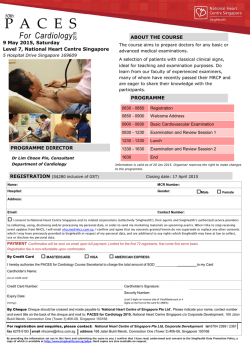
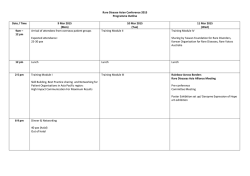
conference program
February 2-3, 2015 ICIT 2015 2015 International Conference on Information Technology ICIMA 2015 2015 3rd International Conference on Intelligent Mechatronics and Automation ICKE 2015 2015 International Conference on Knowledge Engineering ICOIA 2015 2015 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Agriculture ICIIN 2015 2015 4th International Conference on Intelligent Information Networks QUALITY HOTEL MARLOW www.qualityhotelmarlow.com.sg Add: 201 Balestier Road Singapore 329926 Email: [email protected]| Tel: (65)6355 9988 | Fax: (65) 6255 0998 Programme 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES WELCOME LETTER 3 OVERVIEW 4 KEYNOTES 6 DETAILED SCHEDULE 9 SESSION 1: Robotics and Automation 11 SESSION 2: Network and Communication Engineering 13 SESSION 3: Data Mining 16 SESSION 4: Cloud Computing and Algorithms 19 SESSION 5: Software Engineering and E-learning 22 SESSION 6: IT and its Applications 26 CALL FOR PAPERS 31 FEEDBACK 37 2 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES Dear Participants, Welcome to 2015 Singapore Conferences! We are confident that over the three days you will get the theoretical grounding, practical knowledge, and personal contacts that will help you build a long-term, profitable and sustainable communication among researchers and practitioners in a wide variety of scientific areas with a common interest. For the conferences, we had received more than 160 submissions, and around 65 excellent papers were accepted for presentation. Congratulations for these papers. We wish to thank our outstanding keynote speakers Prof. Maode Ma, Dr. Ka Wai Gary Wong, and Prof. Chiharu Ishll for sharing their deep insights on Information Technology, Intelligent Mechatronics and Automation, and Knowledge Engineering. Special thanks also go to all the researchers and students who participate in the conference with their work. Hope you enjoy the conference, the food, the hospitality, and the beautiful and charming environment of the city of Singapore! IACT Conference Organizing Committee 3 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES Conference Agenda Overview Monday, Feb. 2, 2015 10 :00 am to 5:00 pm Lobby Arrival and Registration Tuesday, Feb. 3, 2015 Opening Ceremonies 8:45am to 9:00am Prof. Maode Ma Nanyang Technological University, Singapore Keynote Address-1: 9:00am to 9:50am Prof. Maode Ma Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 9:50am to 10:10am Group Photo & Coffee Break Quality Ballroom Keynote Address-2: 10:10am to 11:00am Dr. Ka Wai Gary Wong The Hong Kong Institute of Education, Hong Kong 11:00am to 11:50pm Prof. Chiharu Ishll Hosei University, Japan 12:00pm to 1:30pm Lunch Keynote Address-3: Restaurant Session 1: Robotics and Automation——9 presentations Session 2: Network and Communication Engineering——10 1:30pm to 3:50pm Diamond Room presentations Emerald Room Session 3: Data Mining——10 presentations 3:50pm to 4:10pm Quality Ballroom Coffee Break Session 4: Cloud Computing and Algorithms——11 Quality Ballroom Session 5: Software Engineering and E-learning——12 Diamond Room presentations 4:10pm to 6:30pm presentations Session 6: IT and its Applications ——12 presentations 6: 30pm to 8:30pm Emerald Room Restaurant Dinner 4 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES Instructions for Oral Presentations Devices Provided by the Conference Organizer: Laptops (with MS-Office & Adobe Reader) Projectors & Screen Laser Sticks Materials Provided by the Presenters: PowerPoint or PDF files Duration of each Presentation (Tentatively): Regular Oral Session: about 15 Minutes of Presentation, including 2-3 Minutes of Q&A Plenary Speech: 50 Minutes of Presentation, including 5 Minutes of Q&A NOTICE: *Certificate of Participation can be collected in front of the registration counter. *Certificate of Presentation will be issued at the end of each session by the session chair *The organizer will not provide accommodation, so we suggest you make an early reservation. *One best presentation will be selected from each session. The best one will be announced when each session ends, and the certificate will be awarded by the session chair after each session in the meeting room. *The attendee should provide the author’s authorization or attendee’s passport ID when the attendee is none of the authors. 5 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES Security Enhancements over the Communication Networks in Smart Grid Prof. Maode Ma Nanyang Technological University, Singapore Abstract: The ever growing demand of energy all over the world has compelled a shift from the traditional power distribution system to a more sustainable and efficient system incorporating the advances of information technology and communication and networking technologies. This new energy infrastructure is envisioned not only to provide more optimal energy consumption and better real-time power requirement assessment but also to incorporate renewable energy generation sources at both consumer and provider sides for environment friendly power generation. The implementation of such infrastructure demands the deployment of efficient communication networks among various entities of the smart grid system. The architecture of the networks tends to be highly distributed, heterogeneous and complex, incorporating different communication standards and resources. The complexity of the communication networks provides various venues for the adversaries to compromise the communication networks of the smart grid system. The corresponding consequences resulting from these vulnerabilities can range from minimal harm, to entire system shutdown. Such impacts may lead to economic collapse, terrorist invasion and even loss of lives. In this talk, we investigate the security aspects of the home area networks (HANs) and neighborhood area networks (NANs) to support the operation of the smart grid in detail. We explore the vulnerabilities of the HANs and NANs under various malicious attacks and review current major solutions to protect the networks from those attacks. We further discuss the potential research issues to enhance the security functionality of the communication networks in the smart grid. As an example, we will present our recent solution to enhance the security functionality of the HANs in the smart grid. Biography: Dr. Maode Ma received his Ph.D. degree in computer science from Hong Kong University of Science and Technology in 1999. Now, Dr. Ma is an Associate Professor in the School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering at Nanyang Technological University in Singapore. He has extensive research interests including wireless networking and network security. He has led and/or participated in 18 research projects funded by government, industry, military and universities in various countries. He has been a general chair, technical symposium chair, tutorial chair, publication chair, publicity chair and session chair for more than 70 international conferences. He has been a member of the technical program committees for more than 180 international conferences. Dr. Ma has more than 260 international academic publications including more than 110 journal papers and 150 conference papers. He currently serves as the Editor-in-Chief of International Journal of Computer and Communication Engineering and International Journal of Electronic Transport. He also serves as a Senior Editor for IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, and an Associate Editor for International Journal of Network and Computer Applications, International Journal of Security and Communication Networks, International Journal of Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing and International Journal of Communication Systems. He had been an Associate Editor for IEEE Communications Letters from 2003 to 2011. Dr. Ma is the Fellow of IET and a senior member of IEEE Communication Society and IEEE Education Society. He is the Chair of the IEEE Education Society, Singapore Chapter. He is serving as an IEEE Communication Society Distinguished Lecturer. 6 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES Opportunities and Challenges with Mobile Technology in Higher Education Dr. Ka Wai Gary Wong The Hong Kong Institute of Education, Hong Kong Abstract: Nowadays, the development of mobile technology has been rapidly expanded throughout every corner of the world. People can communicate anywhere at any time with minimal boundary because of the high speed of cellular networks such as 3G and LTE. With the fascinating opportunity of the intelligent information networks, the teaching and learning in higher education should take the advantages of the mobility of devices to reach out to every user and learner. In this talk, I will focus on the application oriented technology and share teaching practices, which can be applicable to computer science, mathematics, and engineering education everywhere. Biography: Dr. Gary Ka-wai Wong is currently a Lecturer of the Department of Mathematics and Information Technology in the Hong Kong Institute of Education (HKIEd). Dr. Wong received the B.S. degree in Computer Science and Mathematics (Double Major),Magna Cum Laude, from Brigham Young University Hawaii (BYU-Hawaii) in 2006. He then earned the M.Phil. degree in Electronic and Computer Engineering from The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology in 2009. He received his Ph.D. in Computer Science from City University of Hong Kong in 2012. His research interests include wireless communication and networks, mobile social networking, energy efficiency in wireless communications, mobile learning in mathematics and ICT educations, optimization and mathematical programming, computer science and engineering education, and higher education. Dr. Wong is currently a member of Phi Kappa Phi, ACM, IEEE, and HKCS. 7 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES Applications of Robot Technology to Assistive Devices in Aging Society Prof. Chiharu Ishll Hosei University, Japan Abstract: Japan is going towards an unprecedented ageing society, and facing a serious problem of population aging. The percentage of elderly people of age 65 years or over (aging ratio) is 25.0% in 2013, and it is forecasted that the aging ratio becomes 33.4% in 2035.In this way, Japan has reached a super-aged society which no country in the world has experienced. Becoming the super-aged society, it is necessary to respond to the demand of medical care and nursing of elderly people. One of the solutions is an application of the Robot Technology (RT).In this talk, medical and assistive devices with application of RT which were developed in Japan for use in the aging society are introduced. Some of medical and assistive devices developed in my laboratory are also mentioned. Biography: Prof. Chiharu Ishii received his Bachelor of Engineering degree in Mechanical Engineering from Sophia University in 1992, Master of Engineering degree in Mechanical Engineering from Sophia University in 1994 and Doctor of Engineering degree in Mechanical Engineering from Sophia University in 1997. He worked at Ashikaga Institute of Technology between 1997 and 2002, at Kogakuin University between 2002 and 2009, and at Shibaura Institute of Technology between 2009 and 2010. Since 2010, he has been working at Hosei University, and currently he is a Professor with the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Science and Engineering at Hosei University. Prof. Ishii has received several awards such as The Best Paper Award in the area of Tactile and Haptic Interfaces at the 4th International Conference on Human System Interaction (HSI2011); Best Paper Award at the 1st International Conference on Computer Science, Electronics and Instrumentation (ICCSE2012); Best Presentation Award at the International Conference on Intelligent Mechatronics and Automation (ICIMA2013). Prof. Ishii is currently a member of IEEE, SICE, JSME, RSJ, IEEJ and JSCAS. His research interests are in medical robotics, assistive technology and robust control. 8 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES Detailed Schedule Monday, Feb. 2 Location Lobby Arrival and Registration 10:00– 12:00 13:00 — 17:00 Tips: After sign, you will collect your conference package, including: Original Receipt Journal (Only for Author Attendee, some journals may be posted after the conference) Representative / Pass Card with Tie Printed Program Lunch Coupon Dinner Coupon *Participation Certificate (Presentation Certificate will be collected from Session Chair after the presentation) Conference Souvenir Computer Bag Notice: Please check on all these materials as soon as you get the package; if any of them is not included in the package, please let us know at once; If any of them gets lost after the registration, no additional one would be provided. Your understanding will be appreciated! Each regular registration covers only one package. Additional package will be charged. Some attendees may arrive on Feb. 3, kindly be noted that you can register at the registration desk from 9 am onwards. 9 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES Tuesday Morning, Feb. 3 Opening Ceremony Location Quality Ballroom Opening Ceremonies 8:45am to 9:00am 9:00am to 9:50am Prof. Maode Ma Nanyang Technological University, Singapore Plenary Speech 1: Security Enhancements over the Communication Networks in Smart Grid Prof. Maode Ma Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 9:50am to 10:10am Plenary Speech 2: Opportunities and Challenges with Mobile Technology in Higher Education Dr. Ka Wai Gary Wong The Hong Kong Institute of Education, Hong Kong 10:10am to 11:00am Group Photo & Coffee Break 11:00am to 11:50pm Plenary Speech 3: Applications of Robot Technology to Assistive Devices in Aging Society Prof. Chiharu Ishll Hosei University, Japan 12:00pm to 1:30pm Lunch Time Location Restaurant Tips: Please be noted that lunch coupon is necessary for entering the restaurant. Please arrive at the conference room by 1:20 pm. Thank you! 10 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES Tuesday Afternoon, Feb. 3 -PAPER SESSIONSSession 1: Robotics and Automation Chair: TBA 9 presentations Time: 1:30pm to 3:50pm Venue: Quality Ballroom The Self-Tuning PID Control in a Toggle Mechanism System by Knowledge-based Bounds Ching-Sheng Chi and Chin-Wen Chuang I-Shou University, Taiwan, R.O.C. A005 Abstract—A self-tuning PID controller is proposed in this paper. The tuning rule is based on the expert’s experience. Due to the proposed PID self-tuning method based on the engineer’s experience, the experienced engineers will easily accept it. The proposed controller is applied to the toggle mechanism system. The experimental results are compared with the classical PID controller. Finally, the experimental results show the robust character of the proposed controller. The Motion Planning for Spherical Robot with Two Motors Xin Wang Tongji University, China A006 Abstract—In this paper, we proposed a spherical robot with two motors in the horizontal and vertical directions which derive the robot to do omni-directionally roll. Based on the structure of the robot, we derived the kinematic model using inertial and moving coordinate system. In order to minimize the energy of the system, an optimization problem with two optimization variables which are the parameters to control the angular velocity of the motors is given. After that, a particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm is used to solve the optimization problem. The simulation shows that the motion planning with the algorithm has high precision. Vibration Control of Strain Gradient Nonlinear Micro-Cantilevers Using Piezoelectric Actuators R. Vatankhah, M.A. Nojoumian, H. Salarieh Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran A014 Abstract—A closed-loop control algorithm is used for stabilization of a vibrating nonlinear strain gradient micro Euler-Bernoulli cantilever beam using linear piezoelectric actuation. In this paper, the governing partial differential equation (PDE) of the nonlinear strain gradient beam with piezoelectric actuator is obtained. Galerkin projection method is utilized to reduce the system’s PDE equation of motion into a set of nonlinear ordinary differential equation (ODE) model. The nonlinear system is controlled by a robust linear controller which ensures the stability of the nonlinear system. Numerical simulations are investigated to demonstrate the effectiveness and performance of the designed control scheme. A019 Intelligent Control System Design for a Teleoperated Endoscopic Surgical Robot Alaa Khalifa and Ahmed Ramadan Tanta University / EJUST, Egypt 11 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES Abstract—This paper concerns with the control system design for a teleoperated endoscopic surgical manipulator system that uses PHANTOM Omni haptic device as the master and a 4-DOF parallel manipulator (2-PUU_2-PUS) as the slave. PID control algorithm was used to achieve the trajectory tracking, but the error in each actuated joint reached 0.6 mm which is not satisfactory in surgical application. The design of a control algorithm for achieving high trajectory tracking is needed. Simulation on the virtual prototype of the 4-DOF parallel manipulator has been achieved by combining MATLAB/Simulink with ADAMS. Fuzzy logic controller is designed and tested using the interface between ADAMS and MATLAB/Simulink. Signal constraint block adjusted the controller parameters for each actuated prismatic joint to eliminate the overshoot in most of position responses. The simulation results illustrate that the fuzzy logic control algorithm can achieve high trajectory tracking. Also, they show that the fuzzy controller has reduced the error by approximately 50 percent. Static Analysis on Suitable Arrangement of Tubes of Low-cost Control Valve Using Buckled Tube Abdul Nasir, Tetsuya Akagi, Shujiro Dohta, Ayumu Ono Okayama University of Science, Japan A023 Abstract—Due to its potential to improve human health care and various of the treatments equipments, power assisted nursing care systems have received positive attentions from the global community and also gaining huge demands from the mainstream industry. In such a control system, wearable actuators and control valves are required to be mounted on the human body. Generally, the performance and cost of the pneumatic wearable rehabilitation device depends on the cost and performance of the valve. Therefore, the optimal design of the valve for precise control is required. In this paper, the proposal of the static model and analysis of the servo valve using buckle tubes developed before are described. Application of Pressure Control Type Quasi-Servo Valve to Force Control System Yoshinori Moriwake, Shujiro Dohta ,Tetsuya Akagi, So Shimooka Okayama University of Science, Japan Abstract—Today, the aged people are rapidly increasing and the number of children is decreasing in Japan. This social problem A024 causes the demand of the care and welfare equipments to support a nursing and a self-reliance for the senior. For example, a power assist device for reducing the burden of the user has been researched and developed. The purpose of this study is to develop a small and light-weight pneumatic control valve and to apply it to the care and welfare equipments. In our previous study, the small-sized quasi-servo valve using two inexpensive on/off valves was developed and tested. The pressure control type quasi-servo valve was also proposed and tested by using the quasi-servo valve, a pressure sensor and an embedded controller. In this paper, the pressure control type quasi-servo valve is applied to a force control of the pneumatic cylinder, and its control performance is investigated. E003 Bioenergy Ontology for Automatic Pathway Generation Krishna Sapkota, Pathmeswaran Raju, Craig Chapman, William Byrne, Lynsey Melville Birmingham City University, United Kingdom Abstract—Bioenergy is a renewable energy and is generated by treating biomass with various technologies. Depending upon the nature of biomass, it is more suitable for one technology than others, and they can further be treated with other technologies. Hence, the biomass follows a pathway of technologies, and the pathway is called bioenergy pathway. Currently, bioenergy pathways are created manually: either by manually sketching or by creating the data manually and generating diagrams from the data. Manually generated pathways are prone to human errors. A solution to this is creating semantic pathways automatically. In this paper, we present the bioenergy ontology to generate semantic pathways automatically. In particular, we have leveraged the Semantic Web technologies to represent the bioenergy knowledge and inferred the pathways. The case study has been carried out in one of the INTERREG Project and found promising results. E011 Assessing Mobile Learning Systems Success 12 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES Hsin-Hui Lin, Yi-Shun Wang, and Ci-Rong Li National Changhua University of Education, Taiwan Abstract—With the proliferation of mobile learning in educational context, measuring mobile learning system success has become an important issue for academics and practitioners. Although mobile learning has received much attention among researchers, little research has been conducted to assess the success and/or effectiveness of mobile learning systems. Thus, the main purpose of this study is to develop and validate a multi-dimensional instrument for measuring mobile learning system success (MLSS) based on previous research. This empirically validated instrument will be useful to researchers in developing and testing mobile learning system success model, as well as to educators in understanding MLSS from student perspective and promoting the use of mobile learning systems. T016 Rotating Machinery Vibration Signal Processing And Fault Diagnosis Based on LMD Ruirui Bo and Ze Zhang Inner Mongolia University, China Abstract—There are abundant of fault information in rotating machinery vibration signal. On account of the non-linearity and non-stationarity, the paper first does pre-process to the vibration signal using wavelet threshold de-noising method and this method can bring a smooth signal. Then it decomposes the vibration signal using local mean decomposition(LMD), which is effective to the vibration signal. The LMD decomposes the signal into many PFs as the frequency from high to low. These PFs are composed of the production of envelop signal and pure frequency modulated signal. Finally, it takes most use of the kurtosis which is sensitive to the fault impact. By calculating the kurtosis of PF, it can assess the distribution of fault impact signal in every frequency band, consequently distinguishing the operating state of bearing and recognizing the fault mode according to the growth of turtosis. The experiment of actual bearing vibration signal demonstrates that the methods this paper proposed can effectively diagnose the vibration fault and has good performance. Session 2: Network and Communication Engineering Chair: TBA 10 presentations Time: 1:30pm to 3:50pm Venue: Diamond Room T021 Channel Estimation on the (EW)RLS Algorithm Model of MIMO OFDM in Wireless Communication Suzi Seroja Sarnin, Habibah Hashim, Siti Maisurah Sulong University Technology Mara (UITM), Maylaysia Abstract—This paper study the channel estimation based on the exponentially weighted (EW) RLS algorithm. The advantages of the proposed estimator arise from its implementation in the time-domain, whereas fewer channel parameters are required to be estimated compared with the frequency-domain channel coefficients. In addition, the matrix inversion operation required in LS and LMMSE estimators is avoided here by recursively updating the channel estimates. Therefore, the computational complexity is highly reduced compared to frequency-domain based channel estimation. Furthermore, the proposed estimator has good tracking capability due to exploiting the time correlation between the path gains. This paper provides analysis, evaluation and computer simulations in MATLAB. The performance is evaluated in terms of the MSE of the channel estimate and BER for different Doppler 13 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES frequencies (correspond to different mobility speeds) and Monte Carlo simulations are performed and the MSE and BER performance versus SNR are obtained by averaging over 10000 channel realization. For comparisons, the BER performance is also presented for perfectly known channel at the receiver. In all the simulations, perfect synchronization between the transmitter and the receiver is assumed. T027 Energy-Saving User Association for Uplink Heterogeneous Cellular Networks Tianqing Zhou, Sifan WU, Yafang Wang, Luxi Yang Southeast University, China Abstract—In this paper, we present a scheme that jointly designs user association and power control in uplink heterogeneous cellular networks. Specifically, we formulate a general problem which performs user association and meanwhile minimizes the uplink sum-power under signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) constraints. This is a nonlinear mixed-integer optimization problem, and its optimum solutions are very difficult to be obtained when the problem is large-scale. To solve this problem, we decompose it into a user association problem and a power control problem, and then iteratively solve these two subproblems by designing a two-sided scalable (2.s.s.) algorithm. The proposed algorithm can be well implied in a distributed manner due to its simplification and efficiency. Numerical results show that, compared with the scheme proposed by Roy, the proposed scheme can significantly reduce energy consumption and increase the system throughput. T052 Wireless Sensor Network Based Mobile Tracking System Nyein Aye Maung Maung, Makoto Kawai Ritsumeikan University, Japan Abstract—Mobile target tracking through large-scale wireless sensor networks (WSN) demands a large number of reference nodes, which is not feasible for resource-constrained WSNs. This paper proposes a resource-efficient mobile tracking system which integrates connectivity-based range-free approach and Received Signal Strength (RSS) based ranging approach to improve the tracking performance while reducing the specialized hardware requirement. In our proposed system, regulated hop-count values between static unknown nodes and reference nodes in the targeted area of interest for mobile tracking are first estimated in the network configuration phase. Then, location of the mobile target is tracked based on the regulated hop-count values and the available RSS measurements from its surrounding nodes at each tracking point without any extra hardware. Additionally, estimated location is enhanced by correcting with the known information of maximum velocity of the mobile target. Simulation and experimental results show that the proposed system offers preferable mobile tracking performance with minimum reference node utilization in both small-scale and large-scale networks. T054 Detection of R-peaks in ECG Signal by Adaptive Linear Neuron (ADALINE) Artificial Neural Network Jeong-Hwan Kim, San-Eun Park, Gyeo-Wun Jeung, Kyeong-Seop Kim Konkuk University, Korea Abstract—This research proposes a new method to detect R-peaks in electrocardiogram by using the prediction value from adaptive linear neuron (ADALINE) artificial neural network. With this aim, the weights of four input neurons in ADALINE are updated for each encoded ECG vector-segment and the value of an output neuron is compared with the actual ECG followed by applying finite impulse response filter. Our simulated experiments with the MIT-BIH ECG database that represents the long-term recordings from the heart disease patients show that our proposed algorithm can detect R-peaks in ECG data with the accuracy of more than 99%. T056 RFID Data Processing in Real-Time Monitoring System Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew, Suchart Joolrat, Mongkon Tengrungroj, Patcharaporn Jiranuwattanawong, Channarong Janpanich, Kittiphan Sornsakda Khon Kaen University, Thailand 14 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES Abstract—In every marathon events, runners always prefer the result running time to be confirmed and announced as soon as possible. This paper proposes a real-time monitoring system with RFID data processing that can compute both the finish time and the net time. The net time is used to determine the top runners to receive awards. The running result is determined and declared by the audit committee. Most of the software solutions available on the market are desktop applications. These applications are usually dependent on specific operating systems and have different system requirements for installation. Furthermore, they are generally rigid in terms of structure and functionality. On the other hand, we have developed the system that can read a live running time at the RFID reader points. Then the system shows the live time on the board that can be immediately perceived by runners. We have th evaluated the proposed system in the 11 Khon Kaen International marathon, which is one of the largest marathons in Thailand. The organizers and the runners were pleased with the real time live running time reports as well as the precise net time used to determine the winning runners. T059 Using TOPSIS to Predict Route Safety in Ubiquitous Network Chiung-Ying Wang, Bo-Liang Wu TransWorld University, Taiwan (R.O.C) Abstract—The demand for car navigation applications in route finding has grown tremendously. However, the driver use of GPS navigation to guide the car to unsafe route often happens. In this paper, the goal of the proposed mechanism is able to select the route which satisfies multiple requirements of individual user and improve route safety. In this paper, the proposed mechanism considers various contexts and utilizes Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution, TOPSIS to predict route safety. The contexts of the proposed mechanism are including route information: road distance, road maintenance information, traffic information, mudslide avalanche information; weather information: heavy rain information. The TOPSIS is a multi-criteria decision analysis method and adopted to select route with higher safety for drivers. Finally, our computational results also indicate that the proposed mechanism provides shorter road maintenance distance, less traffic jam, fewer rainfalls and less mudslide avalanche degree than shortest route. Therefore, the proposed mechanism efficiency improves route safety for drivers. This paper for applications in the automotive navigation devices, and it has benefits to enhance route safety. T064 Transitive trust methods for routing in WSNs Wang Na, Wang Tianhua Shanghai Second Polytechnic University, China Abstract—The goal of this paper is to introduce two trust methods for routing in wireless sensor networks. The two methods consider transitivity of trust. When computing routing trust value, they use optimistic and pessimistic ways respectively. These trust methods can select a trust routing for precise data transmission. A simulation is given and shows that this trust model has a higher performance than ECCR in reliability. T3007 Analysis and Optimization of Distributed Antenna-Aided Heterogeneous Networks Relying on Fractional Frequency Reuse Lang Zhong, Guangjun Li, Xuemin Yang,Shuisheng Lin University of Electronic Science & Technology of China Abstract—In distributed antenna-aided Heterogeneous Networks, macro cells (MCs) always suffer co-channel interference (CCI) from femtocells (FCs). Hence, in this paper, the downlink (DL) signal to interference ratio (SIR) of MCs and the interferential constituents are investigated. To decrease this adverse impact of FCs and achieve high spectral efficiency, a joint optimization of Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) and optimal frequency allocation (OFA)among mobile stations (MSs) is proposed to improve both the cell planning and the frequency allocation. Simulation results show high feasibility of PSO algorithm and prove that 15 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES compared with conventional static system and PSO scheme, the proposed PSO-OFA joint optimizing scheme has significant performance improvement and also achieve some degree of controllability. A3003 Solar Powered Gravity-Feed Drip Irrigation System Using Wireless Sensor Network Angelina Ho Mei Yi, Muhammad Zaharul Asyraf Bin Zaharin, Ionel Valeriu Grozescu, and Hawa ZE Jaafar Universiti Putra Malaysia (UPM), Malaysia Abstract— A Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) to automatically irrigate the crops using soil moisture content values obtained from the soil moisture sensor is designed. Gravity-feed drip irrigation is actuated according to the needs of the crop by using a relay to on a solenoid valve when the soil is dry, which is determined by soil moisture content below 60%. End devices communicate with the Coordinator via Xbee communication links. CN0008 A Review of Mobility Management in Integrated UMTS and WLAN Networks Maushumi Barooah, Diganta Kumar Pathak, and Ishita Roy Karmakar Assam Engineering College, India Abstract—In today’s age of Next Generation Internet there have been a plethora of diversified overlapping networks where each of these communication technologies are optimized to provide user specific services and Quality of Service(QoS) parameters. The main objective of next generation networks focus at high bandwidth and high mobility. There are WiFi hotspots (WLAN) providing high data rates within smaller areas and UMTS networks providing larger coverage areas with low data rates. These two complementary networks can be combined to quench the thirst for ubiquitous communication enabling the smart mobile user to roam seamlessly between these technologies for best possible services. To ensure Always Best Connectivity, one of the main short comings to be addressed is efficient handoff management and there are a lot of works already published addressing various issues of efficient handoff management till date. This paper provides a comprehensive detail of different handoff management strategies reported so far in a systematic manner and also throws light on a particular scheme of handoff management between UMTS and WLAN providing QoS to the mobile users. Session 3: Data Mining Chair: TBA 10 presentations Time: 1:30pm to 3:50pm Venue: Emerald Room T010 Application of Clustering for Customer Segmentation in Private Banking Xuan Yang, Jin Chen, Pengpeng Hao, Yanbo J. Wang China Minsheng Bank, China Abstract—With fierce competition in banking industry, more and more banks have realised that accurate customer segmentation is of fundamental importance, especially for the identification of those high-value customers. In order to solve this problem, we collected real data about private banking customers of a commercial bank in China, conducted empirical analysis by applying K-means clustering technique. When determine the K value, we propose a mechanism that meet both academic requirements and practical needs. Through K-means clustering, we successfully segmented the customers into three categories, and features of each group have been illustrated in details. T017 An improved clustering algorithm for big data based on K-means with optimized clusters’ number 16 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES Lianjiang Zhu, Tao Du, Shouning Qu, Kai Wang, Yong Zhang University of Jinan, China Abstract—To improve the processing ability of big data, a new clustering algorithm is proposed which is designed based on K-means. In this algorithm, a concept of ―Silhouette Coefficient‖ is defined to estimate the result of clustering. Based on silhouette coefficient, the optimized clusters’ number would be chosen, and then K-means algorithm would be operated with this clusters’ number. The algorithm is tested by a real production big data set and compared with classical K-means. The result of experiment proves that the improved algorithm has more reasonable result of clustering with little extra calculation. T025 Research On Non Rigid Registration Algorithm of DCE-MRI Based On Mutual Information and Optical Flow Shihua Yu, Rui Wang, Kaiyu Wang, Mengmeng Xi and Hui Liu Dalian University of Technology, China Abstract—Image matching plays a very important role in the field of medical image, while the two image registration methods based on the mutual information and the optical flow are very effective. The experimental results show that the two methods have their prominent advantages. The method based on mutual information is good for the overall displacement, while the method based on optical flow is very sensitive to small deformation. In the breast DCE-MRI images studied in this paper, there is not only overall deformation caused by the patient, but also non rigid small deformation caused by respiratory deformation. In view of the above situation, the single-image registration algorithms cannot meet the actual needs of complex situations. After a comprehensive analysis to the advantages and disadvantages of these two methods, this paper proposes a registration algorithm of combining mutual information with optical flow field, and applies subtraction images of the reference image and the floating image as the main criterion to evaluate the registration effect, at the same time, applies the mutual information between image sequence values as auxiliary criterion. With the test of the example, this algorithm has obtained a better accuracy and reliability in breast DCE-MRI image sequences. T026 Polygon Intersection Based Algorithm for Fuzzy Set Compatibility Calculations Sukgamon Sukpisit, Supaporn Karnsomkeat, Pannipa Sae Ueng, Apirada Thadadech, Srdjan Skrbic Prince of Songkla University, Thailand Abstract—PFSQL is an extension of the SQL language that allows usage of fuzzy logic in SQL queries. In query statements, variables can take both fuzzy and non-fuzzy values. Normally, different types of values cannot be compared directly. Therefore, it is necessary to implement fuzzy compatibility calculation to solve this problem. This paper proposes a method of fuzzy compatibility calculation implementation that determines compatibility degree of two fuzzy sets. The compatibility value is calculated using polygon intersection algorithm. To prove the correctness of the proposed method, the application has been developed and tested with 360compatibility cases of different randomly generated fuzzy values. The experimental results show that our algorithms can handle various types of intersections between any two fuzzy sets. T031 An Intelligence Based Clustering Approach For Optimization of Web Elements Shashi Mehrotra, Shruti Kohli Birla Institute of Technology Ex Noida, India Abstract—With the massive increase in the use of internet and web data, retrieval of relevant information quickly is very important. Due to massive increase in the web usage, some efficient technique is required for data analysis. Grouping of object is required for efficient data analysis. Clustering on-line result is a challenging technique. Search option is excessively used in almost every website. The study proposes a hybrid clustering algorithm to optimize search result of the website. The domain of the website is medical. Matrices will be used to analyze user behaviour. User trust will be measured. Clustering of search result will facilitate users to get the relevant information in a quick manner. T034 Applying Data Mining Techniques and extended RFM Model in Customer Loyalty Measurement 17 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES Panwad Bunnak, Sotarat Thammaboosadee and Supaporn Kiattisin Mahidol University, Thailand Abstract—This paper proposes a loyalty measurement model of individual customer for the benefit in creating of marketing campaign and activities as well as the suitable products and services for customers and establishment of good customer relationship. This study adapts the concept of RFM (Recency- Frequency-Monetary) model and applies to database of customer purchases and the customer type. The business type of selected organization is commercial business. To apply the RFM concept to find customer loyalty according to type of customer, the customer loyalty is partitioned into 5 classes using k-means clustering algorithm and is heuristically assigned customer types: Platinum, Gold, and Silver. Type of customers is then brought into consideration the extending of the RFM Model with customer analytics to make it even better customer classification performance. Finally, the classification system generates decision rules to find out the loyalty of new future customers using C4.5 decision tree algorithm. T036 Gold Price Volatility Prediction by Text Mining in Economic Indicators News Chanwit Onsumran, Sotarat Thammaboosadee and Supaporn Kiattisin Mahidol University, Thailand Abstract—This paper focuses on the text mining approach of the gold prices volatility prediction model from the textual of economic indicators news articles. The model is designed and developed to analyze how the news articles influence gold price volatility. The selected reliable source of news articles is provided by FXStreet which offers several economic indicators such as Economic Activity, Markit Manufacturing PMI, Bill Auction, Building Permits, ISM Manufacturing Index, Redbook index, Retail Sales, Durable Goods Orders, etc. The data will be used to build text classifiers and news group affecting volatility price of gold. According to the fundamental of data mining process, each news article is firstly transformed in to feature by TF-IDF method. Then, the comparative experiment is set up to measure the accuracy of combination of two attributes weighting approaches, which are Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Chi-Squared Statistic, and three classification algorithms, which are the k-Nearest Neighbour, SVM and Naive Bayes. The results show that the SVM method is the most superior to other methods in both attributes weighting and classifier viewpoint. T058 Expert System for diagnosis of discus fish disease using fuzzy logic approach Novita Hanafiah, Kelvin Sugiarto, Yulius Ardy, Ruben Prathama, Derwin Suhartono Bina Nusantara University, Indonesia Abstract—Discus fish is a favourite fish because of its beauty and unique characteristic, ranging from a variety of style, colour and shape. This fish has become one of the profitable business opportunities for fish farmers, mainly for export to overseas because the price is quite expensive. However, Discus fish is difficult to maintain since it is susceptible to various diseases. An expert system application utilizing fuzzy logic is presented to resolve this problem by diagnosing diseases of the discus fish. It is expected to help beginner fish farmers to detect the disease in the earliest time. Besides diagnosing, this desktop-based application can be exploited to get more information about the diseases in order to prevent and treat the Discus fish. The algorithm shows a good result which achieves 90.32% of accuracy. A020 Segmentation of Breast Thermogram Images for the Detection of Breast Cancer – A Projection Profile Approach Dayakshini, Surekha Kamath, Keerthana Prasad and Rajagopal K.V Manipal Institute of Technology, Manipal University, India Abstract—This paper presents a method for segmenting the left and right breast from breast thermogram images using projection profile approach. Horizontal Projection Profile (HPP) method is used for detecting the upper and lower borders of the breast and Vertical Projection Profile (VPP) method is used for detecting left and right borders of the breast thermogram image. The results of segmentation are satisfactory. Generalization of this method can be done for various types of breast thermogram images by 18 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES standardizing the height, background and removal of the noise present in the image. E008 Generating the Movie Domain Specific Sentiment Lexicon Using NLP and SVM Method Yoosin Kim, Do Young Kwon, Seung Ryul Jeong Kookmin University, Republic of Korea Abstract—Nowadays, online user-generated contents, or called consumer word-of-mouth, directly influence to real world, and there are many attempts to analyze them using opinion mining. For sentiment analysis, general dictionaries have been used frequently, but much research mentioned domain specific sentiment dictionary should ensure higher performance than general sentiment dictionary. And also use of Korean sentiment lexicons is still rare because of the complexity of Korean as an agglutinative language. In order to recover these challenges, this study attempted to develop a movie domain specific sentiment dictionary. We collected movie reviews and applied natural language processing, support vector machines method, and validate it though sentiment lexicon based analysis. As a result, the linguistic feature for the dictionary was consisted with 668 terms on classification accuracy reached 76.69 % in training data and 73.38% in test data. In addition, this domain specific dictionary classified 66.12% of whole review data and achieved 78.68 % of accuracy and 89.64 % of F1 score. It shows that a domain specific dictionary can be generated without manual works; can achieve relatively higher performance; a small scale dictionary can become efficient way for big data analysis. 3:50pm to 4:10pm -PAPER SESSIONSSession 4: Cloud Computing and Algorithms Chair: TBA 11 presentations Time: 4:10pm to 6:30pm Venue: Quality Ballroom T002 Local Search-based Enhanced Multi-objective Genetic Algorithm and its Application to the Gestational Diabetes Diagnosis Jenn-Long Liu, Chung-Chih Li, and Chien-Liang Chen I-Shou University, Taiwan Abstract—In evolutionary computation, several multi-objective genetic algorithms (MOGAs) have been widely used to solve multi-objective optimization problems (MOOPs).The version NSGA-II, developed by Deb et al., is a useful package usinga population-based genetic algorithm to solve optimization problems with multiple objectives subject to constraints. This study proposes an enhanced version of NSGA-II, termed LS-EMOGA herein, which modifies the crossover and mutation operators of original NSGA-II by an extended intermediate crossover and a non-uniform mutation and also incorporates a local search (LS) 19 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES procedure to improve the fine-turning ability of the solution searching. The performance of the proposed LS-EMOGA is assessed by evaluating five benchmark cases of MOOPs. The computed solutions are compared with those of obtained using NSGA-II and proposed MOGA without local search procedure (EMOGA version). Moreover, the proposed LS-EMOGA combines a k-means clustering algorithm to apply to the case diagnosis of gestational diabetic disease. T007 University Research Keywords Analysis Using Proximity Analysis Krittawaya Thongkoo Chiang Mai University, Thailand Abstract—Research management is a process that allows research administration to storing, searching the researchers' information more effectively. And also researchers can search the related research precision. So if the organization has automatic system for storing and searching, the research management will work more effectively. The important technique for making the automatic research management system is Text Mining. Next process is keywords analysis to select keywords. The result from keywords analysis process can be analyzed to know the real research focuses and directions of the university. In this study, a Proximity Analysis method which uses mathematical principles was selected to analyze the keywords. Additionally, CommonKADs methodology is used as an extensive framework for describing knowledge intensive business processes. Subsequently, the researcher policy management can be guided by this research ontology. After that, this information can be combined to decision support system for the university president. The experimental results show that using the proposed framework could reduce the time work of the research management process in Chiang Mai University. T032 TOAST: A Tool for Agile Software Project Management in Cloud Computing Environments Chung Yung, Ming-Cheng Li, and Yu-Tang Lin National Dong Hwa University, Taiwan Abstract—In this paper, we present a software project management of agile development in cloud computing environment, called as TOAST, which is constructed based on the MOAT model. MOAT is a two-layer model of software project management using agile methodology, which is especially designed for managing software projects in cloud computing environments. In MOAT, the primary operations of agile software development are categorized into two layers; namely, the project layer and the task layer. With MOAT, the progress status of an agile software development project is represented easily and clearly. TOAST implements all the MOAT operations using a client/server architecture, of which the TOAST client is deployed as an Android app and the TOAST server is designed to work in the cloud computing environments. Since there is not many, if any, software management tools of agile development available, TOAST is considered as an explorative tool especially for the software industry that aims at the cloud computing environments as the primary computing platform. T044 Generating Affixed Words from a Root Word and Getting Lemma from Affixed Word in Bahasa: Indonesian Language Andri Budiman Oktarino, Dwi Taruna Winahyu, Andrew Halim, Derwin Suhartono Bina Nusantara University, Jakarta, Indonesia Abstract—Previously, there were morphological analyzer and lemmatization method for Bahasa: Indonesian language, yet they have not handled all occurred cases. Therefore, we develop an algorithm which combines two tasks; they are to generate affixed words from a root word and vice versa. The current morphological analyzer to generate affixed words has not covered in analyzing two words, whilst the current lemmatization method cannot find out the lemma from an affixed word which has confix and reduplication. Hence, we will cover these issues in order to enhance the current methods. The algorithm concerns only in Bahasa. The algorithm to generate affixed word is based on the two-level morphological analyzer, while refinement of lemmatization method is based on rule precedence and token checking. After implementing the algorithms, we find out that affixed word produced is 12.63% productive words, 86.98% non-productive words, and 0.39% incorrect words for the affixed word, whilst lemmatization 20 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES can achieve 96.11% accuracy. T050 Chaotic Crossover Operator on Genetic Algorithm Huseyin DEMIRCI, Ahmet Turan OZCERIT, Huseyin EKIZ and Akif KUTLU Sakarya University, Turkey Abstract—In this paper, chaos based a new arithmetic crossover operator on the genetic algorithm has been proposed. The most frequent issue for the optimization algorithms is stuck on problem's defined local minimum points and it needs excessive amount of time to escape from them; therefore, these algorithms may never find global minimum points. To avoid and escape from local minimums, a chaotic arithmetic crossover operator has been employed on a genetic algorithm. Unimodal and multi modal benchmark functions have been used for comparing and test procedures. The genetic algorithm with this new arithmetic crossover operator has yielded better results than original arithmetic crossover operator does. With this new chaos based arithmetic crossover operator diversity and uniqueness of the genetic algorithm’s late population are increased. Therefore, even in the late stages of the optimization process, the genetic algorithm tried to search the entire search space and improved the best solution. T051 Libra: An Adaptive Method for Protecting Memory from Arbitrary Overwrite Chun-Yi Wang, Chieh-Wei Huang, Fu-Hau Hsu and Shih-Jen Chen National Central University, Taiwan Abstract—There have been more vulnerabilities in the Linux kernel in 2013 than there had been in the previous decade. In this paper, the research was focused on defending against arbitrary memory overwrite in privilege escalation. To avoid malicious users getting root authority, the easiest way is to set the sensitive data structure to read-only. But we are not sure the sensitive data structure will never be modified by legal behavior from a normal device driver; thus, we posed a compatible solution between read-only solutions and writable solutions which is based on the mechanism of read-only IDT table to enhance compatibility. The main idea that we posed not only solves the above problem, but also the general problem which is ensuring that important memory values can only be changed within a safe range. It is not just set to read-only. In addition, we do not need to care about if the Linux kernel exists any the vulnerabilities of arbitrary memory overwrite. T1001 Variable Selection Method Based on the Combination of Stability Competitive Adaptive Reweighted Sampling (SCARS) and Genetic Algorithm (GA) Kaiyi Zheng, Yuan Yao National Tsinghua University, Taiwan Abstract—Stability competitive adaptive reweighted sampling (SCARS) is successfully used in variable selection. In order to further refine the results of SCARS, genetic algorithm (GA) is adopted due to its strong ability of dealing with binary problems. SCARS repeatedly run 50 times to obtain 50 variable subsets. Then 50 variable subsets combined with 50 randomly generated chromosomes are set as input of GA.The results showed that in contrast with artificial bee colony (ABC) and particle swarm algorithm (PSO), GA can select variables with smaller prediction errors. T2001 Scheduling optimization algorithm based on Hadoop Zhang Qingnian, Gao Yin, Hu Wenjing and Yang Jie Wuhan University of Technology, China Abstract—With the increasingly sophisticated and popularity of the third-generation communication networks, the size of the network is drastically becomes larger and the equipment complexity is also greatly improved. So how to quickly resolve the call failure and how to ensure the quality of network operation becomes the most urgent task for network maintenance personnel. Call trace system, a new feature derived from signaling trace , as an important subsystem of the network management system is a powerful means to solve call failure problem and guarantee the quality of the network operation. Scheduling in call tracking system 21 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES used in communication is fifo scheduling algorithm of Hadoop. In practical applications, in order to make full use of the resources, different levels of users sharing a cluster, the different types of call tracking data processing will be done in the same cluster. Therefore, on the basis of the fair scheduling, this paper put forward based on the improved algorithm of call tracking system, to improve the system of the department can, better meet the actual demand of the system. T3001 Channel Estimation of MC-CDMA system based on SCBC for high data rate communications Mbembo Loundou Varus , Jie Yang Wuhan University of Technology, China Abstract—The increasing demand for High Data rates in mobile deployment constitutes one of the main research area in this few years. Mobile communication structures must be capable to support and provide high variety of service. Further, many users with different application-and-location-specific, time-varying rate and quality of service (QoS) requirement should be accommodated. In this appreciation, mobile and LTE (Long Term Evolution) are both considered as the main technologies that can be hosted, deployed and capable to offer strong coverage. Among the current techniques, MC-CDMA can provide better performances for high mobility effect with the resistant to various impairments. In this paper we propose a MC-CDMA transmission system for high data rate communications on mobile environments. The results presented are based on mobility context. T3003 Construction of Laboratory Platform based on Cloud Computing Yueping Wu, Yinchun Yang Shanghai Second Polytechnic University, China Abstract—In view of the problem which the present laboratory management cost is too high, resource waste severely, data is not unified, it was proposed that construction of laboratory platform based on cloud computing, the plan aims to construct the virtual pool of resources, and ultimately achieve a unified cloud platform, which build a sharing, dynamic, autonomous service, data center extended with the need, to provide a new IT resource supply mode for the teaching and scientific research. In this mode, teachers and students can get their desktop computing resources in any place at any time, Another important application about cloud computing in the laboratory is the construction of the virtual service, can deploy a server for storage, examination and race in the room in a few minutes by VSphere. Specific benefits are shown in table after the implementation of server virtualization. T3006 A Multitaper Spectral Estimator Based on a Cost Minimization Approach Bo Yan, Haifen Yang, Liang Zhou University of Electronic Science and Technology of China Abstract—A multitaper spectral analysis approach is built based on the minimization of cost function. The performance analysis indicates that this approach has comparative bias and variance as the approach of discrete prolate spheroidal sequence estimator. Compared with the DPSS, instead of solving the problem of matrix eigenvalues, the multitaper here needs less calculation with analytical expression of tapers. The validity of the estimator is verified by the computer simulation of an AR progress discrete as well as a white noise sequence. Session 5: Software Engineering and E-learning Chair: TBA 12 presentations Time: 4:10pm to 6:30pm Venue: Diamond Room 22 T012 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES The Incompatibility of End-User Learning Styles and the Current ERP Training Approach Monta Chayakonvikom, Parin Fuangvut and Nantika Prinyapol Dhurakij Pundit University, Thailand Abstract—ERP education and training is the critical success factor in an ERP implementation project but the ineffectiveness of current ERP training is still reported. Ineffective ERP education and training lead to user resistance towards an ERP system which makes the organization unable to achieve the long term benefits of ERP implementation. The ERP system was developed based on a universal culture and applied equally to all situations without consideration of the differences between ERP design and the organization in reality, which may be problematic. Thereby, the aim of this article is to investigate whether the current ERP training approach accommodates the variety of end-user learning styles. To achieve this objective, a pilot study was conducted to measure the training outcomes of the current ERP training delivered to various groups with different end-user learning styles. In-depth interviews were conducted with 30 end-users who have experience in ERP training during the period of implementation phase in a Thai context. The pilot study result supported the assumption by showing the incompatibility of end-user learning styles and the current ERP training approach, which affects the ERP training outcome. T015 Curriculum Architecture Based on Generalized Multimodal Information Fusion for ITO Training Nan Ma, Hong Bao ,Yun Zhai, Liyi Ma,Wenfa Li Beijing Union University, China Abstract—The "one body two wings" for ITO talents training mechanism proposed by us has been proved its validity in teaching within Beijing Union University. To better support this mechanism, a generalized multimodal information fusion mechanism and the law of multi-measure training need demands were constructed, furthermore, a new curriculum system framework called the general multi-model information fusion system based training course system for ITO talents training, GMSIF, was established in this paper. The GMSIF consists of such three layer architecture as the theory layer, information fusion layer and curriculum presentation layer as well as curriculum evaluation model to realize its reconstruction and optimization. The GMSIF has been employed in the practice in teaching practice recently in Beijing Union University. Curriculum practice indicates that the new curriculum architecture has been powerfully supported the goal of "one body two wings" ITO talents training. T040 FreGsd: A Framework for Global Software Requirement Engineering Abdulaziz Alsahli, Hameed Khan King Saud University, Saudi Arabia Abstract—Software development nowadays is more and more using global ways of development instead of normal development environment where development occurs in one location. This paper is aimed to propose a requirement engineering framework to support Global Software Development environment with regards to all requirement engineering activities from elicitation to finally managing requirement change. Global software environment is more and more gaining better reputation in software development with better quality is resulting from developing in this environment yet with lower cost. However, failure rate developing in this environment is high due to inappropriate requirement development and management. This paper will add to the software engineering development environments discipline and many developers in GSD will benefit from it. T041 Analysis of security vulnerabilities using misuse pattern testing approach Yifan Yuan, Somjai Boonsiri Chulalongkorn University, Thailand Abstract—Vulnerability detection is commonly been executed during the testing phase of software development. Current methods are not able to detect system or software security vulnerabilities of certain types of attacks during the early stages of software development. These attacks include both the ones we did not anticipate as well as the ones unknown during the design phase. In this 23 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES paper we propose a method to detect the security vulnerabilities during the design phase of software development. This approach simulates attacks according to the misuse patterns using model testing method. With this approach, we are able to analyse system security vulnerabilities during the design stage of the system development. The practical example provides evidences the feasibility of our method. T046 Function-oriented Business Process Improvement Framework for Customer Relationship Management Section in Large Scale Organization Suprangtip Poonun, Sotarat Thammaboosadee and Supaporn Kiattisin Mahidol University, Thailand Abstract—Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is critical and essential to such organization, especially to the large scale organization since its involved customers may be covered to the people, citizen, organization or government sections. Anyway, according to the nature and culture of the traditional job design, their business processes are costly and inconsistent because of their actor (or department) oriented design which leads to the difficulties in improvements. This paper proposes an idea of improving the business processes, based on Business Process Improvement (BPI) concept in function-oriented, to solve the existing work problems and suggest the possible solution for the future to achieve the organization goal. The evaluation was done by both the officer and the executive. T047 NYSOL: A User-Centric Framework for Knowledge Discovery in Big Data Stephane Cheung, Masakazu Nakamoto, Yukinobu Hamuro Hokkaido University, Japan Abstract—NYSOL is an integrated framework of knowledge discovery leveraged by a host of data processing and data mining tools, which is underpinned by innovative research activities. Our framework is designed to integrate the process of managing large-scale information assets and knowledge discovery on one platform to improve interoperability between processes. The NYSOL framework simplifies the knowledge discovery process in an efficient manner for novice and expert users. This paper discusses the historical development of NYSOL rooting from basic data processing commands, to the recent growth of the NYSOL software ecosystem to extend support for data mining based on efficient machine learning algorithms. Initial experiments on NYSOL's GGP large-scale information processing architecture with NYSOL distributed file system (NDFS) are also presented. Observed performance of GGP demonstrates reduced overhead for inter-processing time and improvements in overall processing time. T049 3D Catalogue Based on Augmented Reality in Android Operating System Natalia Chandra, Fredy Purnomo, Michael Yoseph Ricky, Christianto Leonard, Arvian Verdian, Hendrick Bina Nusantara University, Indonesia Abstract—Along with the continued development of Smartphone and the era of globalization, human needs are increasing for technology. They continue to look for ways that can ease their lives and it is up to the explanation of the visualization that closer to the actual visualization and support fast, precise and clear retrieval of interactive information. In order to realize the visualization, augmented reality technology is being used. Augmented reality is a technology that uses camera technology to recognize real world, images, objects, and environments and superimposes virtual information and data onto reality in real time. It combines a virtual object into two or three dimensions in a real three-dimensional environment. By developing an application with augmented reality, it can help user to look more detail into a product and give advantages to company to save the brochure production cost. The development of this application is using client-side and server-side, where the client-side will be run on android smartphone and server-side using a php based web service. The goal of this paper is to develop a 3D catalogue that helps to depict a product in interactive ways with zoom, rotate, choose color, and animation features. 24 T053 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES The Evaluation of Study Success between Online Study and Classroom Study Environment Phudinan Singkhamfu Chiang Mai University, Thailand Abstract—Online study has increasingly become more attractive to students at university level due to convenience access to their instructors and to study resources. This study has developed online social network for study. It proposes to provide lesson content availability, past lecture, by sending online study lesson media to students’ mobile phone or tablet. Approximately 85 undergraduate software engineering students participated for 1.5 semesters. In comparing the use of the study toll, and without the tool, the alterations were found between traditional classroom learning style and online study. Also, the study’s aim was to attest the online study tool’s efficiency. However, these results were not obvious when the achievement factor was controlled by the limitation of time. The primary purpose of this study is to evaluate these two groups of students with extended experiment time for a noticeable result by used questionnaires course examination, and inventory of ILP[1] learning process. The observed, shows that students with online study tools scored higher on course examinations after measures by the mentioned methodology. T055 Unlock Screen Application Design Using Face Expression on Android Smartphone Rhio Sutoyo, Jeklin Harefa, Alexander and Andry Chowanda Bina Nusantara University, Indonesia Abstract—Nowadays, smartphone has been shifted as a primary needs for majority of people. This trend is making people do activities on their smartphone such as exchange information, playing games, paying bills, discussing ideas, etc. In almost every smartphone, security features (i.e. password, pin, face unlock) are already built in which are intended to protect the data inside the smartphone. Nevertheless, those security features are not perfect and have flaws either technically or by human errors. This research aim to provide an application that uses people’ facial expressions to improve the security of smartphone, namely Android. We implement face detection and expression recognition in this application as an improvement from the existing unlock screen, which is face unlock. The results that are achieved from this research is an unlock screen application on Android devices that utilizes people’ facial expression changes to open their smartphone. This application can eliminates the technical errors from existing face unlock screen application which can be deceived by photos. T060 Enhancing Server Serviceability for Mobile Applications Seon Hong Park, Jin Su Jeong and Dong Kwan Kim Mokpo National Maritime University, Korea Abstract—In mobile clouding environment, seamless service in cloud servers is one of the essential features to meet the needs of mobile users around the world. However, in some cases, such a server service may be interrupted due to upgrade issues. The changes of the server service often cause the corresponding client program to be upgraded. Depending on the circumstances, the change of the client program may be delayed. Unfortunately, the inconsistency of the program version may result in system crash since the cloud server cannot handle the client request. In this paper, we present a new approach to address the version mismatch by proxy servers based on the adapter design pattern. The primary results show that the proposed approach can enhance the reliability and availability of the cloud server. T3002 Underlying Structure of E_Learning Readiness among Palestinian Secondary School Teachers in Nablus Fuad A.A.Trayek, Mohamad Sahari Nordi, Tunku Badariah Tunku Ahmad, Mohammed AM Dwikat International Islamic University Malaysia, Malaysia Abstract—This paper reports on the results of an exploratory factor analysis procedure applied on the e-learning readiness data obtained from a survey of four hundred and seventy-nine (N = 479) teachers from secondary schools in the city of Nablus, 25 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES Palestine. The data were drawn using a 23-item Likert questionnaire measuring e-learning readiness based on Chapnick's readiness dimensions. Principal axis factoring (PAF) with Promax rotation applied on the data extracted four distinct factors supporting four of Chapnick's e-learning readiness dimensions, namely technological readiness, psychological readiness, technical-support readiness, and equipment readiness. Together these four dimensions accounted for 56% of the variance in Palestinian secondary school teachers' e-learning readiness, with technological readiness explaining 30.2% of the variance. These findings provide empirical support for the construct validity of the items and for the existence of these four factors that underlie e-learning readiness. T3004 Component-based Verification Model of Sequential Programs Pei He, Achun Hu, Dongqing Xie, Zhiping Fan Guangzhou University, China Abstract—Hoare’s logic helps with program state descriptions, but is difficult to manipulate. Model checking emerged as a new trend in program verifications is best applied to system designs rather than implementations. This paper is committed to establish a component-based verification framework that combines both of them. The method applied consists of two steps: regarding predicates as states and connecting them with functional components in light of their relationships. Once a framework is set up, both program generation and verification can be automatically carried out. The principle presented here is not only applicable to sequential programs, but also to other types of program structures and paradigm such as iteration, branch structure and grammatical evolution, etc. Session 6: IT and its Applications Chair: TBA 12 presentations Time: 4:10pm to 6:30pm Venue: Emerald Room A001 Options for Land Conservation Practices Based on Land Uses in Kungkai Watershed, Bengkulu, Sumatera, Indonesia Muhammad Faiz Barchia Faculty of Agriculture, University of Bengkulu, Indonesia Abstract— This research aims to determine options for land conservation practices based on land uses and functions in Kungkai watershed, Bengkulu, Sumatera, Indonesia. The research was conducted from March to May, 2013 in the Kungkai watershed geographically lying on between 102022’25‖ - 102036’15‖ Lat., and on 3048’25‖ - 407’37‖ Long. This area is involved of Seluma District, Bengkulu Province, Sumatera, Indonesia, with run-off along 45 km to Indian Ocean, covering of 33,134.04 ha. Land functions over the Kungkai consists of forest conservation areas of Bukit Daun and Bukit Sanggul, Semidang Bukit Kabu wildlife hunting area, and agriculture cultivation area, and of the Semidang Bukit Kabu enclave. The Kungkai watershed currently is under environmentally pressures in which 40% more categorizing poor to very poor conditions. The Semidang Bukit Kabu wildlife hunting area covering 2,275.35 Ha, or 6.88% of the Kungkai watershed almost all under poor conditions. This wildlife hunting area must be conducted reforestation and re-vegetation. People living, and their activities on the wildlife hunting area have to re-settle, and out of it. The Bukit Daun and Bukit Sanggul have any opportunities as an area of social forestry introducing agro-forestry cultivation models with planting of multi-purposes tree species. All areas of agriculture cultivation on the watershed need land conservation tillage and management with environmentally sounding for their 26 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES sustainability productivities. Options for land management practices using cover crops, minimum tillage, till bench terrace implementation needed for sustainable agriculture on the Kungkai watershed. A010 Focused ultrasound induced anti-cancer drug delivery with PLGA-DTX encapsulated alginate microbeads Zhen Jin, Yongjin Choi, Hyunchul Choi and Sukho Park Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea Abstract—Recently, to improve drug delivery efficiency in cancer therapy, many researchers have been concentrated on drug delivery system and drug loaded micro/nano particles. In addition, as induction methods for drug delivery, ultrasound, magnetic field, and infra-red light based inducting methods can be considered. Among them, focused ultrasound is regarded as a promising candidate for drug delivery system because it can penetrate into a deep site of soft tissue and focus its energy on the target lesion. In this paper, we fabricated PLGA(poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid)-DTX(docetaxel) encapsulated alginate microbeads with single-emulsion technique and aeration method. In order to choose an appropriate operating parameters (input voltage, duty factor, and burst period) of the focused ultrasound, the pressure and the temperature of focal area induced by focused ultrasound were measured with UT-325 digital thermal detector and needle hydrophone (Muller-platte needle probe, Germany). These measuring results were compared with the simulation results using COMSOL Multiphysics 4.3a. In addition, the drug releasing rates of the PLGA-DTX encapsulated alginate microbeads induced by the focused ultrasound were tested. Through these experiments, we determined the appropriate focused ultrasound parameters as input voltage 500 Vpp, duty factor 25%, and burst period 20 . Finally, we tested cell cytotoxicity of PLGA-DTX encapsulated alginate microbeads combined with the focused ultrasound induction. We found that the focused ultrasound induction enhances anti-tumor effect more than 10 %. Consequently, we confirmed that the focused ultrasound can be an effective induction method for anti-cancer drug delivery system. A017 Light-assisted Direct Writing, Visualizing, Analyzing System for Micro Pattern using Biomaterials Li Hao, Seong Young Ko, Jong-Oh Park, and Sukho Park Chonnam National Univ, Republic of Korea Abstract—Micro-patterning techniques for additive manufacturing, known as three-dimensional (3D) printing is driving major innovation in many years. Especially in the arrangement of biomolecules and cells at micro-scale, it allows the development of clinically relevant tissues composed of multiple cell types in complex architecture. However, most micro-patterning techniques are just focusing on printing, not for visualizing or analyzing. We report here a multifunctional platform which can be used for light-assisted direct-writing, visualizing, and analyzing for biomaterials. The thermal responsive hydrogel poly-N-isopropylacrylamide (PNIPAM) sample solution was chosen to evaluate this multifunctional platform. The sample was put on the substrate and its polymerization process was recorded and analyzed under the direct writing system and vision system. Besides, the swelling/de-swelling properties of PNIPAM were studied by the cooling system. The multifunctional platform developed in this paper could be used for various applications such as, microfluidics, drug delivery, cell and tissue culturing, high resolution 2D/3D printing, visualize the polymerization procedure, and analyzing or stimulation the micro-pattern. A018 Design of 3-D compound Tactons for navigation information display Zhen Jia, Jianqing Li, Wanpei Geng Southeast University, China Abstract—Different from transformational Tactons, compound Tactons are a sequence of two or more one-element Tactons. Previous studies have investigated the perception of transformational Tactons which encode two or more dimensions of information using various vibrotactile parameters. Little has been done on how to design compound Tactons to present non-visual information effectively. This paper investigates recognition rates for compound Tactons which encode multidimensional navigation information. Experimental results show that overall identification rate for three-parameter Tactons is 92.65% by using different vibrotactile 27 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES parameters, suggesting compound Tactons are a promising method of conveying complex information. This study will guide designers to select suitable compound Tactons for use when navigating in a virtual or real urban environment. T008 A Framework for Information Accuracy (IA) Assurance Practices in Tourism Business (TB) Sivakumar Pertheban, Mohd Naz'ri Mahrin and Bharanidharan Shanmugam Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Abstract—Tourism Business (TB) is the world prominent profitable industry. Development and future of the TB recognized as financial driven to increase and contributes to a country financial performance. The major concerns in current TB, information’s are mean to be overwhelming, lack of accurate information and unfiltered information that makes available through web repositories, social networks and tourists/travellers service/agencies or information centres’. Failure of Information Accuracy (IA) Assurance in TB influences poor decision making capability among the tourists/travellers. Tourism related information’s can be improved to obtain good trust, reduce discrepancy and increase IA Assurance. As the quality of the information is vital, IA Assurance is the major research concern to ensure the only trusted and accurate information available for tourists/travellers as a guide to make a decision. This paper will address the issues of IA in TB to propose IA Assurance Practices Framework for TB to ensure a good accuracy level of information being used for decision making. T014 Designing Basic Relational Database for Analysis Land-Use Change Orawit Thinnukool, Noodchanath Kongchouy Chiang Mai University, Thailand Abstract—The processing and analysis of spatial data especially land-use are becoming increasingly dependent on the methodology used in managing the data rather than only using only Geographic Information System (GIS) software. Our approach in handling spatial data for recorded land-use data using basic land-use concept saves cost and is effective for developing land-use analysis. The aim of the study is to design and explain how land use data can be retrieved and managed by a free. The example was used to analyze land-use change, with freely available tools. These tools can handle the spatial data very well. The computation was based on the actual number of observations via Google Earth with free version on pilot area. The results demonstrate the use of normal statistics analysis for prediction in the analysis of land use change is easy to understand. T024 An Edge-Based Algorithm for Spatial Query Processing in Real-Life Road Networks Ye-In Chang, Meng-Hsuan Tsai, and Xu-Lun Wu National Sun Yat-sen University, Taiwan Abstract—Due to wireless communication technologies, positioning technologies, and mobile computing develop quickly, mobile services are becoming practical and important on big spatiotemporal databases management. Mobile service users move only inside a spatial network, e.g. a road network. They often issue the K Nearest Neighbor (KNN) query to obtain data objects reachable through the road network. The challenge problem of mobile services is how to efficiently answer the data objects which user interest to the corresponding mobile users. Lu et al. have proposed a RNG (Road Network Grid) index for speeding up the KNN query on real-life road networks. Since they divide the road, this makes the number of points of the graph increase. It increases the execution time of constructing the index structure. Therefore, in this paper, we propose a network model that captures the real-life road networks. We map the real-life road networks into graph directly. Then, based on our network model, we propose an EBNA (Edge-Based Nine-Area tree) index structure to make the search time of obtaining the interest edge information quickly. From our simulation result, we show that the performance of constructing the EBNA index is better than constructing the RNG index and the performance of the KNN query processing by using EBNA index is better than the KNN query processing by using RNG index. T029 The Relationship between Technology Planning Capability Enhancement, the Technology Roadmap, and Innovation 28 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES WON IL LEE Hanbat National University, South Korea Abstract—This paper studies the link between enhanced technology planning capabilities, the adoption of a technology roadmap, and innovation in organization in R&D organizations. A case study approach was used to examine the implementation of a technology management framework, the degree of institutionalization of a technology roadmap, and the impact on innovation. Based on the case analysis, the following propositions are suggested.(P1) The establishment of a technology management framework can have a positive effect on the adoption and utilization of a technology roadmap. (P2) The adoption and utilization of a technology roadmap map can have a positive effect on innovation within an organization. Thus, this study analyzes the mechanism of technology planning and its effect on innovation within an organization. T035 Discovering Association between Metabolic Syndrome and Its Related Chronic Diseases Represented by ICD-10 Code Supak Iamongkot, Sotarat Thammaboosadee and Supaporn Kiattisin Mahidol University, Thailand Abstract—This paper applies the association rules method to discover the relationship between metabolic syndrome and its chronic diseases. The sample data used in this research is medical records specified to metabolic syndrome patients in a large government hospital. The Apriori and FP-Growth algorithms are chosen to be compared in the performance and applicable results of extracting the relationship of the metabolic syndrome patient records represented by ICD-10 code. The results show that the Apriori can extract 6 rules and 724 rules from FP-Growth. The comparative results between Apriori and FP-Growth found that 6 rules are common. The overall results show that the metabolic syndrome patients mostly have strong relationships with hypertension, obesity and diabetes. Interestingly, these diseases often occur with the patients was diagnosed that was metabolic syndrome. Additionally, the results would bring to the suggestion in metabolic syndrome patients to know about the relationship of these chronic diseases. Moreover, the physicians could use this guide for the treatment strategy in the future. T045 Variability Model Implementation on Key Performance Indicator Application Meiliana, Derwin Suhartono Bina Nusantara University, Indonesia Abstract—Key Performance Indicators evaluate the success of an organization of a particular activity. A case study describes a continuous improvement of key performance indicators’ specification process that is updated beginning of each year on Bina Nusantara University. The process is specified based on organization’s goal, and will be break down to all existing unit with different specific performance indicator. This specification process will lead to variability indicators in several available roles. Variability model used in this paper was designed from a design pattern as one of variability mechanism that is modelled to reflect metric specification process. Variability occurs as varying degree of metrics entity specification process, which is similar to Key Performance Indicator specification process. Modelling variability on key performance indicator specification process aims to support flexibility on specifying generic goal to specific measurement or indicators. Implementing variability model to key performance indicator specification process is the focus of this paper, with support tool of Key Performance Indicator specification process provided. T057 Internet CaféManagement System with Remote Control and Bypass Features Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew, Channarong Janpanich, Suchart Joolrat, Patcharaporn Jiranuwattanawong, Kittiphan Sornsakda, Arnut Chaosakul Khon Kaen University, Thailand 29 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES Abstract—Currently we are now in the digital era where the smart phones and the internet fee are cheaper. However, there is still the need for the internet caféfor teaching, training, or students with financial problems. Thus, it is important to have efficient internet cafésoftware to management college cluster rooms. There are existing internet caféprograms, but they can setup on only Windows XP and users must login twice to authenticate the service. We have designed and developed the system that consists of three parts: web service, web application, and windows application. The purpose of web service is to transfer data between web application and windows application. The developed web application is designed to manage interface and perform remote control on the client computers. Furthermore, for authorized users whose information may not be in the directory service, they can login to the system with the implemented bypass feature enabled by only internet caféstaff. The developed windows application is designed to lock screen and receive order from the web application. With the implemented system, internet café staff feels more convenient in managing computers and students can login to computers more quickly. T3008 A Low Cost Serious Failure Tolerance Solution in Unreliable NoCs Letian Huang, Guangjun Li, Xiaofan Zhang, Zhiyong Guo University of Electronic Science and Technology of China Abstract—Faults may occur in numerous locations of a router in a Network on Chips (NoCs) platform, special in low power NoCs. Most of the researchers only focus on the effects of the faults in the data path. However, the effects in the control path may cause more seriously failure in NoC such as deadlock or live lock. In this paper, we analysis the probability of the serious failure in NoCs and propose a mechanism to reduce the failures. This mechanism is called LCEC, standing for four distinguishing characteristics of the proposed method as Low Cost Error Correct. The proposed mechanism is not limited to special types of faults or specific router components while it has the capability to tolerate faults by using simple error correct codes and scaling the clock frequency. Tips: The best paper will be selected after each session and the certificate will be awarded by the chair. Good Luck! Tuesday Evening, Feb. 3 6:30 pm to 8:30 pm--Dinner Location Restaurant Tips: The Dinner will start at 6:30pm. Please kindly attend on time with bringing the Dinner Coupon. 30 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES 31 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES 32 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES 33 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES 34 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES 35 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES 36 2015 SINGAPORE CONFERENCES Please take a few moments to provide us some important feedback about your professional development of Singapore conferences. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Conference Feedback Use the key below Very Good□ Good□ Poor□ Use the ranking key above as appropriate to answer the questions below on the blank spaces provided at the end of each questions How was the overall organization of the conference How do you rate the registration area How do you rate the presenter(s) Did you gain any helpful skills How was the format of the meeting in terms of lunch, coffee breaks? Overall, how were the conference facilities How was the reception you received at the conference How was the venue List other locations where you think future meeting should be held Why did you choose that venue? Generally, how was the whole experience at the meeting, and given another chance would you attend or recommend next year's conference? Comments and Suggestions 37
© Copyright 2026