monitoreo de la coagulación. - Grupo Mexicano para el Estudio de
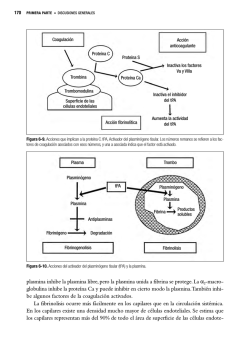
Dr. Alejandro Díaz Carrillo Medicina del Enfermo en Estado Crítico Medicina de Urgencias Terapia Intensiva Fundación Clínica Médica Sur Grupo Mexicano para el Estudio de la Medicina Intensiva MONITOREO DE LA COAGULACIÓN. COAGULACIÓN • Proceso mediante el cual la sangre pasa de un estado líquido al de un gel elástico. • Es el resultado de la interacción de los elemento solubles y celulares de la sangre completa y el endotelio. Furie B, Furie BC. Mechanisms of thrombus formation.N England Med 2008; 359:938-949 MONITOREO DE LA COAGULACIÓN MODELO DE LA “CASCADA”: 60´S Flores-Rivera O, Meza-Márquez JM, Nava-López JA. Fisiología de la coagulación. Revista Mexicana de Anestesiología 2014; 37:5582-5586 MONITOREO DE LA COAGULACIÓN. FALLAS DEL MODELO CASCADA… • No explica la coagulación in vivo. • Es un sistema integrado, dos vías interrelacionadas. • Los procesos moleculares ocurren en las superficies de la células. • No explica algunos aspectos fisiopatológicos. Furie B, Furie BC. Mechanisms of thrombus formation.N England Med 2008; 359:938-949 MONITOREO DE LA COAGULACIÓN. MODELO CELULAR MONITOREO DE LA COAGULACIÓN. MODELO CELULAR Flores-Rivera O, Meza-Márquez JM, Nava-López JA. Fisiología de la coagulación. Revista Mexicana de Anestesiología 2014; 37:5582-5586 MONITOREO DE LA COAGULACIÓN. Flores-Rivera O, Meza-Márquez JM, Nava-López JA. Fisiología de la coagulación. Revista Mexicana de Anestesiología 2014; 37:5582-5586 MONITOREO DE LA COAGULACIÓN. Furie B, Furie BC. Mechanisms of thrombus formation.N England Med 2008; 359:938-949 MONITOREO DE LA COAGULACIÓN. Johansson P. Coagulation monitoring of the bleeding traumatized patient. Curr Opin Anesthesiol. 2012: 25:235–241 MONITOREO DE LA COAGULACIÓN. Johansson P. Coagulation monitoring of the bleeding traumatized patient. Curr Opin Anesthesiol. 2012: 25:235–241 MONITOREO DE LA COAGULACIÓN. PRUEBAS ESTÁNDARES • • • • • • • TP TTPa TT Fibrinógeno. Test de fibrinólisis. Recuento de plaquetas. Tiempo de sangrado. PRUEBAS VISCOELÁSTICAS. • Tromboelasografía. • Troboelastometría. Davenport R, Khan S. Management of major trauma haemorrhage: treatment priorities and controversies. British Journal of Haematology. 2011; 155: 537–548 MONITOREO DE LA COAGULACIÓN. MONITOREO DE LA COAGULACIÓN. PRUEBAS ESTÁNDARES. • Evalúa solo los primeros 60 segundos de la formación del coagulo. • Solo miden la coagulación plasmática y no la de la sangre total. • No valoran la calidad del trabajo plaquetario. • No evalúan los sistemas fibrinolíticos. • El TP, TTPa no evalúan la fibrinólisis. • TP, TTPa, INR no son predictores de sangrado. • Se realizan a 37º centígrados y con pH de 7.5 De Lange NM, Lance MD, De Groot R, Beckers EAM, Henskens YM, Scheepers HCJ. Obstetric hemorrhage and coagulation: an update. Thromboelastography, thromboelastometry, and conventional coagulation tests in the diagnosis and prediction of postpartum hemorrhage. Obstetrical and Gynecological Survey. 2012; 67: 426–435. MONITOREO DE LA COAGULACIÓN. PRUEBAS DE VISCOELÁSTICAS. • Medición dinámica y global. • Integra las diferentes fases de la coagulación. • Se realiza a temperatura del paciente (la hipotermia esta considerada). • Fácil de usar e interpretar. • Resultados en pocos minutos. • Guía para el uso de hemoderivados. Collis RE, Collins EW. Haemostatic management of obstetric haemorrhage. Anaesthesia. 2015; 70:78–86 Besser MW, Ortmann E, Klein AA. Haemostatic management of cardiac surgical haemorrhage. Anaesthesia. 2015; 70 :87–95 MONITOREO DE LA COAGULACIÓN. VISCOELÁSTICAS ESTÁNDARES. Valoración rápida de la coagulación. Valoración tardía de la Aplicable a pie de cama. coagulación. Diagnóstico rápido. Dependiente de laboratorio. Permite instauración de tratamiento Diagnóstico tardío. precoz. Retraso del inicio del tratamiento. De Lange NM, Lance MD, De Groot R, Beckers EAM, Henskens YM, Scheepers HCJ. Obstetric hemorrhage and coagulation: an update. Thromboelastography, thromboelastometry, and conventional coagulation tests in the diagnosis and prediction of postpartum hemorrhage. Obstetrical and Gynecological Survey. 2012; 67: 426–435. MONITOREO DE LA COAGULACIÓN. TROMBOELASTOGRAFÍA. Inicio del coágulo Ángulo Alfa R Estabilidad del coágulo Fuerza del coágulo K Coagulación MA LY30 Fibrinólisis Thakur M, Ahmed AB. A review of Thromboelastography. Int J Periop Ultrasound Appl Technol. 2012; 1:25-29. MONITOREO DE LA COAGULACIÓN. TROMBOELASTOGRAFÍA. Normal Prolongada (anticoagulación, déficit de factores) Amplitud máxima disminuida (trombocitopenia, antiagregantes plaquetarios) Fibrinólisis. Hipercoagulabilidad. Coagulación Intravascular Diseminada. (etapa temprana) Coagulación Intravascular Diseminada. (etapa tardía) Thakur M, Ahmed AB. A review of Thromboelastography. Int J Periop Ultrasound Appl Technol. 2012; 1:25-29. TROMBOELASTOMETRÍA. MONITOREO DE LA COAGULACIÓN. Dekker SE, Viersen VA, Duvekot A, de Jong M, Van Den Bron CE, Van de Ven PH, et al . Lysis onset time as diagnostic rotational thromboelastometry parameter for fast detection of hyperfibrinolysis. Anesthesiology 2014; 121: 89–97. MONITOREO DE LA COAGULACIÓN. TROMBOELASTOMETRÍA Dekker SE, Viersen VA, Duvekot A, de Jong M, Van Den Bron CE, Van de Ven PH, et al . Lysis onset time as diagnostic rotational thromboelastometry parameter for fast detection of hyperfibrinolysis. Anesthesiology 2014; 121: 89–97. MONITOREO DE LA COAGULACIÓN. Dekker SE, Viersen VA, Duvekot A, de Jong M, Van Den Bron CE, Van de Ven PH, et al . Lysis onset time as diagnostic rotational thromboelastometry parameter for fast detection of hyperfibrinolysis. Anesthesiology 2014; 121: 89–97. MONITOREO DE LA COAGULACIÓN. Dekker SE, Viersen VA, Duvekot A, de Jong M, Van Den Bron CE, Van de Ven PH, et al . Lysis onset time as diagnostic rotational thromboelastometry parameter for fast detection of hyperfibrinolysis. Anesthesiology 2014; 121: 89–97. MONITOREO DE LA COAGULACIÓN. Dekker SE, Viersen VA, Duvekot A, de Jong M, Van Den Bron CE, Van de Ven PH, et al . Lysis onset time as diagnostic rotational thromboelastometry parameter for fast detection of hyperfibrinolysis. Anesthesiology 2014; 121: 89–97. MONITOREO DE LA COAGULACIÓN. TROMBOELASTOMETRÍA • • • • Test global y diferencial. La muestra no precisa preparación. Es fácil de usar en áreas críticas. Resultado en menos de 15 minutos. Dekker SE, Viersen VA, Duvekot A, de Jong M, Van Den Bron CE, Van de Ven PH, et al . Lysis onset time as diagnostic rotational thromboelastometry parameter for fast detection of hyperfibrinolysis. Anesthesiology 2014; 121: 89–97. MONITOREO DE LA COAGULACIÓN. TROMBOELASTOMETRÍA Permite identificar de forma rápida: • • • • • • • Déficit de factores. Déficit de fibrinógeno. Déficit de función plaquetaria. Fibrinólisis. Presencia de heparina. Funcionalidad del fibrinógeno y las plaquetas. Efecto positivo de la aprotinina sobre las plaquetas. Dekker SE, Viersen VA, Duvekot A, de Jong M, Van Den Bron CE, Van de Ven PH, et al . Lysis onset time as diagnostic rotational thromboelastometry parameter for fast detection of hyperfibrinolysis. Anesthesiology 2014; 121: 89–97. CONCLUSIONES. • El monitoreo de la coagulación debe ser dinámico y de forma global. • Las pruebas estándar solo evalúan la coagulación plasmática in vitro por lo que deben utilizarse con reserva. • Las pruebas de viscoelasticidad (TEG y ROTEM) miden la coagulación de forma completa y en forma dinámica. • El ROTEM además nos proporciona un test diferencial lo que permitirá una terapia orientada.
© Copyright 2026