor stage efficiency, has been identified and analysed. Keywords: Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), Centrifugal Compressor, Turbocharger, Diffuser, Design of Experiments (DOE) * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. Taimoor Asim. Tel.: +44-1484-472323; e-mail: [email protected] 77 - Effect of solar heat flux and thermal loading on the flow distribution within the riser pipes of a closed-loop solar thermo-syphon hot water system Basim Freegah a-b * Taimoor Asim c and Rakesh Mishra d a c d Al-Mustansiriya University, Baghdad, Iraq b University of Huddersfield, Queensgate, Huddersfield, HD1 3DH UK ABSTRACT Solar energy is one of the main sources of renewable energy that is abundantly available throughout the world. Solar energy can be used for useful purposes through a number of mechanical artefacts. One such artefact is known as Thermo-syphon, which typically contains water as its working fluid. One of the major applications of Thermo-syphon is within the residential and industrial units, where a constant supply of hot water is required. The use of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) based solvers has recently been proven capable of predicting the flow behaviour within thermo-syphons with reasonable accuracy. Hence, the present study focuses on using a commercial CFD based solver to predict the flow behaviour within the riser pipes of a thermo-syphon with varying solar heat flux and thermal loading conditions. In order to qualitatively and quantitatively analyse the flow structure within the riser pipes of the thermo-syphon, velocity magnitude and static temperature distributions within these pipes is analysed in detail. The results depict that the solar heat flux has a significant impact on the velocity magnitude and static temperature profiles within the riser pipes. Furthermore, it has been observed that the thermal loading has negligible effects on the velocity magnitude and static temperature profiles within the riser pipes. The data has also been used to develop novel design correlations. Keywords: Velocity Magnitude, Static Temperature, Computation Fluid Dynamics (CFD), Closed-loop Thermo-syphon, Solar Energy * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. Taimoor Asim. Tel.: +44-1484-472323; e-mail: [email protected] 37 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Abstracts Buenos Aires, Argentina 92 - Condition monitoring system of mine air compressors based on ZigBee Sheng Fu , Yinbo Gao * and Hao Lin College of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Electronics Technology, Beijing University of Technology, Chaoyang District, Beijing, 100124, China ABSTRACT In the current mine air compressors monitoring system there are some difficulties in the installation and maintenance because of the wired connection. To solve the problem, this paper introduces a new air compressors monitoring system based on ZigBee in which the monitoring parameters are transmitted wirelessly. The collecting devices are designed to form a cluster network to collect vibration, temperature and pressure of air cylinders and other parameters. All these devices are battery-powered. Besides, the monitoring software in PC is developed using MFC. Experiments show that the designed wireless sensor network works well in the site environmental condition and the system is very convenient to install since the wireless connection. This monitoring system will have a wide application prospect in the upgrade of the old monitoring system of the air compressors. Keywords: Condition Monitoring; Wireless Sensor Network ; Air Compressor. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +0-086-010-67396781; fax: +0-086-010-67396781; e-mail: [email protected] / [email protected] 97 - Qualitative condition monitoring of a conveyor unit using a state observer Philipp Varley a a University of Huddersfield, School of Computing and Engineering, Queensgate, Huddersfield, HD1 3DH ABSTRACT Conveyor systems are the backbone of modern material handling systems. Whereas the optimisation of the hardware has advanced in recent years, the controls and inherent condition monitoring lacked attention, thus not making use of the computational capabilities of modern industrial controllers. Current condition monitoring systems confine themselves to runtime measurements and limit themselves to continuous and discrete dynamics, which makes them impractical for modern application on conveyors used for positioning and high dynamic tasks. This paper presents an approach towards determining the current condition of a conveyor unit by using a state observer residing in the industrial controller. This approach allows for a wider application of condition monitoring of conveyors, inasmuch both dynamic and continuous systems can be monitored. Moreover, this paper details the architecture of such a system, the control loops required and the expected outcome this research aims at. In order to show the practical implementation of this approach, the present paper portrays such a system in a high dynamic metering belt conveyor. This example will show the advantages of an approach which makes use of a state observer as compared to that which assumes discrete dynamics. Further, the potential utilisation of the results gained from the evaluation of the measurements is pointed out. Keywords: Material handling; Conveyor system; fault detection/diagnosis; Preventive diagnostics. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +49 175 8188615; e-mail: [email protected] 38 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Resúmenes de trabajos Buenos Aires, Argentina 102 - Flow Diagnostics in Centrifugal Pumps by Motor Current Signature Analysis Subhashis Nandy a, Atiq Ur Rehman b, Anuj Jain b, Rakesh Mishra c, and R.K. Tripathi d a Department of Ocean Engineering and Naval Architecture, Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, India b Department of Applied Mechanics, Motilal Nehru National Institute of Technology Allahabad, India c School of Computing and Engineering, University of Huddersfield, United Kingdom d Department of Electrical Engineering, Motilal Nehru National Institute of Technology Allahabad, India ABSTRACT In this study, flow diagnosis of two geometrically similar centrifugal pumps but with different operating efficiencies is carried out using motor current signature analysis (MCSA). Consumption of current by the induction motor (called motor current) is measured using current sensor. DAQ card are used for experimental data acquisition. Data are recorded and currents are measured for different flow rates for both the centrifugal pumps and then are processed in LabVIEW to study the correlation between flow rate and current spectrum. Certain harmonic components in the stator current spectrum are developed when problem occurs in the pump. It happens because the noise and oscillations are induced in the shaft due to cavitation and change in flow rate. These eventually modified the already present harmonics in the current spectrum corresponding to the periodic small torque induced every time a blade hits the fluid. . It is therefore, explained very clearly the reason behind the abnormality in the pump. During this suitable operating zone, it is clearly shown that the efficiency of the pump is maximum and current consumption is comparatively low as compared with the other operating zones. The location of the best efficient zone is properly recognized through the motor current spectrum which is the uniqueness of this study. Keywords: Condition Monitoring; Wireless Sensor Network ; Air Compressor. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +0-086-010-67396781; fax: +0-086-010-67396781; e-mail: [email protected] / [email protected] 110 - Modelling and measurements of dynamic ring gear strains of slowly spinning main gearboxes in wind turbines Martin-Christopher Noll a , Dominik Radner a , Dennis Witter a and Ralf Schelenz a a Chair for Wind Power Drives, RWTH Aachen University, Campus Boulevard 61, 52074 Aachen, Germany ABSTRACT Condition monitoring (CM) of main gearboxes in wind turbines (WT) mainly relies on mechanical vibrations. However, low revolution speeds, low damage cycling frequencies, long recording periods and highly dynamic and stochastic wind loads lead to difficult damage detections in the first planetary stage. It was shown by NASA that signals of ring gear strains can be used for the CM of planetary helicopter gearboxes. To gain a deeper understanding of these signals, in this paper, dynamic ring gear surface strains of WT-gearboxes in undamaged condition are modelled, measured and evaluated. First the complex strain condition on ring gears of planetary gears is investigated with analytical and numerical models. In a second step strain measurements are conducted on 0.85 MW and 3 MW gearboxes deployed on WT-system test rigs at RWTH Aachen University. Measurements are taken in pure torque as well as combined torque and non-torque load conditions. Measured signals compare well to modelled results and show high signal-to-noise ratio and good repeatability even at low revolution speeds. The comparison of tooth root and ring gear strains shows that the planetary load sharing can be inferred from the strain signal. Furthermore a direct correlation to the dynamic input torque exists. Keywords: Wind Turbine, Planetary Gearbox, Surface Strain, Ring Gear, Modelling, Measurement. * Corresponding author. Martin-Christopher Noll Tel.: +49-241-80-95925; Fax: +49-241-80-92885; e-mail: [email protected] 39 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Abstracts Buenos Aires, Argentina 117 - A diagnosis method of the small end fault on reciprocating compressor connecting rod Zhiwei Mao a, Jinjie Zhang b, and Zhinong Jiang a, * a Diagnosis and Self-Recovery Engineering Research Center, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029, P. R. China. b College of Information Science and Technology, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029, P. R. China. ABSTRACT The connecting rod is the key moving part of a reciprocating compressor, of which the stress state is extremely complicate and the wear fault of the small end is always a bottleneck problem in the field of fault monitoring and diagnosing. This paper is aimed to present a new method to diagnose the above wear fault. Firstly, a contact model of a clearance in the revolute joint of the small end of a connecting rod bearing (SECRB) was established and a multi-body simulation tool was utilized to do simulation and to obtain the dynamic influence of wear gap in SECRB of a slider-crank mechanism. Secondly, the characteristics of the wear fault of SECRB were extracted, on which the appearance mechanism was studied based on stability. Then, a new approach to monitoring and diagnosing this wear fault by analyzing the angle domain of vibration signals was proposed. Finally, the availability was verified by conducting an experiment on a reciprocating compressor. And the experimental results show that this method can not only accurately diagnose the wear fault of SECRB but also approximately estimate its severity. This study laid a foundation for the online monitoring and early warning of this fault. Keywords: Reciprocating compressor; Fault monitor and diagnosis; Dynamic simulation; Angle domain. * Corresponding author. e-mail: [email protected] 127 - Online Detection System of Inter-turn Stator Winding Fault by Negative Sequence in Induction Motors Makoto Kanemaru a *, Mitsugi Mori a, Mitsuru Tsukima a, Toshihiko Miyauchi b, Kenji Onishi b, and Kazufumi Hayashi b a Advanced R&D Center, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, 8-1-1, Tsukaguchi-Honmachi, Amagasaki, Hyogo 661-8661, Japan b Power Distribution Systems Center, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, 8 Houraicho, Marugame, Kagawa 763-0662, Japan ABSTRACT Winding insulation failures account for around 15% of total faults of induction motors in industries. It is believed that those failures start as minor inter-turn faults that finally lead to serious insulation breakdowns. Therefore, online detecting technique in early stage could be quite advantageous to avoid those serious failures in advance. In this study, we focused on asymmetries of the three-phase circuit, and investigated the negative sequence components of the line current and voltage under various complicated conditions, such as unbalanced supply voltages, several numbers of shorted turns and various loads. Based on these experimental results and steady-state equivalent circuit models of induction motor, we have developed the online detection algorithm of inter-turn stator winding fault to provide an early warning of impending failures. The proposed algorithm utilizes off-diagonal term of the sequence component admittance matrix calculated from negative sequence current, voltage and admittance. In order to improve fault detection performance, the algorithm is exposed to normal operating range of the motor in the learning stage. Keywords: Induction motor, negative sequence components, inter-turn fault detection, online. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +81-6-6497-7122; fax: +81-6-6497-7122; e-mail: [email protected] 40 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Resúmenes de trabajos Buenos Aires, Argentina 128 - Effects of Blade Trailing Edge Angle on the Performance of a Centrifugal Pump Impeller Atiq Ur Rehman a, Shivam Srivastava a, Anuj Jain a *, Akshoy Ranjan Paul a and Rakesh Mishra b a Department of Applied Mechanics, Motilal Nehru National Institute of Technology Allahabad, India b School of Computing and Engineering, University of Huddersfield, United Kingdom ABSTRACT Centrifugal pump is one of the most widely used devices to transport fluids in industries and buildings. A lot of research has been carried out to make it more efficient. With the development of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), the parametric study of a centrifugal pump has become much easier and through this tool the complex internal flow can be well predicted to expedite the pump design procedure. The primary objective of this work is to analyze the effect of trailing edge angle of three twisted blades of a radial flow pump impeller on the local flow field and on the global hydraulic performance of a centrifugal pump impeller using three-dimensional steady-state analysis with the help of commercial CFD software Ansys –BladeGen. In this analysis, three impellers are modelled using BladeGen tool with different trailing edge angles in the range of 16, to 27degrees keeping the blade wrap angle constant.The calculations are performed only on the impeller instead of the complete pump for time and cost-effectiveness without compromising the accuracy of the predictions. The results revealed that at the design point, the impeller head increases by 4% with an increase in blade trailing edge angle from 16 to 27 degrees. It is however, found that the input power also increases simultaneously which leads to a marginal dip of 0.5% in the hydraulic efficiency. Keywords: Centrifugal pump impeller,Trailing edge angle, Wrap angle, CFD. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +91-9415305131; e-mail: [email protected] 130 - Investigating optimal parameters of abrassive water jet cutting process: engineering robust design based approach R.M. Chandima Ratnayake a and Felix Santhiapillai a a Department of Mechanical and Structural Engineering and Materials Science, University of Stavanger, N-4036, Stavanger, Norway. ABSTRACT The machining parameters with existing machining facilities are important for small and medium scale manufacturing firms as they run with tight profit margins. In this context, it is vital to investigate the effectiveness of the currently available statistical approaches for regular applications. This manuscript uses engineering robust design (ERD) approach for investigating the optimal abrasive water jet metal cutting parameters for existing machinery. First, the manuscript illustrates a mathematical framework which is possible to utilize for regular metal cutting applications. Secondly, it utilizes the mathematical framework for turning the machining parameters. Experimentation has been performed to establish the initial machining parameters via expert knowledge based levels. Optimal parameter have been calculated based on the experimental results. Then, the theoretical value of metal cutting output quality parameter has been calculated. Finally, a verification experiment has been performed to investigate the consistency of the experimentally observed machining parameters. Experimental and verification results have been reported. Keywords: Engineering robust design; machining parameter; Abrassive water jet cutting. * Corresponding author. [email protected] 41 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Abstracts Buenos Aires, Argentina 132 - Observer-based Fault Detection and Diagnosis for Mechanical Transmission Systems with Sensorless Variable Speed Drives Samieh Abusaad a, Fengshou Gu* a, Andrew D. Ball a a Centre for Efficiency and Performance Engineering, University of Huddersfield, Huddersfield, U.K. ABSTRACT Observer based approaches are commonly embedded in sensorless variable speed drives. It estimates system variables to produce errors or residual signals in conjunction with corresponding measurements. The residual signals then are relied to tune control parameters to maintain operational performance even if there are considerable disturbances such as noises and component faults. Obviously, this control strategy outcomes robust control performances. However, it can result in adverse consequences to the system when faults progress to high severity. To prevent the occurrences of such consequences, this research proposes the utilisation of residual signals for detecting component faults so that alerts can be raised for incipient faults. Based on gear transmission system with a sensorless variable speed drive (VSD), observers for speed, flux and torque are developed for examining their residuals under different fault conditions. Two types of common gearbox faults: tooth breakage with different degrees of severities and shortage of lubricant at different levels are investigated. It shows that different residual signals can be based on to indicate different faults, showing that the observer based approaches are effective for monitoring VSD based mechanical systems. Keywords: Observerbased fault detection, Lubricant quality, Motor electrical signature analysis, Sensorless VSD, Gearbox. * Corresponding author. e-mail: [email protected] 42 Resúmenes de trabajos COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina SESIÓN: ANÁLISIS DE VIBRACIONES / SESSION: VIBRATION ANALYSIS 11 - Journal Bearing Lubrication Monitoring using Spectrum Cluster Analysis of Vibration Signals Osama Hassin a* , Nasha Wei b , Hossein Towsyfyan a, Fengshou Gu a and Andrew D.Ball a a School of Computing and Engineering, University of Huddersfield, Queens gate, Huddersfield, HD1 3DH, UK b Department of Economics and Management, Taiyuan University of Science and Technology, Shanxi, P.R. China ABSTRACT Journal bearings are critical components for many important machines. Lubrication analysis techniques are often not timely and cost effective for monitoring journal bearings. This research investigates into vibration responses of such bearings using a clustering technique for identifying different lubrication regimes, and consequently for assessing bearing lubrication conditions. It firstly understands that the vibration sources are mainly due to the nonlinear effects including micro asperity collisions and viscous shearing interactions. These excitations together with complicated vibration paths are difficult to be characterized in a simple linear way for the purpose of condition monitoring. Therefore, a clustering analysis technique is induced to classify the vibration responses in high frequency ranges around 10kHz into different representative responses that corresponding to different on bearing modulus characteristics. In particular, the analysis allows sensitive signal components and sensor positions to be determined for monitoring the journal bearing effectively. Test results from self-aligning spherical journal bearings show that it allows different lubricant oils and different lubrication regions to be identified reliably, providing feasible ways to online monitoring bearing conditions. Keywords: Journal bearings, vibration, bearing modulus, lubrication regimes, spectrum clustering * Corresponding author. Tel.: +44(0)7460808732; e-mail: [email protected] 75 - A novel criterion for the selection of resonance bands in Complex Shifted Morlet . Wavelet based demodulation of defective rolling element bearings vibration response Konstantinos Gryllias a*, Christos Yiakopoulos a and Ioannis Antoniadis b a KU Leuven, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Division PMA, Celestijnenlaan 300, BOX 2420, Leuven, 3001, Belgium b National Technical University of Athens, School of Mechanical Engineering, Heroon Polytechniou 9, Zografou, 15780, Greece ABSTRACT Rolling element bearings consist the most common, widespread and important machine element in rotating machinery, since they act as the “interface” where the rotor forces are transferred to the stationary part of the machine. Complex Shifted Morlet Wavelets (CSMW) present a number of advantages, such as the maximal time-frequency resolution, when used for the demodulation of the vibration response of defective rolling element bearings focusing towards the fault detection and diagnosis. In this paper an invariant subspace approach is applied after the appropriate transformation of the signal by a wavelet structure; in order to exploit the rotation invariance of the underlying signal subspaces. Furthermore a novel criterion is proposed for the optimal automatic selection of both the center frequency and the bandwidth of the applied wavelet window. The criterion is based on the maximisation of the mean non zero singular value of the corresponding singular value decomposition problem. The effectiveness and the robustness of the newly introduced criterion are evaluated in a number of numerical and industrial cases involving defective rolling element bearings and a comparison between various analogous criteria (such as the Spectral Kurtosis, the Crest Factor, the Smoothness Index, the Peak Energy) is performed. Keywords: Condition Monitoring; Fault detection/diagnosis;Wavelets * Corresponding author. Tel.: +32-16-32-30-00; e-mail: [email protected] 43 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Abstracts Buenos Aires, Argentina 79 - Grinding chatter detection based on built-in encoder Yao Liu a, Xiufeng Wang a *, Jing Lin b, Wei Zhao c a School of Mechanical Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Shaanxi 710049, China b State Key Laboratory for Manufacturing Systems Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Shaanxi 710049, China c Qinchuan Machine Tool & Tool Group Share Co., Ltd, Baoji, Shaanxi 721009, China ABSTRACT Monitoring and detection of chatter are the key techniques to guarantee the productivity and performance of grinding process. Basically, lateral vibration is usually employed to detect chatter during grinding process, and there has been few related reports about chatter detection using torsional vibration information in the literature. As torsional vibration of rotating axis is also one important phenomenon of chatter, a convenient, reliable and low-cost technique to detect chatter in grinding process based on built-in encoder signal is presented in this study. The theoretical foundation of chatter detection using torsional vibration information was presented first. Followed with experiments executed on a gear grinding machine. The fluctuations of the transient angular speed, i.e. torsional vibration of grinding wheel spindle and work piece axis, were extracted from the built-in encoder signal. Lateral vibrations of the machine tool were also acquired and presented as a reference. Analysing results showed that chatter will excite harmonics of grinding wheel spindle rotational frequency in both lateral vibration and angular speed fluctuation, forming a frequency band. When chatter emerged, the amplitude of chatter frequency band increased dramatically, resulting in the larger fluctuation of the angular speed. All these characteristics enable grinding chatter to be detected reliably using built-in encoder. Keywords: Grinding chatter detection; Torsional vibration; Encoder signal; Fluctuation of transient angular speed. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +86-29-82667938; fax: +86-29-83237910; e-mail: [email protected] 87 - Application acoustic emission techniques in helicopter main gearbox bearing defect identification Fang Duan a *, Faris Elasha b, Matthew Greaves c, and David Mba a a School of Engineering, London South Bank University, London, SE1 0AA, UK b Faculty of Engineering and Computing, Coventry University, Coventry, CV1 5FB c School of Aerospace, Transport, and Manufacturing, Cranfield University, Bedford, MK43 0AL, UK ABSTRACT Helicopter transmission integrity is critical to the safety operation. Of all mechanical failures in helicopter transmission, the main gearbox (MGB) failures contribute approximately 16%. Great effort has been paid in early prevention and diagnosis of MGB failures. As a commonly employed monitoring technology, vibration analysis suffers from strong background noise due to variable transmission paths from the bearing to the receiving externally mounted vibration sensor. The background noise can mask the vibration signature of interest. This paper reports on an investigation to identify the presence of a bearing defect in a CS-29 ‘Category A’ helicopter main gearbox with the acoustic emission (AE). This investigation involved performing the tests for fault-free condition, minor bearing damage and major bearing damage conditions within a helicopter gearbox under different power levels. The bearing faults were seeded on one of the planet gears of the second epicyclic stage. To overcome the issue of low signal to noise ratio (SNR), a AE sensor was directly attached on the dish of planet carrier. The AE signal was transferred wirelessly to avoid complex wiring inside MGB. The analysis results proved the feasibility of using AE sensor as in-suit bearing defect identification Keywords: Helicopter Main gearbox, Acoustic Emission, bearing defect diagnostics. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +44-207-815-7578; e-mail: [email protected] 44 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Resúmenes de trabajos Buenos Aires, Argentina 93 - Study on active control of rotor unbalanced vibration based on variable frequency dynamic vibration absorber Ting Tu a, Lidong He a a Beijing University of Chemical Technology,15 Beisanhuan East Road, ChaoYang district, Beijing, 100029, China ABSTRACT A new kind of variable frequency dynamic vibration absorber (VFDVA) which is used to suppress the rotor unbalanced vibration near the critical speed online has been researched in this paper. The problem of the new two resonant peaks caused by traditional passive dynamic vibration absorber (DVA) in the rotor system has been solved by this VFDVA. Also, the active control system for the VFDVA based on LABVIEW Software Platform is presented. It can automatically adjust the DVA’s frequency by using speed on-off control strategy. When the rotor starts up or slows down to near the critical speed, the VFDVA’s frequency is tuned to be consistent with the natural frequency of the rotor system by increasing the subsystem mass, so that the rotor vibration can be suppressed. Oppositely, when it is away from the critical speed, the VFDVA’s frequency is tuned to be much larger than the natural frequency of the rotor by removing the increased mass so the two resonant peaks are avoided. Additionally, a single-span rotor test bench has been established to test the rotor start-up and shut-down process. The experimental results show that the active VFDVA can suppress the rotor vibration while through the critical speed effectively and avoid the two resonant peaks caused by traditional DVA simultaneously. Keywords: Variable frequency dynamic vibration absorber; active control; critical speed; rotor. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +86-10-6444-3098; fax: +86-10-6444-6043; e-mail: [email protected] 100 - A research on the dynamic characteristics of gas pulsation in elbow of reciprocating compressor piping system Lisi Liu a , Lanqing Ma a, Quyang Ma a and Guoan Yanga a * a Diagnosis and Self-Recovery Engineering Research Center, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing and 100029, China ABSTRACT The gas pulsation caused by intermittent operation of reciprocating compressor severely affects the stable operation of the compressors, and is the main reason for the piping vibration. This research is based on the plane wave theory, and studied the effect of elbow on gas pulsation in the piping system. Considered the presence of gas vortex in the elbow, the transfer matrix of the pulsation pressure in elbow is proposed, and the relation between elbow radius and amplitude of pressure pulsation is found. The Computational Fluid Dynamics has been provided to validate the rationality of the conclusions. The research on the dynamic characteristics of gas pulsation in elbow in this paper can be used to guide the vibration suppression of reciprocating compressors and complex pipelines in factories. Keywords: Reciprocating compressor; gas pulsation; elbow; CFD. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +86-010-6444-3098; fax: +86-010-6444-6043; e-mail: [email protected] 45 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Abstracts Buenos Aires, Argentina 105 - A fault diagnosis method based on spectral kurtosis and three-order cumulation Xintao Xu a, Lingyang Li a, Xiao Yang a and Huaqing Wang a * a College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, No.15 in East Road of North Third Ring, Chaoyang District, Beijing, 100029, China ABSTRACT Detecting transient vibration signatures is of vital importance for fault detection of the rotating machinery.However,for the traditional envelope analysis,the parameters of band-pass filter is usually determined by the artificial experience. To provide a theoretical basis for filter parameters setting,the fast kurtogram is widely applied.The optimal parameters is determined via a dyadic and ternary grid which maximises its kurtosis.In spite of being particularly suited to many detection problems,the fault features cannot be extracted effectively as a result of the influence of the mild outliers.This paper proposes a new method of constructing a matched filter based on spectral kurtosis and high-order cumulation.In order to eliminate the gaussian white noise effectively, the three-order cumulation of the signal is used;then,calculating spectral kurtosis of three-order cumulation;finally,a matched filter is constructed to detect fault characteristic.Results shows that the proposed method is effective for diagnosing the fault of rolling bearing. Keywords: Spectral kurtosis; Three-order cumulation; fault diagnosis. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +86-138-0102-3830; fax: +86-010-6441-6122; e-mail: [email protected], [email protected] 113 - Vibration analysis of a twenty mill roll grinding machine with a spalling defect on the tip Fang Guo a, Zhili Shi a, Yilin Yuan b and Yimin Shao a * a State Key Laboratory of Mechanical Transmission, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400000, China b Ningbo Baoxin Stainless Steel Co.,Ltd, Beilun District, Ningbo 315807, China ABSTRACT Spalling faults on the surface of the tip of a roll grinder can be caused due to impurities and contact fatigue in the process of its work, which can affect the roller surface quality seriously. To detect this fault, according to the contact relationship between a localized spalling fault on the surface of the tip and the roller, a three-dimensional nonlinear dynamic contact finite element model of a roller grinder system considering a localized spalling fault on the surface of the tip is proposed in this paper. The elastic contact deformations between the roller and the drag tile, the bending deformation of the roller, and the nonlinear dynamic contact deformation between the roller and the tip are considered in the proposed model. The proposed method is applied to investigate the effects of the spalling sizes on the vibrations of the grinder. The numerical results show that the proposed method can provide a new approach for the condition monitoring and the detections of the faults in the roll grinding machine. Keywords: Twenty mill rolling grinder machine; roll grinder tip; spalling fault; vibration characteristics. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +86-023-6511-2520; fax: +86-023-6518-6195; e-mail: [email protected] 46 Resúmenes de trabajos COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina SESIÓN: ENSAYOS NO DESTRUCTIVOS / SESSION: NON-DESTRUCTIVE TESTING 04 - Evaluación y monitoreo estructural de edificio industrial con vibraciones debidas a máquinas utilizando técnicas dinámicas no destructivas Norma L. Ercoli a *, María H. Peralta a y Leonel O. Pico a a Docentes-Investigadores, Facultad de Ingeniería - CIFICEN-UNICEN, Av. Del Valle 5737- 7400 – Olavarría. Buenos Aires. Argentina RESUMEN El diseño de estructuras de edificios industriales es complejo pues está asociado a la diversidad y naturaleza de los procesos involucrados según el destino, con presencia de equipos y sistemas que generan vibraciones. Dada esa complejidad, en muchos casos, es necesario evaluar edificios construidos en los que, en condiciones de servicio, se detectan respuestas vibratorias indeseadas. En el presente trabajo se evalúa un edificio que aloja equipos de zaranda y trituradora en instalaciones de una planta de fabricación de cemento de Olavarría, Buenos Aires. Se trata de una estructura de hormigón armado de cuatro niveles que, en condiciones de servicio, presenta vibraciones que se deben cuantificar por la incidencia de las mismas en el funcionamiento de los equipos y/o para evitar daños en la estructura. A tal fin, se plantea un programa de monitoreo para evaluar el comportamiento real en servicio a través de la instrumentación de mediciones experimentales con técnicas dinámicas no destructivas. Se instrumentan modelos computacionales determinando las características dinámicas y la respuesta estructural en el estado de servicio. La complementariedad de las técnicas permite establecer criterios para el comportamiento estructural adecuado, según códigos internacionales, y postular recomendaciones relativas a la selección de los montajes antivibratorios. Palabras clave: Vibraciones de máquinas; Comportamiento estructural; Técnicas Dinámicas no Destructivas * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. Tel.: +54-2284-45-1056; fax: +54-2284-45-1055; e-mail: [email protected] 10 - INTRODUCCIÓN al comportamiento de nanopartículas magnetizables en la detección y estudio de discontinuidades microestructurales. German Scillato a, Ricardo Echevarría a a Universidad Nacional del Comahue, Facultad de Ingeniería,Lab. de END (LEND) Calle Bs. As 1400, Neuquén CP 8300, Argentina RESUMEN El presente trabajo describe los primeros estudios para la potencial aplicación de NANOPARTICULAS FERROMAGNETICAS en el método de Ensayos No Destructivos de Partículas Magnetizables, con el fin de analizar su comportamiento sobre discontinuidades y características de materiales a una escala microscópica. Se sintetizaron, y utilizaron nanopartículas ferromagnéticas, del tipo Core-Shell, que permiten combinar dos o más propiedades a la vez, por un lado su tamaño nanométrico y por el otro características de fluorescencia, ambas fundamentales para dicho ensayo. Las nanopartículas se caracterizaron con las técnicas de TEM, AFM, DRX e IR para determinar su tamaño, estructura cristalina, composición química y presencia de grupos funcionales. Se utilizó microscopía de fluorescencia para estudiar y analizar su comportamiento sobre diferentes tipos de discontinuidades microestructurales, como bordes de grano, microfisuras por daño por hidrógeno, pitting de corrosión y cambios de permeabilidades magnéticas en aceros Duplex. Se ofrecen propuestas para continuar con la línea de investigación. Palabras clave: Manejo de instalaciones; Centrales de potencia/componentes;detección de fallas/diagnóstico * Autores a quien dirigir correspondencia. [email protected] [email protected] 47 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Abstracts Buenos Aires, Argentina 13 - Evaluación estructural de recipientes a presión mediante magnetometría y Small Punch Test Aníbal Di Luch *, Carlos D. Anello, Rodolfo Kempf, Joaquín Sacanell y Ana M. Fortis CNEA, Av. Gral Paz 1499 (B1650KNA), Bs. As., Argentina RESUMEN La radiación neutrónica provoca la fragilización del recipiente a presión (RPR) de acero de los reactores nucleares de modo que, bajo ciertas condiciones accidentales, se puede producir su rotura catastrófica, el fin de la planta y la eventual dispersión de material radiactivo. Para asegurar la integridad y el servicio prolongado de este componente estructural bajo condiciones extremas como altas temperaturas e irradiación neutrónica, se realizan ensayos mecánicos convencionales o se aplican técnicas indirectas como rayos X, ultrasonido…etc. Como alternativa, los ensayos mecánicos con probetas reducidas en masa como el ensayo de punzonado o Small Punch Test (SPT) pueden considerarse como no destructivos y, además, permiten caracterizar mecánicamente regiones muy pequeñas como por ejemplo, las zonas afectadas térmicamente de las uniones soldadas. Su aplicación reduce notablemente la dosis de exposición y requiere cantidades tres órdenes de magnitud menores de material a ensayar. Se presenta el diseño del sistema de medición de SPT para su aplicación en la determinación del estado de fragilización del material del RPR de la central Atucha II sometido a distintas dosis de radiación en el reactor experimental RA1. Se comparan los resultados de los ensayos mecánicos convencionales con ensayos magnéticos. Palabras clave: Small Punch Test, SPT, ensayos miniatura, evaluación estructural, ensayos no destructivos * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. Tel.: 6772-7352 e-mail: [email protected] 18 - Modelado térmico y termografía de probetas Charpy ensayadas en altas temperaturas por corriente eléctrica Pedro A. Ferreirós a-b-c *, Paula R. Alonso a-b, Pablo H. Gargano a-b y Gerardo H. Rubiolo a-b-d a Gerencia de Materiales (GAEN) - Comisión Nacional de Energía Atómica (CNEA), Av. General Paz 1499, B1650KNA, San Martín, Buenos Aires, Argentina. b Instituto Sabato - Universidad Nacional de San Martín (UNSAM)-CNEA, Av. General Paz 1499, B1650KNA, San Martín, Buenos Aires, Argentina. c Universidad Tecnológica Nacional, Facultad Regional Haedo (UTN-FRH), París 532, 1706, Haedo, Buenos Aires, Argentina. d Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET), Av. Rivadavia 1917, C1033AAJ, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires, Argentina. RESUMEN El ensayo de impacto Charpy, es el método más utilizado industrialmente para detectar la Temperatura de Transición Dúctil-Frágil (BDTT) de los materiales. En la mayoría de los metales y aleaciones comerciales la BDTT se encuentra entre temperaturas próximas a la ambiental y criogénicas. El desarrollo de nuevos materiales para diversas aplicaciones, presenta situaciones donde la BDTT se ubica a temperaturas considerablemente superiores, es decir mayores a los 500ºC. El ensayo Charpy operativamente no puede ser utilizado a tan elevadas temperaturas, ya que el procedimiento convencional de extracción de probetas térmicamente estabilizadas en un horno hasta su colocación en la máquina para el ensayo, produce un desfasaje de la temperatura del ensayo en decenas grados en pocos segundos. Por lo tanto diseñamos un accesorio que puede agregarse a una máquina de Charpy y que calienta in situ a la probeta a ensayar. La zona de la entalla de la probeta es calentada por corriente eléctrica en pocos segundos y mantenida a temperatura (400≤T≤725ºC) hasta que el péndulo de ensayo se encuentra próximo a la probeta. En el presente trabajo se modela el perfil de temperaturas presente en la probeta y se compara con datos experimentales medidos por termografía y con termocuplas. Palabras clave: : Charpy; alta temperatura; calentamiento in situ; modelado térmico; termografía. * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. P. A. Ferreirós. Tel.: +054-11-6772-7247; fax: +054-11-6772-7362 e-mail: [email protected] 48 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Resúmenes de trabajos Buenos Aires, Argentina 20 - Sistema rápido de inspección de ejes ferroviarios Jose Brizuela a *, Alejandro García b, Carlos Desimone b y Rodrigo Romero c a Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET), Avda. Gral Paz 1499, San Martín, B1650KNA, Argentina. b Comisión Nacional de Energía Atómica (CNEA - INEND - UAENDE), Av. Gral. Paz 1499, San Martín, B1650KNA, Argentina c Comisión Nacional de Energía Atómica (CNEA - IAMEND - UAENDE), Av. Gral. Paz 1499, San Martín, B1650KNA, Argentina RESUMEN El transporte ferroviario posee un alto impacto socio-económico dentro de las regiones que comunica. Por tanto, su operación segura demanda excelentes condiciones de la infraestructura fija y rodante. En particular, el buen estado de los ejes resulta fundamental para garantizar la seguridad operativa, puesto que su fallo conlleva un alto riesgo de descarrilamiento con consecuencias potencialmente severas. Las grietas superficiales son el principal defecto en un eje, se originan por fatiga del material y se forman en zonas inaccesibles; generalmente en áreas de presión (debajo de las ruedas, poleas, engranajes, etc,). La verificación de estas fallas se realiza aplicando técnicas de ultrasonidos (UT). No obstante, el complejo diseño del eje y el restringido acceso que se tiene al componente cuando está montado, hacen que la tarea de inspección sea dificultosa y costosa en términos de mantenimiento. El presente trabajo, describe el diseño de un sistema prototipo para la inspección de ejes sólidos basado en tecnología de Phased Array (PA). La propuesta permite evaluar de manera rápida, fiable, y con elevada resolución, la integridad de los ejes montados en el tren con un mínimo desarme de piezas. Se presentan simulaciones del diseño y validación de resultados, obtenidos de una bancada experimental. Palabras clave: Ejes ferroviarios; END industrial; imagen ultrasónica; Phased Array; mantenimiento ferroviario * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. Tel.: +54-11-6772-7616; fax: +54-11-6772-7355; e-mail: [email protected] 21 - Inspección de tubos realizados en plásticos reforzados con fibra de vidrio Jose Brizuela a *, Alejo Minetti b, Carlos Desimone c y Alejandro García c a Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET), Avda. Gral Paz 1499, San Martín, B1650KNA, Argentina. b Instituto Tecnológico Sábato - Universidad Nacional de San Martín (ITS-UNSAM), Av. Gral. Paz 1499, San Martín, B1650KNA, Argentina c Comisión Nacional de Energía Atómica (CNEA - INEND - UAENDE), Av. Gral. Paz 1499, San Martín, B1650KNA, Argentina RESUMEN Históricamente las tuberías de transporte de gas, agua, hidrocarburos, etc., se construían a partir de tubos de aceros o aleaciones unidas por soldaduras, y en menor medida, utilizando concreto o cerámica. Desde hace algunas décadas, con el desarrollo de nuevos materiales, y en particular los basados en compuestos de resinas epoxis reforzados con fibra de vidrio (ERFV), se ha logrado la fabricación de componentes con características estructurales, térmicas y químicas, muy superior a las alcanzadas con materiales tradicionales. Estas atractivas ventajas, asociadas a un bajo costo, han impulsado a que muchas industrias, y en especial la petroquímica, utilicen tuberías ERFV como alternativa al acero. Las tuberías de ERFV igualmente requieren del aseguramiento de su integridad, sin embargo, representan una tecnología relativamente nueva en comparación al desarrollo alcanzado con los materiales clásicos. Por tanto, el uso de técnicas convencionales de Ensayos No Destructivos (END), como herramientas de inspección, queda limitado y no se puede garantizar un alto nivel de confianza. En el presente trabajo se aborda la implementación de la tecnología de Ultrasonidos por Phased Array (PAUT) como método END para evaluar el estado de tuberías ERFV en servicio y se describe el desarrollo de un sistema de análisis de datos. Palabras clave: Materiales compuestos; END; imagen ultrasónica; Phased Array; tuberías plásticas * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. Tel.: +54-11-6772-7616; fax: +54-11-6772-7355; e-mail: [email protected] 49 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Abstracts Buenos Aires, Argentina 35 - Casos de análisis de vibraciones en máquinas críticas en la industria, utilizando equipos de medición multicanal Marcelo Bulfón JPS Argentina – Carlos Pellegrini 763 – 4º Piso – C.A.B.A.- Argentina - C1009ABO- RESUMEN Sabido es que el monitoreo de vibraciones es una de las claves en el desarrollo moderno de la industria y su transformación en su derrotero, que va desde el mantenimiento a la rotura, hasta la aplicación de técnicas predictivas en el mantenimiento bajo condición. Podríamos dividir en dos grandes grupos las técnicas de estudio de vibraciones aplicadas al mantenimiento. Las primeras son aquellas que utilizan equipos de medición portátil, armados con uno o dos sensores de vibración. Sobre este tipo de equipamiento se basa la práctica diaria del mantenimiento predictivo en la industria. En segundo lugar encontramos aquellos equipos de medición equipados con múltiples sensores. La diferencia entre ellos no es solo cuantitativa, ya que además permiten el registro simultáneo de los datos generados de la dinámica compleja de las máquinas. Existe un grupo de máquinas que ya sea por su tamaño, potencia, velocidad de giro o tipo de soportación requieren de la utilización de herramientas de análisis más complejos e integrales. En la presentación se resumen varios casos de estudio tomados de nuestra experiencia con equipamiento multicanal. Palabras clave: Manejo de instalaciones; Centrales de potencia/componentes;detección de fallas/diagnóstico. 49 - Mediciones especiales en la Central Nuclear Atucha II Federico Elfi 1a, Andres Bello 2a y Pablo Tabla 3a a Centro de Ensayos No Destructivos y Estructurales, Grupo Vibraciones Mecánicas, Universidad Tecnológica Nacional, Facultad Regional Delta, San Martín 1171, Campana (CP 2804) Buenos Aires, Argentina RESUMEN El Programa de Puesta en Marcha (PeM) de la Central Nuclear Atucha II requiere la realización de numerosas pruebas que tienen como objetivo demostrar la confiabilidad de equipos y sistemas. Durante las mismas se llevaron a cabo una serie de mediciones a fin determinar el estado tensional de componentes del sistema primario y secundario, con la finalidad de verificar los modelos de cálculo que se utilizaron en la fase de diseño. En este trabajo se presentan, en particular, resultados de mediciones tensionales (deformación y desplazamiento) en cañerías del sistema primario asociadas al generador de vapor, y en cañerías de alimentación de agua al mismo principalmente durante rampas de calentamiento y presión. Se describen el tipo de instrumentación utilizada en base a requerimientos de diseño, puntos de instrumentación, sistema de adquisición de datos y procesamiento de los mismos, así como las correcciones efectuadas en estos a partir de ensayos de laboratorio. Finalmente se discuten algunas de las mediciones realizadas. En base a los datos obtenidos, se corroboraron los modelos de elementos finitos utilizados en la etapa de diseño. Palabras clave: Mediciones especiales; Puesta en marcha; Central nuclear;mediciones tensionales. * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. [email protected] [email protected] 50 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Resúmenes de trabajos Buenos Aires, Argentina 50 - Calificación y certificación de personal en ensayos no destructivos comparación entre sistema ISO 9712 y sistema SNT TC 1A (ASNT) Ing. Claudio Carballal Nivel 3 IRAM NM ISO 9712, Nivel 3 ASNT, Nivel 3 NAS 410, Director GEND, Universidad Tecnológica Nacional Regional Delta, San Martin 1171, Campana, (2804) Argentina RESUMEN La necesidad de personal competente para la realización de los Ensayos No destructivos es un requerimiento muy importante en toda la industria . Para determinar la competencia de un individuo se desarrollaron sistemas que evalúan si el personal tiene el entrenamiento necesario, a cumplido satisfactoriamente con examinaciones escritas y prácticas, y tiene la suficiente experiencia para realizar correctamente la inspección en el método o técnica que es competente . El personal que cumple con estos tres requerimientos ademas de cumplir con la aptitud visual se dice que está calificada, una vez cumplida esta etapa la persona se certifica de en el método de ensayo que califico .La forma de la certificación dependerá del sistema elegido. Hay muchos sistemas de certificación de personal en END que adoptan los países, la industria o que solicitan códigos o estándares como ser API, ASME, ASTM, DIN, JIS, NANDTB, etc. Los sistemas de calificación y certificación mas adoptados son ISO 9712, ASNT/ANSI CP189 - NAS 410/EN4179 - EN 473 - SNT TC 1A, pero en general se pueden dividir en dos tipos principales, los denominados sistemas centrales de certificación ( third party certification ) y los denominados sistemas de certificación del empleador ( employer - based). El presente trabajo desarrolla la diferencia entre estos sistemas de certificacion de personal END, que algunos ya cumplieron los 40 años desde su primera edición. Palabras clave: Calificacion y certificacion de personal en END, sistemas centrales de certificación, sistemas de certificación del empleador, SNT TC 1A, ISO9712. * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. Tel.: +54-3489 420400 int. 5109; e-mail: [email protected], [email protected] 57 - Mediciones de comportamiento estructural en condiciones complejas Mario Modesti a, Daniel Conte b *, Alexis Caro b y Dimas Benasulin a a U.T.N., Fac. Reg. Córdoba, LabSen, Cdad. Universitaria 5000 Córdoba, Argentina b U.T.N., Fac. Reg. Córdoba, GIMSE, Cdad. Universitaria, 5000 Córdoba, Argentina RESUMEN Para el estudio de estructuras mecánicas en condiciones operativas particularmente complejas, como el caso del análisis de vibraciones de un componente de carrocería de un camión, se desarrolla el presente trabajo consistente en un sistema de adquisición de datos con conectividad múltiple. Las mediciones se realizan en condiciones operativas reales con el objeto de obtener información sobre los sometimientos debidos al viento, de manera que la estructura objeto del análisis estará expuesta a la velocidad y vórtices de aire. La tecnología empleada incluye MEM’s (Microelectromechanical systems) que permiten una masa muy pequeña en el transductor de medición de aceleración en tres ejes con una respuesta en frecuencia capaz de medir con un tiempo de muestreo de 10 mSeg. El sistema es capaz de adquirir datos de eventos particulares a relevar con el objeto de obtener el espectro vibracional del sistema bajo inspección. Es abierto en código y capaz de relevar cualquier tipo de transductor acondicionado o no, constituyendo una red donde cada medición dispone de su propia CPU de adquisición, con capacidad de almacenamiento. Se propone con este sistema, caracterizar las modalidades de vibración del sistema bajo estudio dando como resultado las frecuencias naturales que componen las solicitaciones mecánicas por efectos del viento. Palabras clave: vibraciones, adquisición de datos, frecuencia natural, MEMS * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. Cel.: +54 9 351 6143502; Tel: *54 351 5986000 int. 5-1119; e-mail: [email protected]; [email protected] 51 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Abstracts Buenos Aires, Argentina 60 - Estudio de la condición de las brocas de taladrado mediante Emisión Acústica y Redes Neuronales. Guido Ferrari a, Martin Gómez a-b a CENES - Dpto. Ing. Mecánica, Fac. Reg. Delta, UTN, San Martin 1171, Campana, Buenos Aires, Argentina. b Dpto. Proyecto ICES y Ondas Elásticas, CNEA , Av. G. Paz 1499 San Martín, Buenos Aires, B1650KNA, Argentina. RESUMEN El control y monitoreo en línea del estado de la herramienta durante el proceso de mecanizado ayuda a disminuir los costos de fabricación y a aumentar la calidad en piezas mecanizadas. Los centros de mecanizado comerciales, en general, censan pocas variables con capacidad de reconocer el estado de la herramienta. Siendo los parámetros más monitoreados la corriente consumida y la fuerza sobre la herramienta, donde ambas magnitudes aumentan con el incremento del desgaste. Las técnicas de monitoreo indirecto, en conjunto con métodos de análisis de señales, pueden proveer información útil para reconocer tal condición. La Emisión Acústica (EA) es una técnica indirecta que ha demostrado gran potencial para ser implementada como parte de un sistema de monitoreo del estado de la herramienta. En el presente trabajo se expone para un proceso de taladrado en metales, como pueden ser identificadas distintas condiciones de los filos de corte a partir de la medición simultánea de la EA y otros parámetros mecánicos del proceso de corte. Los parámetros de EA utilizados fueron: Amplitud, RMS, Potencia Media, y otros. Con estos parámetros se alimentó una red neuronal tipo Kohonen que dio como resultado un mapa con la clasificación de las diferentes condiciones de desgaste de las brocas. Palabras clave: Ensayos no destructivos, Emisión Acústica, Redes Neuronales, Desgaste, Mecanizado. * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. Guido Ferrari Tel.: +54-03489-420400 e-mail: [email protected] 61 - Evaluación de las condiciones de servicio de puentes peatonales María Inés Montanaro a , María Laura Godoy a * e Irene Rivas a a Docentes Investigadoras- Área Estructuras-Facultad Ingeniería UNICEN, Av. Del Valle 5737, Olavarría 7400, Argentina RESUMEN Las estructuras en general y los puentes en particular presentan deterioros durante el transcurso de su vida útil. Es sumamente importante su detección para realizar una adecuada reparación estructural. Esto requiere la ejecución de tareas de inspección, evaluación y diagnóstico. El arroyo Tapalqué atraviesa la planta urbana de la ciudad de Olavarría haciendo necesaria la presencia de numerosos puentes que vinculan los diferentes barrios emplazados en sus cercanías. Particularmente hay siete puentes colgantes peatonales de similar tipología estructural. Están formados por dos estructuras metálicas sobre las que apoyan cables que, mediante péndolas sostienen el tablero de madera. La Municipalidad de Olavarría y la Facultad de Ingeniería de la UNCPBA firmaron un convenio para la evaluación del estado de conservación de dichos puentes. La tarea consistió en la realización de un ensayo no destructivo de inspección visual de las partes componentes de los puentes con la finalidad de arribar a un pormenorizado diagnóstico. Se recomendaron acciones tendientes a restablecer condiciones adecuadas para su uso. De acuerdo al grado de importancia y de afectación, las acciones se diferenciaron entre reparaciones de inmediata resolución y reparaciones que pudieran concretarse en un lapso de tiempo mayor, sin que esto signifique riesgo para la estructura. Palabras clave: Puentes; Inspección Visual; Patologías * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. Tel.: +0-2284-45-1055; fax: +0-2284-45-1055; e-mail: [email protected] 52 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Resúmenes de trabajos Buenos Aires, Argentina 64 - Evaluación de la integridad estructural de la unión entre la conexión o “Bota de Condensación” y el cuerpo cilíndrico de un recipiente contenedor de presión, mediante el método de elementos finitos, bajo los lineamientos del Código ASME Sección VIII División 2 “Diseño por Análisis”. Héctor Sanzi a *, Gustavo Elvira a y Alejandro Turel a a Grupo de Investigación Ingeniería Estructural (GIIE),Universidad Tecnológica Nacional – Facultad Regional Haedo, París 532, Haedo (1706), Buenos Aires, Argentina. RESUMEN Las conexiones de proceso e inspección, soldados al cuerpo de un recipiente contenedor de presión, requieren de la verificación estructural para cumplir con los códigos de aplicación. Bajo el estado de carga por presión interior y como mandatorio en el código ASME Sección VIII División 1, se debe verificar la necesidad de colocar un refuerzo adicional o “Pad” alrededor de la conexión, con el objeto de compensar en un balance geométrico, el área transversal del material retirado, asegurando de esta manera la integridad estructural de la unión. Algunos diseñadores han propuesto para el caso particular de las conexiones utilizadas para recolección de condensados que se encuentran ubicadas en la parte más inferior del cuerpo cilíndrico del recipiente, denominadas comúnmente “Botas de Condensado” y sin un sustento teórico y/o práctico, utilizar como refuerzo parte del cuerpo cilíndrico del recipiente, prolongándolo hacia el interior de la conexión. De esta manera se evitaría la colocación del refuerzo en la zona de unión. Este diseño no afectaría la descarga del proceso. En este trabajo se presenta, a partir del método de elementos finitos, bajo los lineamientos de diseño del Código ASME Sección VIII División 2, Parte 5 “Diseño por Análisis”, un estudio detallado de dicha propuesta con el objeto de analizar la propuesta y verificar la integridad estructural de los elementos que conforman la unión. Palabras clave: Conexiones en recipientes, Aberturas en recipientes, Botas de condensado, Elementos finitos. * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. Tel.: 011-4383-1128; e-mail: [email protected] 65 - Análisis de Ruido Magnético Barkhausen en acero AISI 304 Neyra Astudillo Miriam Rocío a-c *, Núñez Nicolás a, López Pumarega María Isabel a, Ruzzante José a-b, Gómez Martín a-b-c, Ferrari Guido b, Rodrigues Padovese Linilson d a Dpto. Proyecto ICES y Ondas Elásticas, CNEA , Av. G. Paz 1499 San Martín, Buenos Aires, B1650KNA, Argentina. b CENES - Dpto. Ing. Mecánica, Fac. Reg. Delta, Universidad Tecnológica Nacional, San Martín 1171, Buenos Aires, 2804, Argentina. c Instituto Sabato, Universidad Nacional de San Martín, Av. G. Paz 1499, San Martín, Buenos Aires, B1650KNA, Argentina. d LADIN, Departamento de Ingeniería Mecánica, Escuela Politécnica, Universidad de San Pablo, Av. Prof. Mello Moraes 2231, San Pablo, 05508-900, Brasil. RESUMEN Cuando los materiales ferromagnéticos son sometidos a campos magnéticos variables, la variación en la inducción magnética ocurre de manera discontinua como resultado del movimiento de las paredes de los dominios magnéticos. Esos saltos discretos producen señales conocidas como Ruido Magnético Barkhausen (RMB). El RMB es sensible a las alteraciones microestructurales, tensiones y deformaciones plásticas del material. Como consecuencia, puede ser utilizado como Ensayo No Destructivo en una gran cantidad de aplicaciones, por ejemplo monitoreo de variaciones microestructurales, control de calidad de tratamientos superficiales, degradación, tensiones, etc. Este trabajo es la continuación del estudio de ensayos de tracción, hasta rotura, en probetas uniaxiales de acero inoxidable austenítico AISI 304, en las cuales, como consecuencia de la deformación aparece una fase ferromagnética que produce RMB. Las mediciones se realizaron a diferentes cargas con el fin de observar cómo cambiaban las características de la señal de RMB. Para el análisis se estudiaron distintos parámetros, tales como el valor RMS, el coeficiente de asimetría, la posición y la altura del pico máximo, correlacionándolos con la carga aplicada. Los resultados muestran una dependencia entre los diferentes parámetros y los valores de la carga aplicada. Palabras clave: Ruido Magnético Barkhausen; Ensayo no destructivo; Aceros austenitico. * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. Tel.: +54-11-6772-7766; fax: +54-11-6772-7134; e-mail: [email protected] 53 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Abstracts Buenos Aires, Argentina 68 - La simulación numérica como herramienta de evaluación de recipientes a presión Leonel Osvaldo Pico a-b *, María Laura Godoy a y Luis María Arrien b a Área Estructuras - Dpto. Ing. Civil - Facultad Ingeniería UNICEN, Av. Del Valle 5737, Olavarría 7400, Argentina b Área Mecánica- Dpto. Ing. Electromecánica - Facultad Ingeniería UNICEN, Av. Del Valle 5737, Olavarría 7400, Argentina RESUMEN La simulación numérica por medio del Método de los Elementos Finitos (MEF) es una herramienta útil para la predicción del comportamiento estructural. Actualmente, las simulaciones numéricas son consideradas una técnica de ensayo no destructivo. El creciente desarrollo de la potencia de las computadoras y la implementación del MEF permite el estudio del comportamiento mecánico-estructural de recipientes a presión. En este trabajo se analizan las tensiones y las deformaciones de un recipiente de aire comprimido a baja presión. Se midieron espesores por medio de ultrasonido en diferentes lugares del recipiente. Se realizaron modelos numéricos con MEF reproduciendo los espesores medidos experimentalmente y a partir de la resolución numérica se determinaron las tensiones y deformaciones dentro del recipiente. Los datos hallados se compararon con los criterios establecidos en las normativas. Los resultados obtenidos permiten inferir si el recipiente analizado cumple o no con lo establecido por los códigos de diseño. Palabras clave: Recipientes a Presión; Inspección Visual; Herramientas Computacionales; Análisis Mecánico Estructural. * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. Tel.: +0-2284-45-1055; fax: +0-2284-45-1055; e-mail: [email protected] 69 - Caracterización de recubrimientos obtenidos a partir de film líquidos por interferometría de baja coherencia Georgina L. Luna a, Pablo M. Tabla a, Marcelo D. Sallese a, Eneas N. Morel a y Jorge R. Torga a a Laboratorio de Optoelectrónica y Metrología Aplicada, Facultad Regional Delta, Universidad Tecnológica Nacional, Campana (2804), Bs As , Argentina RESUMEN En este trabajo se presenta la interferometría de baja coherencia como una técnica sin contacto para caracterizar recubrimientos obtenidos a partir de un film líquido depositado sobre distintos materiales. Nos referimos específicamente a recubrimientos poliméricos, barnices, pinturas y lacas entre otros, con la única condición de que sean transparentes o semitransparentes en la región del espectro electromagnético en el rango entre el visible y el infrarrojo lejano (400nm a 2000nm). La técnica permite la medición de espesor y homogeneidad del recubrimiento, o sea que puede ser utilizado como técnica de monitoreo del producto final o para estudio de su evolución temporal en el proceso de formación del film, por ejemplo en procesos de secado, polimerización o cambios estructurales. Se presenta la configuración experimental del sistema en distintas variantes incluyendo un sistema modular que puede ser adaptado a aplicaciones industriales, monitoreo en línea o sistemas de control de calidad. Se presentan también mediciones en muestras de distintos recubrimientos depositados sobre metales y vidrios. Se muestran resultados obtenidos en la medición de espesores, topografía de superficie y tomografía del material. También se presentas datos sobre las características y limitaciones del método propuesto como: valores máximos de distancia, resolución espacial y profundidad de penetración en el material. Palabras clave: Ensayo óptico no destructivo, interferometría, recubrimientos. * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. [email protected] 54 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Resúmenes de trabajos Buenos Aires, Argentina 74 - La simulación numérica como herramienta de evaluación de recipientes a presión Caro Agustín a, Gómez Martína b * a IT Sabato, UNSAM, Av. G. Paz 1499 San Martín, Buenos Aires, Argentina . b Dpto. Proyecto ICES y Ondas Elásticas, CNEA , Av. G. Paz 1499 San Martín, Buenos Aires, B1650KNA, Argentina. RESUMEN El taladrado de materiales compuestos es de gran interés en la industria aeroespacial. Las piezas ensambladas pueden llevar una gran cantidad de perforaciones. El astillado y la delaminación son problemas muy frecuentes en este tipo de proceso mecánico. Hay otras situaciones que son importantes a evaluar en estos procesos como por ejemplo conocer a que capa del compuesto ha llegado la herramienta, con el objetivo de no perforar capas siguientes. Con este fin, se han implementado una serie de ensayos iniciales para poder determinar de manera no destructiva la posición de la punta de la mecha en el interior de un compuesto sándwich. Para esto se han construido probetas multicapas especialmente diseñadas, compuestas por distintos materiales con el fin de determinar el pasaje de la punta de la mecha en cada una de estas capas, a partir de la medición de las ondas elásticas de Emisión acústica (EA) generadas durante el corte. Se colocó un sensor de EA en cada una de las probetas maquinadas y se midieron las señales generadas durante el corte. Se utilizaron mechas con distinta condición (estado de los filos) para evaluar el alcance del método. Se midieron distintos parámetros característicos de las señales de EA como la amplitud, el valor RMS, la potencia media y la frecuencia media, con el fin de caracterizar el corte de cada material constituyente del multicapa. Palabras clave: Emisión acústica; materiales compuestos multicapas; taladrado. * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. Tel.: +54-11-6772-7766; e-mail: [email protected] 85 - Detección por imágenes del daño incipiente por corrosión sobre superficies metálicas Néstor O. Fuentes a * a Comisión Nacional de Energía Atómica - GASNyA - PNGRR. Av. del Libertador 8250 - C1429BNP - CABA. Argentina RESUMEN Los importantes avances en el diseño y caracterización del comportamiento de superficies funcionales sobre materiales metálicos, hace imprescindible una detección temprana de cualquier daño que, alterando la topografía de la superficie, modifique la función específica para la que fue creada. En tal sentido, la caracterización de la topografía de la superficie funcional (rugosidad, dibujo geométrico, longitudes de escala típicas) resulta el primer paso para la el monitoreo y determinación del estado de sus propiedades. Con tal propósito, se decidió emplear la técnica RIMAPS y el método de Variogramas para el análisis de imágenes digitales de diversas superficies metálicas para evaluar el grado de detección temprana del daño por corrosión incipiente que pueden producir distintos agentes químicos. El empleo combinado de ambas técnicas permite obtener las direcciones topográficas principales de las superficies observadas como así también las longitudes de escala típicas de las mismas, cuyas modificaciones respecto de la condición inicial ponen en evidencia el daño temprano por corrosión. Se presentan los resultados de evaluaciones para distintos tiempos de ataque corrosivo sobre distintas superficies metálicas. Palabras clave: Detección por imágenes; técnica RIMAPS ; detección temprana de daño. * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. Néstor O. Fuentes. Tel.: +54-11-4704-1480; Fax: +54-11-4704-1174; e-mail: [email protected] 55 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina 90 - Análisis comparativo en la determinación de ferrita delta para aceros inoxidables austeníticos Eduardo Asta a *, Francisco Cambiasso b y Juan C. Ríos b a ESAB Argentina/Universidad Tecnológica Nacional-FRH, Calle 18 N° 4079, Villa Lynch (1632),Argentina b Universidad Tecnológica Nacional-FRH, Paris532, Haedo (1706), Argentina RESUMEN En la soldadura de aceros inoxidables austeníticos la determinación de ferrita delta (ferrita-∂) resulta muy importante para poder conocer la susceptibilidad que presenta el metal de soldadura a la fisuración en caliente, uno de los problemas más importantes en relación con la soldabilidad, comportamiento metalúrgico y mecánico de este tipo de aceros. La determinación de ferrita-∂ en el metal de soldadura puede realizarse con métodos predictivos a partir de la composición química del metal aportado por el consumible de soldadura (Diagramas de Schaeffler, DeLong, WRC 1988 y WRC 1992) en forma metalográfica y a través de una técnica de ensayo no destructiva utilizando un medidor magnético de ferrita-∂. En este trabajo se presenta un análisis comparativo entre la determinación predictiva de ferrita-∂ y el método magnético utilizando electrodos inoxidables austeníticos para proceso SMAW de diferentes clasificaciones y diámetros. Los aportes utilizados corresponden a distintos lotes de fabricación de dichos consumibles y se ha utilizado una metodología estandarizada para la determinación magnética. El análisis muestra las diferencias y limitaciones entre el método predictivo y el método de ensayo magnético, resultando de utilidad práctica para una adecuada especificación de procedimientos de soldadura y posterior control de las soldaduras de aceros inoxidables austeníticos. Palabras clave: Ferrita-∂; Aceros inoxidables; Diagramas WRC; Diagrama de Schaeffler. * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. Eduardo Asta. Tel.: +54-11-4754-7009; fax: +54-11-4754-7000; e-mail: [email protected] 99 - Validación de modelo de barras combustibles a partir de ensayos hidrodinámicos en el Circuito Experimental de Baja Presión Karim Bonifacio, Mariano Arévalo y Alberto Martin Ghiselli CNE -ENDE-EECE, Buenos Aires (1650), Argentina RESUMEN Los ensayos hidrodinámicos forman parte de la caracterización del diseño de elementos combustibles para reactores de potencia, los cuales son realizados en la facilidad de ensayo del Circuito Experimental de Baja Presión del CAC, que cuenta con secciones de ensayo que reproducen las condiciones geométricas e hidrodinámicas del elemento combustible en el núcleo del reactor. La planificación de estos ensayos requiere un análisis previo de la respuesta dinámica de los componentes del elemento combustible, a fin de optimizar la instrumentación a emplear y evaluar los resultados que se obtengan durante la ejecución del ensayo, para lo que se realizan modelos numéricos del elemento combustible o de sus partes componentes. La simulación de la respuesta vibratoria de componentes estructurales sometidos a la acción de fuerzas originadas en la interacción fluido-estructura presenta dificultades dadas las múltiples variables que intervienen y las características aleatorias del fenómeno. El presente trabajo modela una barra combustible haciendo uso del método de elementos finitos y realimenta el modelo con los resultados de los diferentes ensayos realizados sobre prototipos en el circuito experimental. El resultado es un modelo de barra combustible validado que responde a las distintas condiciones de flujo de agua, obteniendo los comportamientos modales, frecuencias naturales de vibración, valores globales de respuesta vibratoria y espectros de respuesta. Palabras clave: Barras Combustibles; Validación por elementos finitos;Ensayos Hidrodinamicos. * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. Tel.: +00-54-11-67727439; fax: +00-54-11-67727426; e-mail: [email protected] 56 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina 101 - Calificación ambiental de componentes de seguridad de centrales nucleares de potencia Alberto Busto y Viviana Ishida INVAP S.E., Av. Cmte. Luis Piedrabuena 4950, San Carlos de Bariloche (R8403CPV), Argentina INVAP S.E., Esmeralda 356 - PB, C.A.B.A (C1035ABH), Argentina RESUMEN Los componentes de seguridad de las centrales nucleares de potencia requieren de un proceso de calificación, denominado calificación ambiental, que certifique que serán capaces de cumplir con las funciones de seguridad que tienen asignadas durante todo el tiempo de vida calificado y para cualquier condición de servicio, sea ésta normal o anormal. El proceso de calificación ambiental consiste en la aplicación de metodologías de ingeniería conjuntamente con la realización de ensayos ambientales, denominados ensayos de tipo. La validez del proceso de calificación ambiental solo puede asegurarse en la medida que cumpla con los requerimientos regulatorios nucleares nacionales y con un marco normativo técnico que sea sólido y consistente. Los ensayos de tipo deben poder simular las condiciones de servicio durante y después de los eventos base de diseño de la planta; éstas condiciones de servicio son las que surgen del modo de operación normal y durante y después de incidentes operacionales o accidentes. Se describe en este trabajo el conjunto de los ensayos de tipo que se deben realizar para poder certificar que los componentes de seguridad de una central nuclear de potencia se encuentran ambientalmente calificados, y sus diferencias con la calificación ambiental de componentes de seguridad de reactores experimentales. Palabras clave: Calificación ambiental; componentes de seguridad nuclear; ensayos ambientales/ensayos de tipo. * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. Viviana Ishida. Tel.: +54-(011)-4394-3344; fax: +54-(011)-4394-3543; e-mail: [email protected] 107 - Análisis de la integridad estructural en uniones soldadas de aceros estructurales con riesgo a la fisuración en frío en el metal de soldadura Francisco Cambiasso a, Juan C. Ríos a, Juan J. Balderrama a y Eduardo Asta a a Universidad Tecnológica Nacional-FRH, Paris532, Haedo (1706), Argentina RESUMEN La soldadura de aceros estructurales de alta resistencia plantea problemas vinculados con la susceptibilidad a la aparición del proceso asistido por hidrógeno que provoca las denominadas fisuras en frío. Particularmente este problema se pone de manifiesto en el metal de soldadura(MS) debido a la necesidad de utilizar aportes de alta resistencia que generan un incremento de elementos de aleación en la composición química del MS y consecuentemente una microestructura con un elevado porcentaje de zonas locales frágiles(LBZ). Atendiendo al problema en este trabajo se efectúa una evaluación de la tenacidad a la fractura utilizando ensayos de impacto Charpy-V y métodos indirectos de correlación, tanto para el metal de soldadura como la ZAC, correspondientes a la unión soldada de un acero estructural de alta resistencia con proceso FCAW. Esta evaluación permite realizar un análisis crítico de ingeniería (ECA) o análisis de integridad estructural para establecer el nivel de riesgo potencial de fractura frágil en este tipo de uniones, buscando un criterio que permita minimizar la utilización de precalentamiento en ZAC y MS a través de garantizar un nivel mínimo de tenacidad. Palabras clave: Fractura; Aceros Estructurales; Soldadura; Fisuración en Frío. * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. e-mail: [email protected] 57 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina 109 - Estudio de la emisión acústica producida por la falla de la adherencia de insertos metálicos en un panel de fibra de carbono Martín Gómez a-b-c, Aníbal Rodríguez a, Guido Ferrari b, Alfredo Hazarabedian a-c a Comisión Nacional de Energía Atómica , Av. G. Paz 1499 San Martín, Buenos Aires, B1650KNA, Argentina. b CENES - Dpto. Ing. Mecánica, Facultad Regional Delta, UTN, San Martín 1171, Buenos Aires, 2804, Argentina. c Instituto Sabato, Universidad Nacional de San Martín, Av. G. Paz 1499, San Martín, Buenos Aires, B1650KNA, Argentina . RESUMEN La capacidad para soportar carga es un factor crítico para la evaluación de la estabilidad estructural de insertos colocados en paneles de materiales compuestos tipo sándwich. En este trabajo se estudió la emisión acústica (EA) producida al aplicar un esfuerzo de corte a la zona de contacto adhesivo entre un inserto metálico y una placa de material compuesto hasta lograr la falla de la adherencia. Se realizó un ensayo mecánico en el cual el espécimen estaba constituido por un panel tipo sándwich reforzado con fibras de carbono sobre una estructura tipo panal de abejas de aluminio, al cual se le adhirieron dos insertos de forma cilíndrica, fabricados con una aleación de titanio. Los ensayos de corte se realizaron al traccionar un pasante colocado en cada inserto atravesando la placa. Durante todo el ensayo, se midió la EA en ocho canales, con cuatro sensores alrededor de cada inserto. También se registró la carga aplicada en función del tiempo y se confrontó con la EA. Se analizaron parámetros de la EA buscando aquellos más sensibles al daño en la adhesión del inserto al panel. Además, se estudió la localización de las zonas donde se produjo la mayor actividad de la EA y se correlacionó con el daño observado. Palabras clave: Emisión acústica, CFRP, panel reforzado, inserto metálico, falla de adherencia. * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. e-mail: [email protected] 118 - Optimización en el monitoreo de la condición del sistema primario del reactor de investigación RA-6: Tanque de decaimiento. Oscar García Peyrano 1 a *, Martín Garrett 2 a , Matías Marticorena 3 a, Danilo Babaglio 4 a, Roberto Koch 5 a, Julian Martinez 6 a, Juan Vignolo 7 a, Rodrigo Mayer 8 a a CNEA-CAB, Bustillo 9500, San Carlos de Bariloche 8400, Argentina RESUMEN Debido al aumento de potencia que se realizó en el reactor multipropósito RA-6, fueron adoptadas medidas de seguridad para el monitoreo y diagnóstico sobre la integridad estructural del tanque de decaimiento del circuito primario de refrigeración. El tanque de decaimiento es la única pieza que no pudo redimensionarse debido a la ubicación del mismo. Asegurar la condición de las soldaduras en las placas buffer es prioritario en materia de seguridad nuclear. La División de Vibraciones del Centro Atómico Bariloche, desarrolló una herramienta de cálculo numérico que trabaja en conjunto con señales adquiridas en tiempo real que permiten estimar la concentración de tensiones en lugares de difícil acceso con métodos de medición tradicional. Se presentan resultados obtenidos mediante la utilización de la herramienta utilizadas para el análisis de la integridad estructural del tanque de decaimiento - placas buffer- junto con un análisis de fatiga para estimar la vida remanente. Los datos son proporcionados por un sistema de Monitoreo y Diagnóstico de la condición On-Line implementados en el circuito primario de refrigeración. El objetivo de este trabajo es brindar un diagnóstico del estado mecánico del tanque de decaimiento, permitiendo detectar e identificar fallas en forma anticipada mejorando la seguridad de la instalación. Palabras clave: Integridad Estructural; Reactores Nucleares;detección de fallas/diagnóstico; Fatiga/vida remanente. * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. Tel.: +54-0294-444-5100; e-mail: [email protected] 58 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina 119 - Optimización en el monitoreo de la condición del sistema primario del reactor de investigación RA-6: Bomba primario. Oscar García Peyrano 1 a *, Danilo Babaglio 2 a, Martín Garrett 3 a, Matías Marticorena 4 a, Roberto Koch 5 a, Julian Martinez 6 a, Juan Vignolo 7 a, Rodrigo Mayer 8 a a CNEA-CAB, Bustillo 9500, San Carlos de Bariloche 8400, Argentina. RESUMEN Los reactores nucleares experimentales que no son utilizados con fines comerciales puros –reactores escuela - poseen la difícil tarea de justificar sistema que mejores el rendimiento mecánico y optimicen el mantenimiento de los mismos dado a la dificultad de recuperar la inversión de estos sistemas modernos. Sin embargo, el papel de la seguridad y la integridad física de las instalaciones es primordial dado el impacto socio-cultural y ambiental que representan. Un sistema de monitoreo y diagnóstico de la condición debe cumplir entonces las cualidades de ser confiable y económicamente viable. En este trabajo se presenta un Sistema de Monitoreo y Diagnóstico Mecánico Automático Online implementado en el circuito primario de refrigeración del Reactor RA-6, los resultados obtenidos permiten implementar tareas de mantenimiento optimizadas para minimizar el tiempo de parada de la máquina principal del circuito –bomba circuito primario- y anticipar fallas mecánicas. El sistema fue diseñado, instalado y puesto a punto por la División de Vibraciones del Centro Atómico Bariloche – CNEA-. Utiliza técnicas de procesamiento digital de señales –en el tiempo y espectro y correlaciones estadísticas- para realizar el monitoreo y diagnóstico de los siguientes estados del conjunto rotodinámico: desbalanceo, desalineamiento, estado de rodamientos y estado de rodete de bomba. Palabras clave: Monitoreo de la condición; Reactores nucleares; detección de fallas/diagnóstico mecánico. * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. Tel.: +54-0294-444-5100; e-mail: [email protected] 123 - Escaneo láser con luz estructurada. Aplicación a la inspección de componentes ferroviarios. Rodrigo Romero Rosero a , Guillermo Cosarinsky a *, Adrián Bonomi a y Fernanda Ruiz Gale a a Comisión Nacional de Energía Atómica (CNEA – IAMEND - UAENDE), Av. Gral, Paz 1499, San Martín, B1650KNA, Argentina RESUMEN Un escáner láser es un dispositivo empleado para obtener una representación digital tridimensional de un objeto. El método de escaneo presentado utiliza un láser con un elemento refractivo de manera de generar un plano de luz. La intersección de ese plano con el objeto escaneado contornea una sección del mismo. La imagen de esa curva se adquiere con una cámara digital; se registran y se procesan los datos mediante un programa desarrollado por los autores. Moviendo el plano láser respecto al objeto se obtienen distintas secciones de su superficie que se componen para conformar la representación 3D. El sistema de escaneo láser utiliza dos sensores para registrar partes que, de otro modo, quedarían escondidas al emplear un solo sensor. Se describe la calibración de los sensores para obtener un sistema único de referencia, así como también los algoritmos para corregir la distorsión geométrica y para extraer la línea láser que representa el perfil del objeto estudiado. Este trabajo presenta un sistema experimental de inspección de defectos geométricos para evaluar los principales componentes involucrados en la rodadura de trenes: rieles y ruedas. Este sistema podría ser adecuado para operación ya sea en taller o sobre las vías férreas. Palabras clave: Escaneo láser; representación 3D; defectos geométricos; componentes ferroviarios. * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. Tel.: +54-11-6772-7233; e-mail: [email protected] 59 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina 126 - Perfilómetro compacto basado en triangulación láser activa con luz estructurada. Nelson Luque a, Fernanda Ruiz Gale a y Elsa Hogert a a Comisión Nacional de Energía Atómica (CNEA – IAMEND - UAENDE), Av. Gral, Paz 1499, San Martín, B1650KNA, Argentina. RESUMEN Para muchas aplicaciones, en la Industria se observa una creciente demanda de nuevas y más precisas técnicas para caracterizar el estado superficial de componentes, logrando tener un conocimiento preciso de su acabado o de su textura. Dichas técnicas deben ser no destructivas ni invasivas, poseer alta sensibilidad y precisión y ser capaces de relevar el perfil de muestras en tiempo real. Cumpliendo con la mayoría de los requisitos antes mencionados la triangulación láser activa con luz estructurada es una de las técnicas más adecuadas ya que puede ser utilizado en cualquier tipo de superficie reflectora u opaca, independiente de su grado de dureza. El método a realizar es una asociación de la triangulación óptica, utilizando como fuente luminosa luz láser estructurada. El Laboratorio de Óptica y Láser de la CNEA (LOL) ha diseñado y montado un perfilómetro óptico compacto basado en la triangulación láser activa. Este perfilómetro permite relevar el perfil 3D de muestras con alturas comprendidas entre los 5μm y 200μm En este trabajo se muestra el nuevo microtopógrafo láser diseñado y montado en el LOL, sus alcances y limitaciones. Palabras clave: Perfilómetro compacto; Triangulación láser activa; luz estrcuturada; microtopógrafo láser. * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. Tel.: +54-11-6772-7401 e-mail: [email protected] 136 - Medición de espesores en cañerías de acero al carbono aisladas en servicio por medio de Radiografía Digital. Téc. Bruno Ramari * Ing. Jorge Amsler San Lorenzo 4941,Rosario, 2000, Argentia RESUMEN La medición de espesores de cañerías en servicio tiene la particularidad que en muchos casos se encuentran aisladas, con fluidos de procesos, presión y temperatura. Para una inspección de las mismas es necesario retirar la aislación térmica para tener acceso a su superficie y realizar una inspección visual o medición de espesores por ultrasonidos. En algunos casos puede inspeccionarse por radiografía convencional, pero su escasa latitud radiográfica exige el uso de técnicas de film múltiples u otras variantes para conseguir resultados relevantes. En el presente trabajo se consigue la inspección de cañerías aisladas y en servicio usando fuentes de Gammagrafía de Iridio 192 y equipos de Radiografía Digital con Image Plates de fósforo. La tecnología utilizada más sofisticados software de análisis permite la inspección y medición de espesores en forma confiable y precisa. Palabras clave: Radiografia digital, medición de espesore, inspección y ensayos no destructivos.Inspección en refinería. * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. Bruno Ramari. Tel.: +54-03414370475; e-mail: [email protected] 60 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina 138 - Desarrollo e implementación de un dispositivo de inspección ultrasónica para la medición del desgaste en tubos de calandria de la Central Nuclear Embalse Pablo Katchadjian a, Carlos Desimone a y Alejandro Garcia a Carlos Antonaccio b, Fernando Schroeter b, Héctor Molina b a Comisión Nacional de Energía Atómica, Av. del Libertador 8250, CABA (1429), Argentina b Nucleoeléctrica Argentina S.A., Arribeños 3619, CABA (1429), Argentina RESUMEN La Central Nuclear Embalse (CNE) se encuentra cerca del final de su vida útil y debido al tiempo de operación transcurrido se presenta el problema de deformación por creep acelerado de los tubos de presión (TP), lo que lleva a un posible contacto entre los tubos de calandria (TC), concéntricos a los TP, y algunos tubos de inyección de gadolinio (Liquid Injection Shutdown System - LISS), que pasan por debajo de los mismos. Con la determinación del desgaste del TC, se podría determinar la tasa de desgaste y de esa forma tomar medidas menos conservativas sobre la vida remanente del componente. Este trabajo presenta la puesta a punto de una técnica ultrasónica de medición de espesor remanente en los TC. Debido a que el único acceso es a través del interior del TP, es necesario atravesar tres interfaces para poder realizar esta medición, por lo que se hace indispensable emplear una técnica ultrasónica no convencional. Se describen las técnicas ultrasónicas estudiadas, se muestra el diseño e implementación de un dispositivo de inspección y se presentan los resultados de las mediciones llevadas a cabo en el Mock-up para la puesta a punto del sistema. Palabras clave: Ultrasonido, CANDU, Tubo de Calandria, Medición de desgaste. * Autor a quien dirigir correspondencia. Pablo Katchadjian. Tel.: +54-11-6772-7859; fax: +54-11-6772-7355; e-mail: [email protected] 61 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina SESIÓN: GESTIÓN DE ACTIVOS / SESSION: ASSET MANAGEMENT 08 - Just-on Time and Dynamic Maintenance for Turbine, Generator and Gearbox: A Case Study Basim Al-Najjar * a a Professor of Terotechnology, School of Engineering, Linnaeus University, CEO; E-maintenance Sweden AB ABSTRACT Profitable production demands continuously improved maintenance decision accuracy to reduce unplanned stoppages, prolong components/machines life length and maintain production continuity. When CM, e.g. vibration level or oil temperature, value exceeds a warning level, it demands a clear understanding of what happened and how it will develop to avoid failures. It demands also reliable information, e.g. probability of failure, residual life and when is the most profitable time for maintenance. Companies strive to reduce production cost through reducing non-value adding times, e.g. failures, for offering customers lower prices and generating additional competitive advantages. In this paper, a new tool (Prediction of Vibration and oil temperature, PreVib) for predicting the condition of a turbine, generator and gearbox is introduced, discussed and tested. The solution offers a unique opportunity to achieve just in time dynamic and cost-effective maintenance by selecting the most profitable time for maintenance. PreVib is tested in a power plant. The major results: Failures can appreciably be reduced thanks the high precision of prediction ( + 90%), i.e. a negligible difference from the real measurement: PreVib does not demand extensive or additional data, and not replace available maintenance systems. The major conclusion is that applying PreVib, it is possible to reduce failures appreciably, prolong life length of components/equipment and perform profitable maintenance. Keywords: Just in Time Maintenance; Dynamic and Cost-effective Maintenance; Prediction of Vibration Level; Assessment of Probability of Failure; Assessment of Residual Time; Profitable Maintenance Time; Maintenance Decision Accuracy. * Corresponding author. e-mail: [email protected] 09 - Optimal corrective maintenance of manufacturing series systems Zdzislaw H. Klim* a, Marek Balazinski b and Adam W. Skorek c a Bombardier Aerospace, 400, Côte-Vertu Road West, Montréal, H4S 1Y9, Canada b École Polytechnique de Montréal, 2900 boul. Édouard-Montpetit, Montréal, H3T 1J4, Canada c Université du Québec à Trois-Rivières, 3351, boul. des Forges, Trois-Rivières, G9A 5H7, Canada ABSTRACT The optimal maintenance strategy plays an important role in improving reliability and availability of a manufacturing system. In practice, preventive and corrective maintenance is applied to assure an acceptable level of technical system reliability. This paper is intended to provide an optimization procedure for the corrective maintenance of manufacturing series systems. Each failure incurs a cost to execute the corrective maintenance, including parts and labour cost, as well as the cost due to loss of production during down time. Therefore, the total cost of any failure is defined as the sum of all interrelated costs and is combined with the related level of system availability. The optimization problem is defined as the minimization of the total cost of the corrective maintenance associated with the chosen steady state availability for a given reliability of the system. Based on the developed model, the optimal availability of the system under study is derived. In order to illustrate the usefulness of the theoretical results, a case study of manufacturing series system is performed. The developed model might be very useful in an optimal planning of a corrective maintenance policy for a manufacturing series system and result in the system reliability enhancement as well as in decreasing the total cost of corrective maintenance. Keywords: Corrective maintenance, Availability, Optimization, Manufacturing systems * Corresponding author. Zdzislaw H. Klim, Tel.: +1-514-855-5001; e-mail: [email protected] 22 - Managing the value of maintenance comprehensively in a business network context 62 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina Salla Marttonen a *, Maaren Ali-Marttila a, Sanna Pekkola b, Minna Saunila b, Juhani Ukkob, Tero Rantala b, Olli Pekkarinen a, Antti Ylä-Kujala a, Tiina Sinkkonen a and Timo Kärri a a School of Business and Management, Lappeenranta University of Technology, P.O. Box 20, 53851 Lappeenranta, Finland b LUT Lahti, School of Business and Management, Lappeenranta University of Technology, Saimaankatu 11, 15140 Lahti, Finland ABSTRACT Business environments have changed during the last decades, posing new kind of challenges and yet offering new possibilities for industrial maintenance and asset management. As a result there are novel decision-making needs in both strategic and operational maintenance management, calling for identifying, modelling and managing the value of maintenance in networked business contexts. This paper contributes to maximizing the total value of maintenance by describing a range of maintenance management tools constructed in collaboration with case networks from mining and energy industries. The paper results in a framework for managing the value of maintenance. The framework can be applied in comprehensive maintenance management decision making ranging from operative issues to strategic calls in modern network contexts. In addition, the created value management tools are aligned with existing maintenance decision-making tools, the perspective of which is often more technical. Previous research has mostly discussed individual management tools used by single companies. In this paper we argue that due to its business context and multidisciplinary nature, industrial maintenance and asset management would benefit from integrating the use of different management tools in various decision-making situations and developing maintenance management together with other companies in the network, e.g. service providers and equipment manufacturers. Keywords: Maintenance management; Value; Decision-making tools; Maintenance services; Framework; Strategic maintenance; Operational maintenance; Business network * Corresponding author. Tel.: +358-50-322-5374; e-mail: [email protected] 96 - Brake tests to evaluate the human behaviour at different brake pedal characteristics Hermann Retzer a-b *, John Stephenson b, Rakesh Mishra b, Andrew Ball b and Karsten Schmidt c a Continental, Division Chassis & Safety, Frankfurt am Main, D-60488, Germany b University of Huddersfield, Queensgate, Huddersfield, HD1 3DH, UK c Frankfurt University of Applied Sciences, Frankfurt am Main, D-60318, Germany ABSTRACT Brake-by-wire represents the replacement of traditional brake components such as pumps, hoses, fluids, brake boosters, and tandem master cylinders by electronic sensors and actuators. The different design of these brake concepts poses new challenges for the automotive industry with regard to availability and fallback levels in comparison to standard conventional brake systems. In order to evaluate this, the behaviour of 67 participants on different brake pedal characteristics was investigated during a static vehicle braking simulator test. Participants were assessed on their response to the braking modes: normal brake function, booster breakdown and brake circuit failure. The interpretation of these results and an extended driver warning approach fed into a study using a field test. First results suggest that a coordinated driver warning and information concept adapted to the brake failure is helpful in bringing the test vehicle to a safe stop. Keywords: Brake failure, Fallback level, Human Machine Interface (HMI), Field test. * Corresponding author. Hermann Retzer. Tel.: +49-69-7603-5922; e-mail: [email protected] 114 - Service-oriented approach of an eMaintenance Cloud Ravdeep Kour a *, Phillip Tretten a and Ramin Karim a a Division of Operation, Maintenance Engineering, Luleå University of Technology, Luleå, SE-971 87, Sweden ABSTRACT Cloud computing is used by both industry and academia in the understanding of maintenance needs to assist in main63 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina tenance decisions. Decision support based upon the system condition from data and computing within and without the network is needed for efficient decision making for maintenance actions. The aim of this paper is to show the options necessary to develop a maintenance cloud, provide a system wide definition of how a cloud network, and validate the proposed the definitions in a test of the cloud structure in an industrial project. The results were the design and development of a cloud based eMaintenance solution based on service-oriented multi-layer approach, which focused on predictive maintenance, complementing the enterprise resource planning services. The eMaintenance cloud focuses on overall system definition, development and integration. Future work needs to include improved bandwidth, improved and more efficient data processing at the sensor and machine level. Keywords: eMaintenance,cloud computing, iMain, SOA,web services. * Corresponding author. e-mail: [email protected] 116 - Multivariate reliability assessment study for support ring of reciprocating compressor based on multidimensional information Bo Ma a *, Zhinong Jiang a a Diagnosis and Self-Recovery Engineering Research Center, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029, P. R. China. ABSTRACT Support ring is one of the indispensable parts and main wear parts of reciprocating compressor, and its state plays a significant role in reliability and utilization rate of the equipment. To identify the wear condition of support ring effectively and to reduce maintenance uncertainty, a multivariate reliability assessment model for support ring based on multidimensional information is proposed to ensure that the equipment can operate in safety condition for a long period. First, sensitive features that can be the reflections of operating condition of support ring are optimized based on distance evaluation technique. Second, multiple response covariance function is constructed. Third, a reliability assessment model for support ring based on Proportional Covariance Model (PCM) is established by combining the historical failure data with operating condition information of equipment. This method is applied in an engineering case and the result shows that it can realize reliability assessment of equipment accurately. Keywords: Reliability assessment; Multivariate; Support ring; Proportional Covariance Model; Reciprocating compressor * Corresponding author. e-mail: [email protected] 124 - Requalification of offshore assets Gudmestad, Ove Tobias a a University of Stavanger, 4036 Ullandhaug, Norway. ABSTRACT Oil and gas facilities are designed for a commercial lifetime of 20 to 30 years. For an extension of the production period, there will be a requirement for requalification of the facilities. After such long production period, the operator should appreciate the opportunity to ensure that the facilities are fit for the extended lifetime. Of particular importance for the requalification is the technical conditions of the facilities and inspection will be carried out to ensure that the maintenance is sufficient and that the remaining fatigue life is adequate. During the production period, however, several changes in regulatory requirements might have taken place and new information about the physical environmental conditions may be available. This paper will discuss the requirements for the requalification and how new or updated information should be handled. The goal of the requalification process is obviously to ensure safety during the extended lifetime. New information may cause considerable concern, like, for example, worsening of climatological conditions. The paper will suggest that data collection programs, wave modelling and wave tank testing could take place to ensure the continued integrity of the facilities. A case example related to requalification of a North Sea gravity platform will be presented. Keywords: Offshore Facilities Asset Management; Requalification of facilities; Extended lifetime. * Corresponding author. e-mail: [email protected] 64 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina SESIÓN: ANÁLISIS DE PROCESO / SESSION: PROCESS ANALYSIS 23 - A novel transformation of non-stationary signals to periodic signals. Part 1 theoretical foundation Adam Jablonski a * , Tomasz Barszcz a, and Jacek Urbanek a a AGH University of Science and Technology, 30 Mickiewicza Av. 30-059 Krakow ABSTRACT From a mathematical definition, a real vibration signal is not only stochastic but also non-stationary. However, a huge portion of analysis techniques of real signals assumes a sufficient degree of stationarity or sufficient degree of the presence of expected deterministic components for the purpose of, for instance, frequency analysis. On the other hand, if non-stationary processes are of interest (e.g. critical speed location), adequate analysis techniques also exist. The current paper shows updated aspects of a novel technique addressing yet another scenario, i.e. when it is desired to analyse signals as if they were periodic and stationary, while originally they are not. This is for instance a major problem in (almost always frequency-domain-oriented) condition monitoring systems of machinery working in highly varying operational conditions. In this part, a mathematical background of the transformation of vibration signals is shown stepby-step with additional discussion about generalized angular-temporal class of signals. Keywords: Non-stationary signal analysis, generalized anglular-temporal signals, signal modelling. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +48 509-805-483; fax:+48 12 634 3505 ; e-mail: [email protected] 24 - A novel transformation of non-stationary signals to periodic signals. Part 2 application to rotary machinery diagnostic Tomasz Barszcz a, Adam Jablonski a *, and Jacek Urbanek a a AGH University of Science and Technology, 30 Mickiewicza Av. 30-059 Krakow ABSTRACT The first part of the paper has illustrated a mathematical background of the transformation, which enables analysis of non-stationary signals containing phase-locked components as if they were periodic and stationary, while originally they were not. In order to enable such transformation, a recently introduced class of signals, namely generalized angular-temporal signal has been used. In this part, it is shown that such transformation opens new possibilities for analysis of non-stationary signals recorded form rotary machinery working under highly fluctuating operational parameters, where virtually any phase-locked signal component is modulated by, at minimum, speed and load. The paper illustrates implementation of the transformations for signal separation and spectral analysis, not available before for the purpose of fault detection. Keywords: Non-stationary signal analysis, signal separation, machine diagnostics. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +48 509-805-483; fax:+48 12 634 3505; e-mail: [email protected] 65 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina 52 - Numerical study of Nonlinear S0 mode Lamb waves for the detection of material nonlinearity Xiang Wan a-c , Guang-hua Xu a-b * , Qing Zhang a and Peter-W Tse c a School of Mechanical Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China b State Key Laboratory for Manufacturing System Engineering, School of Mechanical Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China c Department of Systems Engineering and Engineering Management, City University of Hong Kong, Tat Chee Avenue, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China ABSTRACT Nonlinear Lamb wave technique has been widely used in evaluating material nonlinearity, assessing structural degradation and detecting micro damages in thin plate-like structures. Theoretical and experimental studies on nonlinear Lamb waves have demonstrated that only specific mode pairs that satisfy phase velocity matching and non-zero power flux conditions exhibit cumulative second harmonic generation. However, there are some limitations using nonlinear Lamb wave technique based on phase velocity matching. In order to overcome these limitations, nonlinear S0 mode Lamb waves at low frequencies based on phase velocity approximate matching is proposed. The proposed method is used to detect material nonlinearity. The numerical results using our proposed method is in accordance with the results using the phase velocity matching method. And these results have proven that our proposed method is feasible and effective. Keywords: Nonlinear Lamb waves; Phase velocity approximate matching; material nonlinearity. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +86-029-8266-3707; fax: 86-029-8266-4257; e-mail: [email protected] 81 - A fault diagnosis method for electro-mechanical and hydraulic integrated system via graphic recognition Zhengkai Zhang a, Yuan Shi a, Lichen Gu a, Xianghui Cao c a School of Mechanical & Electrical Engineering, Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, 710055, Xi’an City, PR China b China Coal Xi’an Design Engineering Co., Ltd, 710054, Xi’an City, PR China ABSTRACT Fault diagnosis of electro-mechanical and hydraulic integrated system is very important in modern industry. In this paper, a automatic fault diagnosis method which based on chain code and neural network is proposed. For this approach, firstly, amplitude, phase of three phase current and voltage obtained from a AC motor driving hydraulic system are synthesized into a Lissajous figure for automatic fault diagnosis. Second, a chain code are used to represent the feature of the Lissajous figure. Then, the feature vectors are input to neural network to identify various kinds of operating condition of AC motor driving hydraulic system. The experimental results obtained from a hydraulic testing platform show that, this method can identify the shaft orbit automatically and achieves satisfactory accuracy. Keywords: Chain code; Lissajous figure; fault diagnosis. * Corresponding author. e-mail: [email protected] 66 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina 95 - Compressive sensing: a new insight to signal processing for condition monitoring and fault diagnosis Gang Tang a, Ganggang Luo a, Yanliang Ke a, Qin Yang a and Huaqing Wang a * a School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Chaoyang District North Third Ring Road 15, Beijing 100029, China. ABSTRACT As the developing of rotary machinery condition monitoring, how to balance the big data acquisition and in-time monitoring efficiency has become an important issue in industrial fields. Due to the traditional Shannon sampling principle, it seems impossible to largely reduce the data amount while preserving useful information. A newly developed theory named compressive sensing provides a new insight to condition monitoring and fault diagnosis. It states that a signal can also be perfectly recovered from under-sampled data. Inspired by it, this paper proposed a strategy to largely reduce the data collection and to detect faults of rotary machinery from only a few signal samples. It can deal with big data and incomplete small samples of condition monitoring simultaneously without completely reconstruction. This will help to greatly reduce the monitoring data while guaranteeing a high accuracy of fault detection. A case study about a roller bearing fault detection illustrates the effectiveness of the present strategy. Keywords: Compressive sensing; signal processing; condition monitoring; fault diagnosis. * Corresponding author. e-mail: [email protected] 104 - An improved Locality Preserving Projection method for fault diagnosis Lingyang Li a, Xintao Xu a, Xiao Yang a and Huaqing Wang a * a College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, No.15 in East Road of North Third Ring, Chaoyang District, Beijing, 100029, China. ABSTRACT Aiming at the shortcoming of the traditional Locality Preserving Projection algorithm that it didn’t use the sample class information effectively, a novel method for fault diagnosis based on an improved Locality Preserving Projection was proposed. By introducing the class information when calculating the distances between sample points, the proposed method increased the distances between different classes of samples, thus improving the cluster situation. In addition, the method to determine the best value of k which represented the number of the nearest neighbors was given. As an example, the proposed method was used in the dimension reduction for the time domain characteristic vector of the rolling bearing signal. Then the classification for the characteristic vector after dimension reduction was performed, and four states of rolling bearings were distinguished successfully. The experiment shows that as a supervised dimension reduction method, the proposed method performs better than the traditional one. Keywords: Locality Preserving Projection; class information; dimension reduction; fault diagnosis. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +86-138-0102-3830; fax: +86-010-6441-6122; e-mail: [email protected], [email protected] 67 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina 137 - Requalification of offshore assets Faris Elasha a * and David Mba s b a Faculty of Engineering and Computing, Coventry University, Priory Street, Coventry, CV1 5FB,UK b School of Engineering, London South Bank University, London, SE1 0AA, UK ABSTRACT Operation and maintenance (O&M) decisions for tidal turbines contributes significantly to the cost of tidal energy production. These decisions generally depend on many factors such as machine health, repair costs, weather conditions, etc. Premature failures in gearboxes result in a significant cost increase due to unplanned maintenance and long downtime. Such gearbox failures have plagued the wind turbine industry for decades despite reasonable adherence to design practices. The tidal turbine gearbox will experience higher torque, thrust and transient events. This paper presents a life assessment methodology for tidal turbine gearboxes which was developed with synthetic data generated using a blade element momentum theory (BEMT) model. The latter has been used extensively for performance and load modelling of tidal turbine. Keywords: Condition monitoring, prognostic model, tidal turbines gerabox. * Corresponding author. Faris Elasha, Tel.: +44-7428141801; e-mail:[email protected] 68 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina SESIÓN: RODAMIENTOS / SESSION: BEARINGS 29 - Ship-borne Satellite Antenna Bearing Fault Diagnosis using Enhanced Empirical Wavelet Transform via Data-driven Adaptive Fourier Spectrum Segment Jun Pan a, Yanyang Zi a, Jinglong Chen a *, and Shuilong Heb c a State Key Laboratory for Manufacturing and Systems Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China b School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Guilin University of Electronic Technology, Guilin 541004, China ABSTRACT An unexpected bearing fault of the ship-borne satellite antenna will result in unacceptable downtime of the system as well as failure of communication task. However, bearing fault diagnosis using vibration signals still is a challenging task because of the system complexity and the multi-modulation feature in the vibration signals. As a novel signal processing method, Empirical Wavelet Transform (EWT) is used to extract inherent modulation information by decomposing signal into mono-components under an orthogonal basis. But the pre-defined segment way of Fourier spectrum without dependence on analyzed signals would result in inaccurate mono-component decomposition. In this paper, the enhanced EWT (EEWT) method with data-driven adaptive Fourier spectrum segment is proposed for ship-borne satellite antenna bearing fault diagnosis. First, inner product is calculated between the Fourier spectrum of analyzed signal and Gaussian function for scale representation. Then, adaptive spectrum segment is achieved by detecting local minima of the scale representation. Finally, empirical modes can be obtained by adaptively merging mono-components based on their envelope spectrum similarity. The adaptively extracted empirical modes are analyzed for bearing fault diagnosis. The application case is used to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method and the results show its outstanding performance. Keywords: Bearing fault diagnosis; empirical wavelet transform; data-driven adaptive Fourier spectrum segment; ship-borne satellite antenna. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +86 29 82667963; fax: +86 29 82663689; e-mail: [email protected] 39 - Bearing fault diagnosis based on discriminative K-SVD for dictionary learning H.D.Yuan *, J Chen and G.M. Dong State Key Laboratory of Mechanical System and Vibration, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, P R China ABSTRACT Sparse representation is applied to classify different kinds of rolling bearing fault.In a sparse-representation-based pattern recognition scheme, the desired dictionary should have not only representational power but also good classification ability. The method of discriminative K-SVD(D-KSVD) is based on the K-SVD algorithm which has been proved effective.Discriminative K-SVD incorporates classification error into the objective function and thus considers the representational power of the dictionary and the performance of a linear classifier simultaneously by the same optimization program.In this paper discriminative K-SVD is used for bearing fault diagnosis through the bearing vibration signals.The experimental rolling bearing has four states,including normal, inner race fault, outer race fault and ball fault. Firstly,for the training set using the D-KSVD algorithm to find the dictionary and solve the classifier.Then for the test set,the classification result can be acquired by combining the trained dictionary and classifier.The result shows that the proposed method is effective for the identification of different bearing fault. Keywords: Sparse representation; Discriminative K-SVD; Dictionary learning;Fault diagnosis; Rolling bearing. * Corresponding author. e-mail: [email protected] 69 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina 41 - Dynamic modeling and vibration simulation for double-row tapered roller bearings with localized surface defects Linkai Niu a , Hongrui Cao a *, and Zhengjia He a a State Key Laboratory for Manufacturing Systems Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, P. R. China ABSTRACT A dynamic model without static constraints is provided for double-row tapered roller bearings (DRTRBs) with localized surface defects. In this model, each bearing component has six degrees of freedom (DOFs) to completely describe its dynamic characteristics. Four types of interactions, i.e. roller-cup, roller-cone, roller-flange, and roller-cage pocket are considered in this model. Relative slip velocities, friction effects and localized surface defects are also considered. The obtained dynamic equations are solved numerically using the fourth order Runge-Kutta-Fehlberg scheme with step-changing criterion. Vibration responses of the DRTRB with localized surface defects are analyzed in both time domain and frequency domain. Effects of defect sizes, defect types, and operating conditions on dynamic characteristics of the bearing are studied parametrically. Numerical results obtained from the current simulation are validated with respect to prior researchers. Keywords: Tapered roller bearing; multiple-row bearing; localized defect; dynamic modeling. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +86-29-82663689; fax: +86-29-82663689; e-mail: [email protected] 44 - Condition monitoring of bearings in parallel operating belt dive systems Dustin Helm a, Alexander Rose a, and Markus Timusk a * a Laurentian University, 935 Ramsey Lake Road, Sudbury P3E2C6, Canada ABSTRACT Condition monitoring of non-stationary machines is an important area of research as current techniques often have difficulty detecting faults with a high degree of accuracy in real world non-stationary conditions. This work will present a method for condition monitoring of parallel machinery (a class of machinery with two or more identical subsystems that simultaneously experience identical duty cycles) operating under non-stationary conditions. The purposed method will detect faults in the machinery by comparing the vibration signals from either subsystem and then classifying them as either faulted or healthy based on signal residuals. Tests were performed on rolling element bearings mounted in idler pulleys in two identical belt drive systems operating on the same duty cycle and the faults detected include outer race, inner race and ball faults of varying degrees of severity. Preliminary results show that this is a promising approach compared to other techniques for condition monitoring of non-stationary machinery. Keywords: Condition monetoring; bearings; non-stationary; fault detection * Corresponding author. Markus Timusk. Tel.: +1-705-675-1151 ex.2243; Fax: 1-705-675-4862 e-mail: [email protected] 70 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina 94 - A classification method via sparse representation for rolling bearing fault recognition Huaqing Wang a, Yanliang Ke a, Ganggang Luo a, Qin Yang a and Gang Tang a * a School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Chaoyang District North Third Ring Road 15, Beijing 100029, China ABSTRACT As a critical equipment of machinery equipment, a rolling bearing often suffers from probably failures, which need to be detected in time to guarantee a running safety of the whole system. The objective of bearing fault diagnosis is to effectively extract fault characteristic frequencies. However, in practice, due to the limit of Shannon sampling principle, large amount of vibration signals and a priori knowledge about the failures are often required. To solve these problems, inspired by a newly developed compressive sensing theory, the present paper proposes a fault diagnosis strategy for rolling bearings through sparse representation. Here a vibration signal is sparsely represented in a learning over-complete dictionary, and the original signal characteristics are preserved by random mapping while dimensionality reducing, finally the category classification of faulty signals are determined through sparsity promoting and optimization strategy. Simulation and experimental results validate the effectiveness of the proposed method for diagnosis of rolling bearings’ faults. Keywords: Rolling bearing; fault recognition; classification; sparse representation. * Corresponding author. e-mail: [email protected] 106 - Fault prognosis for bearings based on morphological fractal dimension and ELM Fang Qi a, Xintao Xu a and Huaqing Wang a * a School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering,Beijing University of Chemical Technology,Chaoyang District North Third Ring Road 15, Beijing 100029, China ABSTRACT The great loss of life and wealth in chemical factory accident brings the need of a proper and effective method of fault prognosis for rolling bearing in the rotary machine. This paper is intended to provide a new view of the fault prognosis for bearings, with a special focus on morphological fractal dimension and extreme learning machine(ELM). The overall prognosis process includes acquisition and pre-processing of data, morphological fractal dimension calculation, ELM prognosis modelling and the result of validation. The morphological fractal dimension is considered as the characteristic value of the fault prognosis, and reflects the process of performance degradation for bearings. The ELM model is introduced and used in the prognosis. The accuracy and stability of prognosis in validation through the whole life data for bearings is also provided. Keywords: Rolling Bearing; Fault prognosis; morphological fractal dimension; ELM. * Corresponding author. Huaqing Wang e-mail: [email protected] [email protected] 71 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina 131 - A robust fault detection method of rolling bearings using modulation signal bispectrum analysis Xiange Tian a, Fengshou Gu a * and Andrew D. Ball a a Centre for Efficiency and Performance Engineering, University of Huddersfield, Queensgate, Huddersfield, HD1 3DH, UK ABSTRACT Envelope analysis is a widely used method for bearing fault detection. To obtain high detection accuracy, it is critical to select an optimal narrowband for envelope demodulation. Kurtogram is an effective method for optimal narrowband selection. However, fast kurtogram is not sufficiently robust because it is very sensitive to random noise and large aperiodic impulses which normally exist in practical application. To achieve the purpose of both denoising and frequency band optimization, this paper proposes a method using modulation signal bispectrum analysis (MSB) for bearing fault detection. Because of the noise elimination and periodic nonlinear content enhancement, MSB allows effective suppression of both stationary random noise and discrete aperiodic impulses. In the meantime, the high magnitudes of MSB can be used to provide optimal frequency bands for fault detection. Both performance evaluation results using simulated data and experimental data show that the proposed method produces more effective and robust detection results for different types of bearing faults, which outperforms the widely used envelope analysis combined with fast kurtogram. Keywords: Modulation signal bispectrum, bearing fault detection, envelope analysis, fast kurtogram. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +44-1484-473548; fax: +44-1484- 473075; e-mail: [email protected] 72 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina SESIÓN COMERCIAL / COMMERCIAL SESSION 47 - Detecting stress corrosion cracking with eddy current array technology Emilie Peloquin Houston,Texas, 77034, USA ABSTRACT The inspection world is always striving for efficiency without compromising accuracy. This paper examines the replacement of Liquid Penetrant and Magnetic Particle testing - two methods that are highly time consuming and limited in accuracy - with Eddy Current technology. Eddy Current has been long known in the aerospace industry for its accuracy in crack inspection of aluminum. Using the same technology, it is now possible to multiplex the signals to create an array of coils (Eddy Current Array). ECA not only provides accurate detection, but permits the creation of a C-Scan image of the returned signal – building a visual reference that is easy to interpret, as well as a means to evaluate depth of the indications. This presentation will discuss the multiple advantages of using Eddy Current Array over other conventional methods and will demonstrate examples of previous inspections for comparison. Keywords: Stress Corrosion Cracking; Eddy Current Array; Magnetic Particle and Liquid Penetrant replacement. 73 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE NOTAS / NOTES 74 Buenos Aires, Argentina COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina NOTAS / NOTES 75 COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE NOTAS / NOTES 76 Buenos Aires, Argentina COMADEM 2015 + X CORENDE Buenos Aires, Argentina NOTAS / NOTES 77 Auspicio Platino / Platinum Sponsorship Auspicio Oro / Gold Sponsorship Auspicio Plata / Silver Sponsorship Auspicio Bronce / Bronze sponsorship Asociación Argentina de Ensayos No Destructivos y Estructurales Avenida General Paz 1499 (1650) San Martín, Buenos Aires Argentina Tel: +54 11 6772 7429 Fax: +54 11 6772 7426 Web: www.aaende.org.ar E-mail: [email protected] JPS Argentina Carlos Pellegrini 763 (C1009ABO) Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires Argentina Tel: +54 11 5219 4861 líneas rotativas Web: www.jpsargentina.com E-mail: [email protected]
© Copyright 2026