Ch 4 motion test review
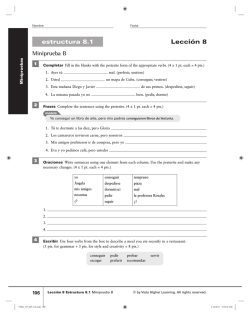
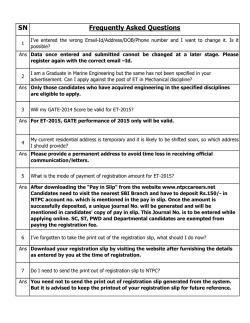
ch 4 review 2015 Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. ____ 1. Speed is a variable that tells you how fast something is going and in what direction. _________________________ ____ 2. A steeper line on position vs. time graph means a slower speed. _________________________ ____ 3. When there is acceleration, a position vs. time graph is a curve. _________________________ ____ 4. Displacement includes both distance and direction. _________________________ ____ 5. Motion occurs when there is a change in speed. _________________________ ____ 6. If you were trying to get out of the way of a storm, you would need to know the speed at which it was moving. _________________________ ____ 7. Acceleration occurs when velocity changes. _________________________ ____ 8. If you roll a ball up a hill, it undergoes positive acceleration. _________________________ ____ 9. When you push on a sled and it begins to go downhill, you cause negative acceleration. _________________________ Completion Complete each statement. Select the correct term to complete each sentence. Terms may be used more than once. constant speed positive average acceleration velocity frames of reference curved displacement instantaneous distance 10 vectors acclerate direction negative resultant vector initial final 10. The total distance traveled divided by the total time of a trip is called ____________________ speed. 11. Speed that stays the same is called ____________________ speed. 12. The speed you have at a specific point in your journey is best called ____________________ speed. 13. The rate of change in the velocity of an object is called ____________________. 14. ____________________ is a measure of how far an object has moved. 15. The speed and direction with which an object moves is its ____________________. 16. The distance an object travels per unit of time is ____________________. 17. The slope of the distance-time graph gives the ____________________. 18. Acceleration occurs when an object changes its ____________________ or ____________________ or both. 19. An object changing its speed from 10 m/s to 3 m/s is undergoing ____________________ acceleration. 20. As a car slows down approaching a red traffic light its ____________________ is negative. 21. When calculating acceleration, to find the change in velocity, you subtract the ____________________ velocity from the ____________________ velocity. 22. The motion of an object looks different to observers in different ______________________________. 23. The direction and length of a straight line from the starting point to the ending point of an object’s motion is ____________________. 24. Displacement and velocity are examples of ____________________ because they have both magnitude and direction. 25. The sum of two or more vectors is called the _________________________. 26. A car’s speedometer measures _________________________. 27. The difference between speed and velocity is that velocity indicates the ____________________ of motion and speed does not. 28. A distance-time graph indicates an object moves 20 km in 2 h. The average speed of the object is ____________________ km/h. 29. A moving object does not ____________________ if its velocity remains constant. 30. A car that increases its speed from 20 km/h to 100 km/h undergoes ____________________ acceleration. 31. A constant slope on a distance-time graph indicates ____________________ speed. 32. Because its ____________________ is always changing, an object moving in a circular path experiences a constant change in velocity. 33. Accelerated motion is represented by a(an) ____________________ line on a distance-time graph. Matching Choose the type of acceleration from the list below that would BEST describe the motion of the objects described. Types of acceleration may be used once, more than once, or not at all. a. positive acceleration b. negative acceleration c. no acceleration ____ 34. A car traveling straight on a highway at 60 mph using cruise control ____ 35. A motorcycle slowing down ____ 36. A baseball dropped from the roof of a building ____ 37. A girl on a skateboard going around a corner at a speed of 3 m/s ____ 38. A truck parked at a rest area Short Answer 39. A truck travels to and from a stone quarry that is located 2.5 km to the east. What is its distance? What is its displacement? 40. A car is driving down a road. Is it possible for its position to be changing and its acceleration to be zero? Is it possible for its velocity to be changing and its acceleration to be zero? 41. A car has an acceleration of –5 m/s2. Describe the car’s motion. Problem 42. A cross-country runner runs 10 km in 40 minutes. What is his average speed? 43. A high speed train travels with an average speed of 227 km/h. The train travels for 2 h. How far does the train travel? 44. Find the acceleration of a car that goes from 32 m/s to 96 m/s in 8.0 s. ch 4 review Answer Section MODIFIED TRUE/FALSE 1. ANS: F, velocity PTS: 1 2. ANS: F faster greater DIF: basic REF: section 4.1 PTS: 3. ANS: REF: 4. ANS: OBJ: 5. ANS: DIF: basic REF: section 4.2 PTS: 1 1 T section 4.3 T 1/1 F, position DIF: basic PTS: 1 STA: PS.B.8.1 | PS.B.8.2 DIF: B PTS: 1 6. ANS: F, velocity DIF: B OBJ: 1/1 STA: PS.B.8.1 | PS.B.8.2 PTS: 7. ANS: OBJ: 8. ANS: 1 T 4/2 F, negative DIF: B OBJ: 2/1 PTS: 1 STA: PS.B.8.1 | PS.B.8.2 STA: PS.B.8.1 | PS.B.8.2 DIF: B PTS: 1 9. ANS: F, positive DIF: B OBJ: 5/2 STA: PS.B.8.1 | PS.B.8.2 | PS.B.8.3 DIF: B OBJ: 5/2 STA: PS.B.8.1 | PS.B.8.2 | PS.B.8.3 DIF: basic REF: section 4.1 PTS: 1 DIF: basic 12. ANS: instantaneous REF: section 4.1 PTS: 1 13. ANS: acceleration DIF: basic REF: section 4.1 PTS: 1 14. ANS: Distance DIF: basic REF: section 4.3 PTS: 1 COMPLETION 10. ANS: average PTS: 1 11. ANS: constant PTS: 1 15. ANS: velocity DIF: B OBJ: 1/1 STA: PS.B.8.1 | PS.B.8.2 PTS: 1 16. ANS: speed DIF: B OBJ: 2/1 STA: PS.B.8.2 | PS.B.8.3 PTS: 1 17. ANS: speed DIF: B OBJ: 2/1 STA: PS.B.8.2 | PS.B.8.3 PTS: 1 DIF: B OBJ: 3/1 STA: PS.B.8.2 | PS.B.8.3 | SI.B.7.7 | SI.B.8.3 18. ANS: speed, direction PTS: 1 19. ANS: negative DIF: B OBJ: 4/2 STA: PS.B.8.1 | PS.B.8.2 | PS.B.8.3 PTS: 1 20. ANS: acceleration DIF: B OBJ: 6/2 STA: PS.B.8.1 | PS.B.8.2 | PS.B.8.3 PTS: 1 21. ANS: initial, final DIF: B OBJ: 5/2 STA: PS.B.8.1 | PS.B.8.2 | PS.B.8.3 PTS: 1 DIF: B 22. ANS: frames of reference OBJ: 6/2 STA: PS.B.8.2 | PS.B.8.3 | SI.B.8.4 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 23. ANS: displacement OBJ: 11.1.1 PTS: 1 24. ANS: vectors DIF: L1 OBJ: 11.1.3 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 25. ANS: resultant vector OBJ: 11.1.3 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 26. ANS: instantaneous speed OBJ: 11.1.4 PTS: 1 27. ANS: direction DIF: L1 OBJ: 11.2.2 PTS: 1 28. ANS: 10 DIF: L1 OBJ: 11.2.3 PTS: 1 29. ANS: accelerate DIF: L2 OBJ: 11.2.4 PTS: 1 30. ANS: positive DIF: L1 OBJ: 11.3.1 PTS: 1 31. ANS: constant DIF: L2 OBJ: 11.3.5 PTS: 1 32. ANS: direction DIF: L2 OBJ: 11.2.3 PTS: 1 33. ANS: curved DIF: L1 OBJ: 11.2.5 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 OBJ: 11.3.4 PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: MATCHING 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: C B A A C 1 1 1 1 1 intermediate intermediate intermediate intermediate intermediate REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: section 4.3 section 4.3 section 4.3 section 4.3 section 4.3 SHORT ANSWER 39. ANS: 5 km, 0 km PTS: 1 DIF: B OBJ: 1/1 STA: PS.B.8.1 | SI.B.8.4 40. ANS: Yes, it could have constant speed. No, a change in velocity is always an acceleration. PTS: 1 DIF: A OBJ: 4/2 41. ANS: The car is slowing down at the rate of 5 m/s every second. PTS: 1 DIF: A OBJ: 5/2 PROBLEM 42. ANS: s = d/t = 10 km/40 min = 0.25 km/min PTS: 1 DIF: A OBJ: 2/1 STA: PS.B.8.1 | PS.B.8.2 | PS.B.8.3 | SI.B.8.4 43. ANS: d = s y = 227 km/h (2.00 h) = 454 km PTS: 1 DIF: A OBJ: 2/1 STA: PS.B.8.1 | PS.B.8.2 | PS.B.8.3 | SI.B.8.4 44. ANS: STA: PS.B.8.1 | PS.B.8.2 | PS.B.8.3 STA: PS.B.8.1 | PS.B.8.2 | PS.B.8.3 vf – vi/t = (96 m/s – 32 m/s)/ 8.0 s = 8.0 m/s2 PTS: 1 DIF: A OBJ: 6/2 STA: PS.B.8.1 | PS.B.8.2 | PS.B.8.3 | SI.B.8.4
© Copyright 2026