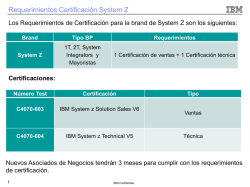
Descargar PDF
NEWS GMV COMPLETES STRATEGIC INVESTMENT IN U.S. COMPANY SYNCROMATICS P. 27 ACTIVE GMV PARTICIPATION IN EGS-CC, THE ESA’S NEW GROUND INFRASTRUCTURE GMV REALIZA UNA INVERSIÓN ESTRATÉGICA EN LA NORTEAMERICANA SYNCROMATICS ACTIVA PARTICIPACIÓN DE GMV EN LA NUEVA INFRAESTRUCTURA EGS-CC DE LA ESA P. 32 ROBOTIC ADVANCES IN SPACE REFUELING SYSTEMS AVANCES EN ROBÓTICA PARA SISTEMAS DE REPOSTAJE ESPACIALES www.gmv.com Nº 60 SEPTEMBER/SEPTIEMBRE 2015 THE NEW TECHNOLOGIES AND THE NEW TRANSPORT AND MOBILITYSERVICES LAS NUEVAS TECNOLOGÍAS Y LOS NUEVOS SERVICIOS DE TRANSPORTE Y MOVILIDAD P. 35 GMV FURNISHES NATO WITH A NEW INTELLIGENCE SYSTEM GMV PONE A DISPOSICIÓN DE LA OTAN UN NUEVO SISTEMA DE INTELIGENCIA P. 43 CARL ZEISS WILL MARKET GMV’S INTRAOPERATIVE RADIOTHERAPY PLANNER CARL ZEISS COMERCIALIZA EL PLANIFICADOR DE RADIOTERAPIA INTRAOPERATORIA DE GMV P. 45 GMV CONSOLIDATES ITS BUSINESS IN NORTH AFRICA GMV CONSOLIDA SU PRESENCIA EN EL NORTE DE ÁFRICA INTERVIEW / ENTREVISTA J. DIONISIO GONZÁLEZ STRATEGIC PLANNING AND OPERATIONS MANAGER MADRID REGIONAL PUBLIC TRANSPORT AUTHORITY (CRTM) DIRECTOR DE PLANIFICACIÓN ESTRATÉGICA Y EXPLOTACIÓN DEL CRTM IF YOU ARE INTERESTED IN MEETING US, WE WILL BE ATTENDING THE FOLLOWING EMPLOYMENT EVENTS SOON SI ESTÁS INTERESADO EN CONOCERNOS ACUDIREMOS A LOS SIGUIENTES EVENTOS DE EMPLEO PRÓXIMAMENTE We’ll be expecting you! If you need any further information you can contact us at [email protected] ¡Te esperamos! Si necesitas más información puedes contactar con nosotros en [email protected] NOVEMBER 3rd of November MADRID FORO DE EMPLEO 3U. Moncloa Campus. Ciudad Universitaria. 4th of November BARCELONA 2N NETWORKING TALENT DAY. Nord Campus at UPC. 5th of November TOULOSE FORUM TOULOUSE. Exhibition and conference venue Diagora. 6th of November LONDON CAREERS IN AEROSPACE LIVE. Royal Aeronautical Society. 26th-29th of November MADRID . CYBERCAMP. BarclayCard Center in Madrid Nº 60 SEPTEMBER SEPTIEMBRE LETTER OF THE 2015 CONTENTS CONTENIDOS 4 SPECIAL ARTICLE / ARTÍCULO ESPECIAL GMV COMPLETES STRATEGIC INVESTMENT IN U.S. COMPANY SYNCROMATICS GMV REALIZA UNA INVERSIÓN ESTRATÉGICA EN LA NORTEAMERICANA SYNCROMATICS 10 INTERVIEW / ENTREVISTA J. DIONISIO GONZÁLEZ Strategic Planning and Operations Manager Madrid Regional Public Transport Authority (CRTM) Director de Planificación Estratégica y Explotación del CRTM 15 ARTICLE / ARTÍCULO THE NEW TECHNOLOGIES AND THE NEW TRANSPORT AND MOBILITY SERVICES LAS NUEVAS TECNOLOGÍAS Y LOS NUEVOS SERVICIOS DE TRANSPORTE Y MOVILIDAD By/por: Sara Gutiérrez Lanza 19 GMV NEWS / ACTUALIDAD DE GMV 19 AERONAUTICS / AERONÁUTICA 20 SPACE / ESPACIO 30 ROBOTICS / ROBÓTICA 33 DEFENSE & SECURITY / DEFENSA Y SEGURIDAD 37 INFORMATION SECURITY / SEGURIDAD DE LA INFORMACIÓN 41 HEALTHCARE / SANIDAD 44 TRANSPORTATION / TRANSPORTE 50 TELECOMMUNICATIONS / TELECOMUNICACIONES 51 PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION AND LARGE CORPORATIONS / AAPP Y GRAN EMPRESA Published / Edita GMV Editorship-Coordination / Dirección-Coordinación Miguel A. Martínez, Marta del Pozo Area Heads / Responsables de área Miguel A. Martínez, Ángeles García, Miguel Ángel Molina, Isabel Tovar Writing / Redacción Ambroise Bidauz-Sokolowski, Alfredo Gadea, Ángeles García, Paulo Gomes, Mariella Graziano, Antonio Hernández, Marta Jimeno, Alberto Medina, Mónica Montalvillo, Tomas Morel, Hector Naranjo, José Neves, Jorge Ocón, Marta del Pozo, Enrique Rivero, Javier Sanz, Mateo Suatoni, Antonio Tabasco, Juan Tejo Art, design and layout / Arte, diseño y maquetación Francisco Huertas, Paloma Casero MORE INFORMATION MÁS INFORMACIÓN [email protected] +34 91 807 21 00 PRESIDENT CARTA DE LA PRESIDENTE I use my car every day as the quickest way, in theory, of commuting from home to work. The trouble is I run into many other car drivers on the freeway with exactly the same idea and between us all we make our journey much slower. Half the world’s population now lives in urban areas and this proportion is set to grow in the future, worsening the already dire traffic situation. Nowadays, however, there is a growing range of alternatives to private car commuting. The local train line, buses and subway trains, plus bikehiring and ridesharing schemes are only some of the more widely adopted methods. Taken singly, these alternative means of transport often fail to provide the direct connection we need but, taken together, they are certainly an interesting option. Youngsters in the USA have now cottoned on to this. In the past the USA has always been the big-car country par excellence but this picture is now changing, and buying a car or even getting a driving license no longer features among top priorities on coming of age. To tap into the full potential of these mixed-mode commuting schemes there is a pressing need for information systems that enable operators to offer a punctual service and users to plan their journeys with trustworthy data. GMV’s wide range in this field caters equally for major public transport operators, who can afford to run servers on their own sites, and also smaller fleets who can use our inhouse MOVILOC® system to manage their fleets over the internet. Our acquisition of a majority share in the company Syncromatics has now enabled us to bring in a new range of US-market-targeted public transport products that complement and top up GMV’s existing range. We give a cordial greeting to a team of professionals who enjoy an excellent reputation among their clients and are certain to help us drive our growth in this market. Utilizo mi coche a diario porque pienso que es la forma más rápida para llegar desde casa al trabajo. Pero en la autopista me encuentro con mucha gente en sus coches que piensa como yo, y entre todos provocamos que el viaje ya no sea tan rápido. La mitad de la población humana hoy vive en zonas urbanas, y esa proporción seguirá creciendo en el futuro, agravando aún más los problemas de tráfico. Por otro lado, existen cada vez más alternativas al transporte individual en coche. Hay trenes de cercanías, autobuses y metro, y también bicicletas de alquiler y coches compartidos, por mencionar solo algunos de los medios más extendidos. A menudo estos medios de transporte no ofrecen la conexión directa que necesitamos, pero en combinación pueden resultar muy interesantes. De ello ya se han dado cuenta los jóvenes en USA, país desde siempre entusiasta de los coches grandes, entre cuyas prioridades ya no figura comprarse un coche, ni siquiera sacarse la licencia en cuanto alcanzan la edad necesaria para ello. Para poder aprovechar ese potencial que tiene el transporte intermodal son esenciales los sistemas de información, que permiten al operador ofrecer un servicio puntual y al usuario planificar su viaje con datos fiables. La amplia oferta de GMV cubre las necesidades de operadores grandes de transporte público con sistemas instalados en las instalaciones del cliente, así como la de flotas más pequeñas con MOVILOC®, nuestro servicio de gestión de flotas a través de internet. Con la adquisición de una participación mayoritaria en la empresa Syncromatics ahora ampliamos nuestra oferta con una gama de productos para el transporte público complementaria a la de GMV y desarrollada específicamente para el mercado norteamericano. Damos la más cordial bienvenida a un equipo de profesionales de excelente reputación entre sus clientes, que nos permitirá crecer de forma acelerada en ese mercado. Cordial greetings, Saludos cordiales, GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 3 © GMV, 2015 SPECIAL ARTICLE / ARTÍCULO ESPECIAL GMV COMPLETES STRATEGIC INVESTMENT IN U.S. COMPANY SYNCROMATICS On 31 July 2015 GMV signed a purchase-and-sale agreement with the shareholders of the California-based technology company Syncromatics Corp. Under this agreement GMV makes a strategic investment in the capital of this company, a supplier of Software as a Service (SaaS) solutions for the intelligent transportation systems (ITS) market. This investment in the Californian technology company boosts GMV’s expansion capacity in the USA and cements its position in the global ITS market. GMV has been pursuing an international growth and expansion strategy for some years now, with the USA always a top priority. The company has been running a US subsidiary since 2004 and had pinpointed a big growth opportunity in the expanding public-transport ITS market. In this context Syncromatics offers GMV an excellent springboard for further growth within this market in the USA. Syncromatics has an unimpeachable reputation on its own patch. It is valued very highly by its clients and its highly skilled managerial, commercial and technical staff are all blessed with excellent local knowledge. Its technological offer is well suited to the US market and is complementary to GMV’s, promising well for the latter’s growth prospects. This share purchase will also bring commercial, technological and operational synergies into play between the two companies, further boosting the company’s growth and the value of its products and services both inside and outside the USA. GMV REALIZA UNA INVERSIÓN ESTRATÉGICA EN LA NORTEAMERICANA SYNCROMATICS El día 31 de julio GMV firma un acuerdo de compra-venta con los accionistas de la compañía tecnológica Syncromatics Corp radicada en California, en virtud del cual GMV realiza una inversión estratégica en el capital de la empresa, proveedor de soluciones SaaS para el mercado norteamericano de sistemas inteligentes de transporte público. Con esta inversión GMV amplía su capacidad de expansión en EE.UU. y consolida su posición en el mercado global de sistemas ITS para el transporte. Dentro de la estrategia de expansión internacional y crecimiento en la que GMV está inmersa desde hace varios años, EE.UU. viene siendo una apuesta prioritaria. GMV ya cuenta con una filial en EE.UU. desde 2004 y había identificado una gran oportunidad de crecimiento en el mercado en expansión de los sistemas inteligentes para el transporte pág. 4 I GMV NEWS nº60 Septiembre 2015 público. En este contexto Syncromatics ofrece a GMV una excelente base para aprovechar ese mercado en expansión y crecer de forma acelerada en EE.UU. Syncromatics tiene una reputación local intachable, está muy bien valorado por los clientes, cuenta con un equipo directivo, comercial y técnico altamente cualificado que conoce muy bien el mercado local sobre el que GMV puede crecer y además cuenta con una oferta tecnológica adaptada al mercado norteamericano complementaria con la de GMV. Por otro lado esta adquisición permitirá la explotación en el futuro de sinergias muy relevantes, tanto comerciales como tecnológicas y operativas, que permitirán multiplicar el crecimiento de la compañía y la creación de valor para GMV dentro y fuera de EE.UU. TECHNOLOGY Syncromatics offers end-to-end operational management systems and advanced passenger-information systems for public bus fleets; this technology might best be defined as a “light, cloud-hosted fleet-management system”. Its business model is SaaS (Software as a Service). Like GMV’s own traditional fleet-management systems, Syncromatics Corp’s solutions are designed to help publictransport companies keep their fleets running to plan, recording along the way transit intelligence of ridership and performance. The ultimate aim is to improve the quality of the service offered to passengers on the strength of better information and impeccable schedule adherence. The SaaS business model is also ideal for the US market and it fits in with and complements GMV’s traditional range of services. As with GMV’s traditional fleet-management systems, the vehicle tracking technology is a key component of Syncromatics Corp’s services although it represents only a small part of the great variety of advanced technologies tapped into to offer a useful end-to-end solution for the target market. The range of solutions offered by Syncromatics includes several of the hallmark features of GMV’s traditional fleet management systems: Real-Time Passenger Information. Providing information about where the next bus is, how full it is, and when it will be arriving to riders. This information is available on the web, on mobile phones, by telephone, by text message, and on solar powered signs at bus stops. Automated Passenger Counting. Using automated infrared sensors mounted above the doorways in each bus, Syncromatics offers a suite of reporting and analysis tools designed to help transit operators make informed decisions based on how riders are using their system Real-Time Dispatching and Analysis Tools. Syncromatics provides a number of real-time services designed to assist your organization’s dispatchers in diagnosing and responding to issues affecting service quality. For example, Syncromatics offers an anti-bunching console which color codes the distance between vehicles on a route so dispatchers can see if buses are too close or too far from each other. In-Vehicle Monitoring and Analysis Technologies. Inside the bus, Syncromatics specializes in a variety of transit technologies that enhance both the rider experience and your organization’s ability to effectively manage the vehicle environment. This includes automated passenger counting, mobile data terminals, and engine telemetry. Extensive Reporting. Data is what drives decisions in a transit operation. The proposed system includes a number of customizable reports, monitoring operational metrics like speed limits, schedule adherence, average passenger wait time and peak traffic periods. OFERTA TECNOLÓGICA Syncromatics ofrece una solución end to end´ de gestión operativa e información avanzada al pasajero para transporte público de autobús que se podría definir como un “SAE ligero en la nube” en un modelo de negocio tipo SaaS (Software as a Service). Al igual que los sistemas que GMV tradicionalmente viene ofreciendo, las soluciones de Syncromatics están encaminadas a ayudar a las empresas de transporte público a mantener su flota funcionando según la planificación prevista, capturar métricas operacionales objetivas de usuarios y rendimiento, y mejorar el servicio prestado a los pasajeros a través de una mejor información y regularidad del servicio. Por otro lado el modelo de negocio SaaS permite disponer de una oferta especialmente idónea para el mercado norteamericano que es además complementaria con la oferta tradicional de GMV. Al igual que en los sistemas SAE tradicionales de GMV, la tecnología de localización de vehículos es un componente clave de la oferta de Syncromatics aunque representa solo una pequeña parte de la gran variedad de tecnologías avanzadas presente para poder ofrecer una solución end to end útil para el mercado. Entre la gama de soluciones que ofrece Syncromatics nos encontramos con varias de las principales funciones típicas tradicionalmente presentes en los SAE de GMV: Información al pasajero en tiempo real (RTPI). Permite al pasajero conocer la localización del siguiente autobús, el número de pasajeros que lleva y cuándo llegará a la parada. Esta información está disponible en la red, en las aplicaciones móviles, por teléfono, por mensaje de texto y en paneles informativos alimentados por energía solar. Conteo automático de pasajeros (APC). Por medio de sensores de infrarrojo instalados sobre las puertas de cada autobús, se ofrecen toda una serie de herramientas de información y análisis creadas para ayudar a los operadores de tráfico a tomar decisiones bien informadas basadas en datos objetivos de utilización que hacen los usuarios de su servicio. Herramientas de análisis y gestión operacional en tiempo real. ofrece diversos servicios en tiempo real para ayudar a los operadores a controlar y distribuir eficazmente sus recursos mediante el diagnóstico y las respuestas más adecuadas a las cuestiones que afectan a la calidad del servicio. Se incluye por ejemplo la función de regulación por frecuencia que controla la distancia entre los vehículos de una misma línea para que no circulen con una separación excesivamente corta o excesivamente larga. Sistemas embarcados de control y análisis. Para el interior del autobús también se ofrece una variedad de soluciones embarcadas que mejoran tanto la experiencia del pasajero como la capacidad del operador para explotar de manera eficaz su flota. Algunos de esos sistemas son el conteo automático de pasajeros, los terminales móviles de datos y telemetría para el control de los motores. Amplia información. La información es el elemento determinante de las decisiones que se adoptan en la operación de una red de transporte. Para reunir la más completa información, el sistema incluye la posibilidad de generar informes en áreas diversas, adaptables a cada necesidad, para la supervisión de parámetros operacionales, como límites de velocidad, cumplimiento de horarios, tiempo medio de espera de los pasajeros y momentos de mayor densidad de tráfico. GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 5 SPECIAL ARTICLE / ARTÍCULO ESPECIAL CLIENTS Syncromatics enjoys an excellent reputation among its clients and boasts a highly skilled managerial, commercial and technical team. Its wide range of technology is perfectly suited to the US market, enabling it to offer innovation and a top-quality service to over 40 bus fleets throughout the USA. City of Los Angeles (LADOT) Los Angeles, CA LADOT operates the majority of the service within the Downtown Los Angeles area, with some routes having up to 14 buses at one time with 5-8 minute headways. Syncromatics developed innovative new software that gave both dispatchers and drivers visibility into the relative spacing of buses. Combined with a deployment of MDTs and engine telemetry for maintenance personnel, LADOT went from no visibility into daily operations to a command center driven by technology. “ I often cite Syncromatics and their work with the Los Angeles Department of Transportation as a great example of a very successful public-private partnership. Syncromatics does not make us just accept their product as-is. Instead they talk with us, listen and proactively learn about our pains. And then they continuously enhance and improve their product and add features to meet our needs” Jim Lefton Executive Officer, Transit Division LADOT Ciudad de Los Angeles (LADOT) Los Angeles, CA LADOT es la entidad operadora de la mayor parte del servicio de transporte urbano en el centro urbano de Los Angeles, con una dotación de hasta 14 autobuses en algunas de sus líneas y una frecuencia de paso de 5 a 8 minutos. Syncromatics desarrolló un nuevo e innovador software que permite a planificadores y conductores visualizar el intervalo relativo entre autobuses. Unido al despliegue de terminales móviles de datos (MDT) y de telemetría para motores para el personal de mantenimiento, LADOT pasó de no tener ninguna visibilidad de las operaciones diarias a operar un centro de mando basado en soluciones tecnológicas. CLIENTES Syncromatics tiene una excelente reputación entre sus clientes y cuenta con un equipo directivo, comercial y técnico altamente cualificado. Dispone de una amplia oferta tecnológica adaptada al mercado norteamericano con la que ofrece innovación y servicio de calidad a más de 40 flotas de autobuses de todo EE.UU.. “A menudo cito a Syncromatics y su trabajo con el Departamento de Transporte de Los Angeles como un magnífico ejemplo de colaboración público-privada de gran éxito. Syncromatics no nos entrega su producto así, sin más, sino que habla con nosotros, escucha y se informa de nuestros retos y dificultades. A partir de ahí, va introduciendo mejoras y añadiendo nuevas prestaciones para dar respuesta a nuestras necesidades.” Jim Lefton Director, División de Transporte LADOT OTHERS CLIENTS / Otros clientes - University of California, Irvine - University of Southern California - University of California, San Diego - University of South Florida - Key West Transit - Cleveland Area Rapid Transit - University of Delaware pág. 6 I GMV NEWS nº60 Septiembre 2015 - BP Oil, Carson Refinery - University of San Diego - Vanderbilt University - Presidio Park Shuttle, San Francisco - Old Dominion University - Cedars-Sinai Medical Center - University of California, Riverside - University of Miami - Cal Poly Pomona - California State University, Long Beach - University of California, San Francisco - University of Pennsylvania - Mississippi State University Merced County - The Bus Merced, CA Merced County Transit needed a complete ITS system passenger information (RTPI), automated passenger counting (APC), and annunciators (AVAS), and they needed it fast. Syncromatics works with alacrity and never loses sight of the needs it has to meet, always delivering a complete turnkey system on time and without overruns even after systemacceptance tests are taken into account. “ Working with Syncromatics allowed us a unique opportunity to drive product development and see measurable results. Passengers, many of whom are City employees, have come to depend on more consistent service on all our downtown routes thanks to this deployment. The data made the difference, and our operations are now much more streamlined and transparent as a result.” Rich Green Transit Manager, Merced County Transit Condado de Merced - The Bus Merced, CA La red de transporte público del condado de Merced necesitaba un sistema inteligente de transporte (ITS) completo -información al pasajero en tiempo real (RTPI), conteo automático de pasajeros (APC) y sistema de anuncios al usuario (AVAS)- y lo necesitaba rápido. Syncromatics actuó con celeridad sin perder de vista las necesidades que debía satisfacer, haciendo entrega del sistema completo en el plazo previsto, incluidas pruebas de aceptación del sistema. “Trabajar con Syncromatics nos ofreció una oportunidad única de promover el desarrollo de productos y ver resultados cuantificables. Los pasajeros, muchos de los cuales trabajan en el centro financiero, pueden disfrutar ahora de un servicio mejor planificado en todas nuestras líneas urbanas gracias a la incorporación de su sistema. Los datos han sido el gran factor de mejora y nuestras operaciones se han beneficiado con ello de una mayor organización y transparencia.” Rich Green Director de Transporte, Transporte Público del condado de Merced Marin Transit – San Rafael, CA San Rafael, CA Marin Transit and Syncromatics have enjoyed a close partnership since the initial deployment of our system in 2009. Marin initially invested in a small fleet of 11 vehicles, and has successfully implemented AVL/MDT, APC, and realtime signage options throughout the county. Following their positive experience with the company and its products, they significantly expanded their coverage to 28 vehicles system wide, with Syncromatics as a reliable partner at every step along the way. “We were very happy with the way the deployment went-it was smooth and it was effortless. At the end of the day, the team made themselves available to us, and we felt like we were dealing with the people and not a large company. I was able to pick up the phone and get answers whenever I wanted them--Syncromatics was there for us, and it speaks volumes with respect to the company and the approach.” Marin Transit – San Rafael, CA San Rafael, CA Marin Transit, entidad encargada del transporte público en el condado de Marin (California), y Syncromatics disfrutan de una estrecha colaboración desde el despliegue inicial de su sistema en 2009. El condado de Marin invirtió inicialmente en una pequeña flota de 11 vehículos en la que ha instalado con éxito sistemas AVL/MDT, APC y opciones de señalización en tiempo real, con servicio en todo el condado. Tras su experiencia positiva con la empresa y sus productos, amplió significativamente la red a 28 vehículos con Syncromatics como socio fiable en cada etapa del proceso. “Nos sentimos muy satisfechos de cómo se desarrolló el despliegue, sin contratiempos ni esfuerzo. A la finalización de la jornada, el equipo se puso a nuestra disposición y sentimos que estábamos tratando con personas y no con una gran compañía. Podíamos coger el teléfono y obtener respuestas siempre que los necesitábamos. Syncromatics estaba siempre disponible para nosotros y eso dice mucho de la empresa y de su filosofía de trabajo.” GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 7 SPECIAL ARTICLE / ARTÍCULO ESPECIAL TEAM Syncromatics was founded in 2006 by engineers from the University of Southern California who had previously worked in the transport industry. Since then the company has gone from strength to strength; it now turns over more than five million dollars a year and has 18 employees with Ian Sephton at the helm. EQUIPO Syncromatics fue fundada en 2006 por ingenieros vinculados a la Universidad de Southern California que habían trabajado anteriormente en la industria del transporte. Desde entonces, la empresa ha experimentado un fuerte crecimiento y en la actualidad factura más cinco millones de dólares y cuenta con 18 empleados. Al frente de la compañía se encuentra Ian Sephton. What does it mean for Syncromatics to bring in an investor like GMV? The strength of GMV’s brand makes a big difference in the US transit market that Syncromatics operates in. Specifically, the presence of GMV’s name and resources makes us much more competitive for larger contracts against larger competitors, and gives us the flexibility to add resources in response to bigger contract wins. We also benefit substantially from GMV’s international operating experience with more involved technologies like scheduling and voice radio integration, which are necessary to compete in the larger transit market. In short, GMV’s investment makes growth easier and faster for us in the US market. ¿Qué supone para Syncromatics la incorporación de un inversor como GMV? La fuerza de la marca GMV representa una gran diferencia en el mercado del transporte público en EE.UU. en el que Syncromatics opera. En especial, la presencia del nombre y los recursos de GMV nos hace mucho más competitivos frente a compañías de mayor dimensión a la hora de conseguir mayores contratos y nos proporciona la flexibilidad de añadir recursos en respuesta a la adjudicación de contratos de mayor importancia. También nos beneficiamos considerablemente de la experiencia operativa internacional de GMV, con una mayor oferta de soluciones tecnológicas, como las de planificación e integración de comunicaciones de voz por radio, necesarias para competir en el mercado de grandes redes de transporte. En pocas palabras, la inversión de GMV facilita nos permite crecer más y más rápido en el mercado estadounidense. ¿Cuáles cree que serán las sinergias más relevantes que podrán ser explotadas gracias al acuerdo GMVSyncromatics? La experiencia con tecnologías similares, el intercambio de información técnica, la fuerza de una marca común y la amplitud de una línea de soluciones especializadas para redes de transporte grandes y pequeñas a escala internacional. ¿Cómo afronta el personal de Syncromatics esta nueva etapa? El personal de Syncromatics se siente especialmente contento ante la posibilidad de aumentar nuestro ritmo de crecimiento y expansión ahora que contamos con un socio mayor. Nuestros equipos de ingeniería y ventas están creciendo con rapidez, lo que proporciona oportunidades de desarrollo profesional de las que antes no disfrutaba nuestro personal. También Members of Syncromatics team with the mayor of Los Angeles / Miembros del equipo de Syncromatics con el alcalde de Los Ángeles pág. 8 I GMV NEWS nº60 Septiembre 2015 Which would you regard as the most important synergies to be exploited on the strength of the GMV-Syncromatics agreement? Experience with similar technologies, sharing of technical information, strength of the common brand, and a depth of specialized offerings from small to large transit properties on an international scale. What is the take of Syncromatics’s personnel on this new stage? The staff at Syncromatics is especially excited about the ability to grow and expand faster now that we have a larger partner. Our engineering and sales teams are growing fast which provides career growth opportunities for our staff that were not previously present. They also recognize the GMV brand and team can only help us as we grow. How is this integration process being viewed by your clients? Many of our clients are especially concerned with the stability and financial strength of Syncromatics itself, and GMV’s presence both operationally and financially is a benefit to that. reconocen que la marca y el equipo de GMV nos ayudarán en nuestro crecimiento. ¿Cómo se percibe este proceso de integración entre sus clientes? Muchos de nuestros clientes tienen especial interés por la estabilidad y la fortaleza financiera de la propia Syncromatics y la presencia de GMV nos beneficia tanto desde el punto de vista de las operaciones como de la solidez financiera. Además, la dirección de GMV ha dejado claro que seguiremos operando en el mismo mercado, con los mismos productos y las mismas personas, lo cual ha tranquilizado a nuestros clientes, que están contentos con nuestro servicio y desean que siga creciendo igual que hasta ahora. ¿Cuáles son los valores de Syncromatics que les identifican como empresa referente en el sector y les distinguen con respecto a la competencia? ABOUT SYNCROMATICS Year founded: 2006 Sector: Transport No. of employees: 18 Turnover: $4 million CEO: Ian Sephton Head office: 523 W 6th St Suite 444 Los Angeles, California 90014 Clients: 40 operators from different states and over 1079 buses, pride of place going to the 300-bus fleet of the Los Angeles Department of Transportation (LADOT). Contact: [email protected] Other information of interest: winner of the California Clean Tech Transportation Prize and one of the quickest growing private firms in 2015, according to Inc. Magazine Additionally, GMV’s senior leadership has made it clear that we will continue to operate in the same market, with the same products and the same people—this is comforting to our clients who are happy with our service and want to see it continue to grow in the same fashion it has before. What are Syncromatics’s hallmark values that make you stand out from your competitors within the sector? Without a doubt, Syncromatics has grown because of our commitment to customer service and relationships. Our product is strong, but what has really helped us grow is our careful handling of unique client situations when things don’t go as planned. Syncromatics and GMV share this value especially a commitment to service and integrity that is especially valued in our market. Further, although Syncromatics has a differing operating model than GMV (we are a hosted service provider), it is one that is a better fit for the small to medium transit properties in which we specialize, and is complementary to GMV’s experience as a more customized solutions provider for larger properties. Sin lugar a dudas, Syncromatics ha crecido gracias a nuestro compromiso con el servicio al cliente y nuestras relaciones con los clientes. Nuestro producto tiene gran solidez, pero lo que nos ha ayudado realmente a crecer es el cuidado que ponemos en cada situación concreta en que las cosas no salen como estaban previstas. Syncromatics y GMV compartimos especialmente este valor —un compromiso con el servicio y la integridad altamente valorado en nuestro mercado. Por otro lado, aunque Syncromatics tenga un modelo de negocio distinto del de GMV (somos un proveedor de servicios alojados), es el que mejor se adapta a las redes pequeñas y medianas de transporte en las que estamos especializados, y es complementario de la experiencia de GMV como proveedor de soluciones más personalizadas para grandes redes. ACERCA DE SYNCROMATICS Año de Fundación: 2006 Sector: Transporte Nº de Empleados: 18 Facturación: 4 M$ Principal ejecutivo: Ian Sephton Sede: 523 W 6th St Suite 444 Los Angeles, California 90014 Clientes: 40 operadores de diversos estados y más de 1.079 autobuses entre los que destaca el departamento de transporte de la Ciudad de Los Ángeles (LADOT) con más de 300 autobuses. Contacto: [email protected] Otros datos de interés: Premio California Clean Tech y una de las empresas privadas de mayor crecimiento en 2015 según Inc. Magazine GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 9 INTERVIEW / ENTREVISTA J. DIONISIO GONZÁLEZ STRATEGIC PLANNING AND OPERATIONS MANAGER MADRID REGIONAL PUBLIC TRANSPORT AUTHORITY (CRTM) DIRECTOR DE PLANIFICACIÓN ESTRATÉGICA Y EXPLOTACIÓN DEL CRTM pág. 10 I GMV NEWS nº60 Septiembre 2015 BIOGRAPHY José Dionisio González García graduated as a civil engineer (Ingeniero de Caminos, Canales y Puertos) from Madrid Polytechnic University (Universidad Politécnica de Madrid: UPM). He then received a postgraduate degree in the Financing of Public Services and Infrastructure from the Civil Engineering College (Colegio de Ingenieros de Caminos, Canales y Puertos: CICCP) and in General Management from the IESE Business School. He also holds the diploma of the Harvard-IESE Leadership and Management Program. Before his current post he worked in the Projects Directorate of the European Investment Bank in Luxembourg and was Head of Concessions and Technical Director of the Consorcio Regional de Transportes de Madrid. He is currently also Secretary General of the Infrastructure Forum, a member of the Executive Board of the International Association of Public Transport (UITP), a member of the Construction and Infrastructure-Financing Committee of Spain’s Professional Association of Civil Engineers (Colegio de Ingenieros de Caminos, Canales y Puertos) and is the author of several technical papers. In 2009 CRTM launched the Modernization Plan of bus passenger transport services, which has now become an international benchmark. What were its objectives and its main lines of action? Service quality is directly bound up with the quality of available information. The Modernization Plan has focused on providing users with real-time information on the next arrival, destination, etc. All this information is given at intermodal transportation hubs, the most important bus-stops and onboard the busses themselves for riding passengers. For this purpose operating firms have been fitted with diverse technology such as advanced fleet-management and passengerinformation systems hooked up to an operation management center, similar to the systems already existing on other means of transport. Each one of these bus operation management centers of the bus operating firms has in turn been linked in with Madrid Region’s Integral Public Transport Management Center (Centro Integral de Gestión del Transporte Público Colectivo de la Comunidad de Madrid: CITRAM), which sees to real-time supervision and coordinates operation of all means of transport within the region. Furthermore, as part of these fleetmanagement systems, operating firms have also fitted contactless technology fare-collection systems, continuing CRTM’s ongoing strategy of recent years. Complete implementation of this technology in all means of transport operating in Madrid region was finally accomplished last December, taking in the Metro system (subway), city buses (EMT), the local commuting train line and light rail transit systems, etc. A key part of the Modernization Plan was a reduction in vehicle age, both maximum age and average throughout the fleet. Incorporation of security measures was another crucial feature (CCTV, connection to a security control center, etc), especially on the most trouble-prone lines and during the most conflictive time periods. Another top priority is to ensure that all buses are accessible for people of reduced mobility; vehicles have also been fitted with environment-friendly measures that more than comply with legal obligations. The Plan also included a series of sociallabor measures (continual top-up training of various staff categories, increasing the ratio of female workers and also hiring more disabled workers, etc), plus managerial improvements with incentives linked to service quality criteria. En 2009, el CRTM puso en marcha el Plan de Modernización del transporte público regular permanente de viajeros de uso general por carretera que, en la actualidad, es un importante referente a nivel internacional, ¿cuál era su objetivo y sus líneas maestras de actuación? La calidad del servicio está directamente relacionada con la calidad de la información disponible. El Plan de Modernización ha potenciado la provisión de información en tiempo real a los usuarios sobre los próximos servicios, tiempo estimado de llegada a destino, etcétera, tanto en los grandes intercambiadores de transporte como en las paradas más importantes e, incluso, en los sistemas embarcados dentro del propio vehículo. Para ello, las empresas operadoras se han dotado de diversas tecnologías, entre ellas, Sistemas de Ayuda a la Explotación con un Centro de Gestión de la Explotación, similar a los que ya disponían otros modos de transporte. Cada uno de los Centros de Gestión de la Explotación de las empresas operadoras de autobuses se han integrado, a su vez, en el Centro Integral de Gestión del Transporte Público Colectivo de la Comunidad de Madrid, CITRAM, desde el que se supervisa en tiempo real y coordina la explotación de todos los modos de transporte de la Comunidad. Por otra parte, e integrados en los SAE, las empresas operadoras han instalado sistemas de billetaje basados en tecnología sin contacto, continuando con la estrategia que el CRTM ha venido desarrollando durante los últimos años, hasta la implantación completa, el pasado mes de diciembre, de dicha tecnología en todos los modos de transporte (Metro, EMT, Cercanías, Metros Ligeros, etc.) que operan en la Comunidad de Madrid. Dentro del Plan de Modernización ocupa un lugar destacado la reducción de la antigüedad de los vehículos, tanto en valores máximos como medios en la flota, así como la incorporación de medidas de seguridad (CCTV, conexión a una Central de Seguridad, etcétera), sobre todo en las líneas y horarios más conflictivos. BIOGRAFÍA José Dionisio González García es Ingeniero de Caminos, Canales y Puertos por la Universidad Politécnica de Madrid (UPM), Máster en Financiación de Infraestructuras y Servicios Públicos (CICCP), Máster en Dirección General (IESE) y titulado del Programa de Liderazgo para la Gestión Pública (Harvard-IESE). Con anterioridad formó parte de la División de Proyectos del Banco Europeo de Inversiones (Luxemburgo) y fue Responsable de Concesiones y Director Técnico del Consorcio Regional de Transportes de Madrid. Actualmente es también Secretario General del Foro de Infraestructuras, miembro del Consejo de Dirección de la Unión Internacional de Transporte Público (UITP), miembro de la Comisión de Financiación de Infraestructuras y Construcción del Colegio de Ingenieros de Caminos, Canales y Puertos de España, así como autor de diversas publicaciones técnicas. GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 11 INTERVIEW / ENTREVISTA What were the main difficulties and how were they dealt with? As of 31 December 2008 Madrid region’s interurban bus network (between builtup areas within the region) was made up by 350 lines with a total length of 20,030 kilometers and 16,891 bus-stops. The city bus network, for its part, comprised 129 lines with 4314 stops and a total line length of 1857 kilometers. This all added up to about 2000 buses run by over 30 different firms. This gives some idea of the sheer magnitude and complexity of the project. Despite these difficulties, it has been carried through successfully, judging from passenger feedback, thanks to the work and commitment of the human team allocated to this strategically important task by the transport operators and the Consorcio Regional de Transportes itself. What are your upcoming strategy lines? The aim is to carry on making progress along similar lines, analyzing and processing all available information exhaustively to sound out demand and passenger behavior in the interests of continually improving service quality and ensuring it meets people’s needs in a swift and efficient way. Along these lines we are now working on the implementation of Business Intelligence and Big Data systems for expert analysis within the Consorcio de Transportes and the subsequent taking of the best-informed decisions. CRTM has recently brought in advanced fleet-management and passengerinformation systems plus electronic fare-collection systems, in which GMV has participated together with other firms. Could you talk us through this process and explain the main benefits for passengers and operators? CRTM defined a set of specifications and technical requirements to be met by transport operators within the Modernization Plan. The operators themselves then chose the best firm to meet these needs, GMV playing a key role among them. The incorporation of this technology into the daily operation of the 2000 buses running in Madrid region was without doubt a watershed in terms of system efficiency. Operating firms were convinced of the advantages of these systems from day one. Passengers, for their part, were supplied with all necessary information for planning their journeys, before, after and during the trip itself and on several different channels (web, smartphone apps, social media, …). In some segments of the transport market, passenger transport among them, ITS systems (fleet-management and farecollection systems, etc) have achieved almost a 100% takeup. What would you consider to be the main reasons for such an across-the-board ITS takeup? Well, the fact is that we consider ITS technology to have made greater headway in private vehicles than public transport, and we have expressed this view on several trade forums. The initial outlay and running costs clearly pay off in terms of benefits, mainly for passengers. This has been borne out by several cost-benefit studies we have conducted to assess implementation of infrastructure-based and vehicle-based ITS technology. Today’s society is becoming increasingly demanding and discerning about service quality. ITS technology is therefore playing a key role in making public transport an attractive mobility alternative, even heading off any image-damaging incidents by means of predictive models such as those Además es también prioritario lograr que todos los autobuses sean accesibles a personas con movilidad reducida, así como que incorporen medidas medioambientales muy por encima de las obligaciones que fija actualmente la legislación vigente. También contemplaba el Plan una serie de medidas socio-laborales (formación continua de los distintos perfiles profesionales, potenciación del empleo femenino, fomento de la contratación de discapacitados, etcétera), así como mejoras en la gestión empresarial incentivada mediante la introducción de criterios de calidad del servicio al ciudadano. ¿Cuáles fueron las principales dificultades y cómo se resolvieron? A 31 de diciembre de 2008, la red de autobuses interurbanos de la Comunidad de Madrid estaba compuesta por 350 líneas, con una longitud total de 20.030 kilómetros y 16.891 paradas. A su vez, la red de autobuses urbanos la componían 129 líneas con 4.314 paradas a lo largo de los 1.857 kilómetros de extensión de las líneas. Unos 2.000 autobuses, gestionados por más de 30 empresas distintas, dan una idea de la magnitud y complejidad del proyecto, que se ha desarrollado pág. 12 I GMV NEWS nº60 Septiembre 2015 de manera satisfactoria, según indican nuestros clientes, gracias al trabajo y compromiso del equipo humano que, tanto los operadores de transporte como el propio Consorcio Regional de Transportes, han dedicado a este proyecto estratégico para todos. ¿Cuáles son sus líneas estratégicas próximas? El objetivo es seguir avanzando en las líneas ya iniciadas, orientadas fundamentalmente a conocer con el máximo detalle el comportamiento de la demanda para prestar una oferta de calidad que se ajuste a las necesidades de los ciudadanos de manera ágil y eficiente, mediante el tratamiento adecuado de la información disponible. En este sentido, estamos trabajando en la puesta en marcha de sistemas de Business Intelligence y Big Data, que facilite el análisis por parte de los excelentes técnicos con que cuenta el Consorcio de Transportes y la toma, posterior, de decisiones. we are currently working on in European Commission projects within CITRAM, Madrid’s 24/7/365 real-time publictransport management control center. New modes of operation are now being brought in such as BRT and high occupancy vehicle (HOV) lanes, while there is an increasing number of intermodal transport hubs within the CRTM. As regards these new developments, which would you rate as the most important improvements made by CRTM in recent years? What measures are now being taken for the specific management of corridors, with trunk lines and feeder routes? From 2004 to 2008 the Consorcio Regional de Transportes de Madrid carried out an ambitious Intermodal Hub Plan. This is a key part of the integrated transport system since it feeds suburban modes of transport swiftly and easily into the urban transport system within the city of Madrid. This modern infrastructure has greatly facilitated changes from one mode of transport to another (it should be remembered here that two thirds of the journeys made in the region of Madrid involve two or more different modes Recientemente CRTM ha implantado Sistemas SAE e información al usuario, así como sistemas de Ticketing, en los que GMV ha participado junto a otras empresas ¿podría explicarnos cuál ha sido el proceso y qué beneficios más destacables ofrecen al usuario del transporte público y a los operadores? El CRTM definió un conjunto de especificaciones y requerimientos técnicos que los operadores de transporte debían cumplir en el marco del Plan de Modernización, siendo éstos los que contrataron a cada una de las empresas industriales, habiendo tenido GMV un papel relevante. Sin duda, la incorporación de la tecnología al servicio de la operación diaria de los 2.000 autobuses que operan en la Comunidad de Madrid ha supuesto un cambio trascendental en la eficiencia del sistema, tanto desde el punto de vista de las empresas operadores, que desde el primer día apostaron por sus ventajas, como para los clientes, que han pasado a disponer de toda la información necesaria para planificar sus desplazamientos antes, durante y después del viaje mediante diversos canales (web, Apps en smartphones, redes sociales, …). of transport). There is a corresponding operation project for each one, detailing the user service plan, operator service plan, maintenance plan, security plan, environmental management plan and quality plan. As for bus lanes and reserved platforms, the high-occupancy and bus lane on the A-6 highway has been a clear success story in terms of project coordination. When it was first set up back in 1995, the first intermodal transport hub of Moncloa was also brought on line (now module A) and line 6 of the Metro was completed as a circular line to round out the intermodal system. Unfortunately, despite the many benefits in terms of time-saving, operational efficiency, fewer negative externalities, etc., it has not yet proven possible to replicate the experience in any other access corridor into Madrid city. Such initiatives, in any case, call for due coordination and liaison between the various government levels (City Council of Madrid, En algunos segmentos de mercado transporte, como es el caso de transporte público de pasajeros, los sistemas ITS (SAE, monética, etc) han penetrado casi al 100%. A su juicio, ¿cuáles son los motivos para que las tecnologías ITS hayan penetrado tanto en ese segmento? Bueno, lo cierto es que nuestra sensación es que se ha avanzado más al respecto en materia de tecnología aplicada al vehículo privado que al transporte público, y así lo hemos expresado en diversos foros especializados. Claramente, la inversión a realizar y los gastos de explotación asociados frente a los beneficios, fundamentalmente para clientes, compensan claramente, como demuestran los diversos estudios de análisis coste-beneficio que hemos venido realizando para evaluar la implantación de tecnologías ITS asociadas a la infraestructura y a los vehículos. En una sociedad que demanda cada vez más calidad, las tecnologías ITS juegan un papel clave para que el transporte público resulte una alternativa de movilidad atractiva, facilitando que podamos, incluso, adelantarnos a la aparición de potenciales incidencias, mediante modelos predictivos como en los que estamos trabajando en el marco de proyectos de investigación de la Comisión Europea en CITRAM, Centro de Gestión 24/7/365 del Consorcio Regional de Transportes de Madrid. Con respecto a los nuevos modos de operación (tipos BRT, BUS VAO, etc) y la importante implantación de estaciones intermodales en el ámbito CRTM ¿cuáles cree que han sido las mejoras más relevantes llevadas a cabo por el CRTM en los últimos años? ¿Qué medidas se están adoptando para la gestión específica de corredores, con líneas troncales y alimentadoras? El Consorcio Regional de Transportes de Madrid desarrolló durante los años 2004 a 2008 un ambicioso Plan de Intercambiadores, piezas clave del sistema integrado de transportes, puesto que canalizan la entrada de los modos suburbanos facilitando la conexión rápida y sencilla con los modos urbanos en el municipio de Madrid. Estas modernas infraestructuras han supuesto, sin duda, un cambio muy relevante en la calidad de los transbordos (debe recordarse que más de 2/3 de los viajes en la Comunidad de Madrid se realizan combinando 2 ó más modos de GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 13 Regional Authority of Madrid and central government). The Consorcio Regional de Transportes de Madrid is still working on this and has made it a top-priority action within Madrid region’s Strategic Sustainable Mobility Plan 2013-2025. In liaison with city councils, for example, we are currently studying the possibility of restructuring bus transport networks within various municipalities of the metropolitan area, with urban lines feeding into interurban lines and trunk services to Madrid from the intermodal nerve centers of each municipalities. In particular we are now working on 2 NFC-related alternatives: firstly, cellphone fare payment using the telephony operator’s SIM card (Telefónica, in this case) in a pilot scheme jointly with Madrid’s Municipal Transport Company (Empresa Municipal de Transportes: EMT); secondly, virtualization of the Public Transport Card in the user’s cell phone. By means of these initiatives we are striving to strike the right balance between security requirements of our fare-payment systems and flexibility and the necessary client-centeredness for passengers making over 5 million daily journeys in the 40 transport operators working in Madrid region. At the same time CRTM is developing internet-based pre-payment systems and is also looking at any other initiative that might favor easy and convenient access to our integrated public transport system (direct-debit arrangements, etc.), always phasing them in with all due allowance for the corresponding learning processes and joint maturation of technologies that will soon be part of our everyday lives. Madrid sigue trabajando y que están recogidas como actuaciones prioritarias en nuestro Plan Estratégico de Movilidad Sostenible de la Comunidad de Madrid, con horizonte 2013-2025. En ese contexto, en colaboración con los Ayuntamientos, estamos estudiando la posible reestructuración de las redes de transporte por autobús en distintos municipios del área metropolitana, de modo que las redes urbanas actúen como alimentadoras de las líneas interurbanas, con servicios troncales a Madrid desde los puntos neurálgicos de Intermodalidad de cada municipio. piloto con diferentes tecnologías, entre ellas el pago por móvil. En concreto, en este momento, estamos trabajando en 2 vías alternativas aplicando la tecnología NFC: por un lado, el pago por móvil empleando la tarjeta SIM del operador de telefonía (Telefónica, en este caso), en un proyecto piloto conjuntamente con la Empresa Municipal de Transportes de Madrid, y, por otro, en la virtualización de la Tarjeta Transporte Público en el propio teléfono móvil. Se trata de iniciativas en las que buscamos combinar los exigentes requerimientos de seguridad de nuestros sistemas de pago con la flexibilidad y necesaria orientación a los clientes que realizan más de 5 millones de viajes diarios en los 40 operadores de transporte que operan en la Comunidad de Madrid. En paralelo, CRTM está desarrollando sistemas de pre-pago a través de internet, así como cualquier otra iniciativa que facilite el acceso cómodo y sencillo a nuestro sistema de transporte público integrado (domiciliación bancaria, etc.), respetando los convenientes y, sin duda, necesarios procesos de aprendizaje y maduración conjunta de tecnologías que son ya casi una realidad. What will the future fare payment systems be like? How can new technologies help here? It goes without saying that an attractive public transport system has to be run with fare payment systems suited to society’s current demands, similar to the means of payments used by people in other transactions of their daily lives. Within this context CRTM has been participating for some years in several benchmarking studies to identify best practices while also phasing in the corresponding pilot schemes with different technology, including cell-phone fare payment. transporte). Cada uno de ellos cuenta con el correspondiente Proyecto de Explotación, en el que se detalla el Plan de Servicios a los usuarios, Plan de Servicios a los operadores, Plan de Mantenimiento, Plan de Seguridad, Plan de Gestión Medioambiental y Plan de Calidad. Con respecto a los carriles bus y plataformas reservadas, la experiencia del Bus-VAO en la carretera A-6 ha sido un claro ejemplo de éxito de este tipo de iniciativas, destacando la óptima coordinación de proyectos, ya que, cuando se puso en marcha en 1995, entró también en servicio el primer Intercambiador de Moncloa (actual módulo A) y se cerró como circular la línea 6 de Metro. Lamentablemente, a pesar de los numerosos beneficios en términos de ahorros de tiempo, eficiencia en la operación, menores externalidades negativas, etc., hasta la fecha, no ha sido posible replicar el modelo en ningún otro corredor de acceso a Madrid. Se trata, en cualquier caso, de actuaciones que requieren de la concertación de los distintos niveles de la Administración (Ayuntamiento de Madrid, Comunidad de Madrid y Estado), sobre las que el Consorcio Regional de Transportes de pág. 14 I GMV NEWS nº60 Septiembre 2015 ¿Cuál serán las futuras formas de pago en el transporte? ¿Cómo pueden ayudar las nuevas tecnologías en este ámbito? Es evidente que un sistema de transporte público atractivo debe contar con sistemas de pago adaptados a las demandas de la sociedad, similares a los que emplean los ciudadanos en otro tipo de transacciones en su vida diaria. En este contexto, CRTM está participando desde años en varios estudios de benchmarking con objeto de identificar las mejores prácticas y, a su vez, poniendo en marcha las correspondientes pruebas ARTICLE / ARTÍCULO THE NEW TECHNOLOGIES AND THE NEW TRANSPORT AND MOBILITY SERVICES LAS NUEVAS TECNOLOGÍAS Y LOS NUEVOS SERVICIOS DE TRANSPORTE Y MOVILIDAD New technologies are changing the way we tackle nearly all our daily tasks, from shopping or consuming services to communicating with each other, among many other examples. Mobility and transport are no exception; both sectors are now increasingly taking up performance-improving technology of all types, including onboard telematic devices and smartphones. In the transport and mobility sector, indeed, this ongoing technological transformation is being largely driven by telematics. Vehicle use is now being conceived in a new way; a whole host of applications and devices is now turning vehicles into connected fleets running on much more efficient lines. The connected car is one of the most far-reaching innovations in over a century of the automobile sector. Connectivityempowered cars offer a vast range of incredible opportunities to consumers, the car industry and the mobile communications industry. Nowadays it is possible to glean all sorts of profile information as people are moving about on their daily journeys, especially car drivers, both professional and private, to find out their real needs. Las nuevas tecnologías están cambiando la forma en que realizamos casi todas las tareas diarias, desde comprar o consumir servicios hasta comunicarnos, entre otras muchas. La movilidad y el transporte no son una excepción y cada vez van incorporando más rápidamente todo tipo de tecnologías que permiten llevar a cabo su optimización, gracias a numerosos dispositivos, entre ellos los dispositivos telemáticos embarcados y los Smartphones. En el sector del transporte y la movilidad, parte de esta transformación tecnológica se está llevando a cabo a través de la telemática. Existe una nueva forma de concebir el uso de los vehículos, que pueden mejorar su eficiencia al mismo tiempo que tienen acceso a gran variedad de aplicaciones, gracias a la utilización de dispositivos que los convierten en vehículos conectados. El automóvil conectado es una de las innovaciones más interesantes que se han producido en más de un siglo de desarrollo del sector de la automoción. La incorporación del poder de la conectividad a los automóviles ofrece una gama de oportunidades increíbles para el consumidor, la industria de la automoción y la industria de las comunicaciones móviles. Hoy en día, es posible obtener mucha información sobre los perfiles según los cuales la población se desplaza, y en particular los usuarios de vehículos, tanto profesionales como privados, y saber qué necesidades presentan, lo que cambia radicalmente la manera de entender el transporte. La telemática se puede entender como una captura de información y la utilización de la misma para aplicarla de manera diferente a como se ha hecho hasta ahora. Así, se recoge una cantidad ingente de datos que se trasladan a través de la red de telecomunicaciones para procesarlos con diferentes propósitos y obtener conclusiones relativas a la velocidad del vehículo, el consumo de combustible, el mantenimiento del vehículo o el perfil de utilización del mismo que lleva a cabo el conductor. GMV lleva varios años ofreciendo tecnología para dar respuesta a diferentes tipos de aplicaciones telemáticas, basadas todas ellas en el paradigma de la conexión del vehículo y del usuario del mismo con una plataforma remota que es capaz de ofrecer diferentes tipos de servicios, entre ellos: - Sistemas de Pago por Uso. Seguros PAYD / UBI - Llamadas de emergencia eCall y bCall - Conducción energéticamente eficiente - Otras SISTEMAS DE PAGO POR USO. PAYD / UBI Muchos agentes están potenciando el uso de los datos telemáticos registrados para poder disponer de variables más precisas que respaldan los productos de pago basado en el uso, como es el caso de los seguros PAYD (Pay As You Drive). Los seguros de Pago por Uso representan un cambio en los modelos utilizados hasta ahora, basados en el análisis de riesgos. A medida que los modelos de riesgos se convierten en más sofisticados mediante el uso de análisis aplicados a los datos generados por el uso que se hace del vehículo, aparece un perfil de conductor más preciso. Los programas de Pago por Uso basados en sistemas telemáticos están modificando drásticamente los modelos utilizados tradicionalmente por las aseguradoras, beneficiando tanto a los GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 15 ARTICLE / ARTÍCULO This is completely changing our way of understanding transport. Telematics can be understood as the capturing of information before using and applying it in a different way from the past. A huge amount of data can now be picked up and transmitted on the telecommunications network to be processed for several different purposes. Conclusions can thus be drawn on vehicle speed, fuel consumption, vehicle maintenance or driver use-profile. For several years now GMV has been offering telematic-application technology based on the idea of connecting vehicles and users to a remote platform that can then offer various types of services, such as: - Pay-per-use systems. UBI / PAYD insurance - eCall and bCall emergency call systems - Energy-efficient driving - Others PAY-PER-USE SYSTEMS. PAYD / UBI Recorded telematic data is now being taken up and used by an increasing number of agents to underpin their use-based payment products such as pay-as-you-drive (PAYD) insurance. PAYD is a paradigm shift on the traditional riskanalysis insurance models. As risk models become more sophisticated, on the basis of vehicle-use data, the end result is a more accurate driver profile. Pay-per-use programs based on telematic systems are drastically changing the models traditionally used by insurers, to the benefit of both drivers and the insurers themselves. The more precise data trawl helps to bring risk assessment more in line with the real situation, trimming insurance premiums and encouraging better driver behavior. call is handled. Precise localization of the broken-down vehicle and swift allocation of the right breakdown resources in each case are essential for system user satisfaction. In some cases bCall diagnostic information will enable remote diagnosis of the situation, ensuring beforehand that the resources actually sent are best suited to the real needs of the broken-down vehicle. ECALL AND BCALL EMERGENCY CALL SYSTEMS The eCall system is based on fitting vehicles with an electronic safety device that can call emergency services automatically or manually in the event of an accident. This means that roadside services can get to the exact spot in a matter of minutes. Under the bCall or breakdown-call system, drivers send a manual alert to a control center in the event of a vehicle breakdown. It works on a similar basis to eCall; in principle no additional hardware needs to be fitted (unless certain breakdown-diagnosis information is to be sent automatically from the vehicle); it differs mainly in the sort of information sent, the nature of the call and the way the ENERGY EFFICIENT DRIVING Until now information on each vehicle’s average fuel consumption and CO2 emissions has been obtained from a standardized methodology based on the legislative framework; actual CO2 emission data has not yet been available. Now, however, the fitting of new onboard equipment will make it possible to calculate real vehicle-emission profiles as opposed to the energy labelling of vehicles as laid down by EU legislation. Emission profiles are directly bound up with real driver behavior; driver-profile information can therefore be a crucial management tool for drivers themselves, fleet managers, service providers and authorities/governments in terms of obtaining, comparing and exchanging real CO2 emission figures per vehicle. presenta diversas similitudes con eCall, no necesitando, en principio, elementos hardware adicionales (salvo que se plantee enviar determinada información de diagnosis de la avería, obtenida automáticamente desde el vehículo), diferenciándose por la naturaleza de la información transmitida, la naturaleza de la llamada y la gestión que la misma recibe. La localización precisa del vehículo averiado y la rápida asignación de los recursos apropiados son esenciales para la satisfacción de los usuarios. En algunos casos, la información de diagnóstico bCall ayuda a los expertos técnicos a llevar a cabo diagnosis remotas, garantizando de esta manera la asistencia más apropiada a las necesidades reales de la situación de avería del vehículo. conductores como a las aseguradoras, al proporcionar datos que facilitan una evaluación de riesgos más ajustada a la realidad, traduciéndose en unas primas de seguro con precios más ajustados, y un mejor comportamiento al volante por parte de los conductores. LLAMADAS DE EMERGENCIA ECALL Y BCALL eCall se basa en la incorporación en nuestros vehículos de un dispositivo electrónico de seguridad que permite llamar a los servicios de emergencia en caso de producirse un accidente de tráfico, tanto de manera manual como automática, que será capaz de informar a los trabajadores de los servicios de atención de emergencia sobre el accidente, proporcionando información sobre la localización exacta del mismo, de manera que se pueda facilitar la llegada de los equipos de rescate en cuestión de pocos minutos. Los sistemas bCall o llamada para solicitar asistencia en caso de avería son sistemas en los que el conductor de forma manual envía una alerta a un centro de control en caso de detectar una avería en su vehículo. Su funcionamiento pág. 16 I GMV NEWS nº60 Septiembre 2015 Energy efficient driving (eco-driving) is a form of driving that cuts fuel consumption, greenhouse-gas emissions and accident rates. It is a driving style more in line with modern engines: intelligent, smooth and safe driving techniques that reduce fuel consumption by about 5-10%. The knock-on benefits for drivers are reduced running costs, fewer accidents and lower noise- and emission-levels. Several European countries have now brought in successful energy-efficient-driving programs. Eco-driving training courses can help drivers cut fuel consumption by between 5 and 20%. The rollout of applications of this type calls for a series of vehicle-informationrecording technologies. This information then needs to be properly processed to provide all users (drivers, fleet managers, public authorities, etc.) with feedback on the best driving style to meet energy efficiency targets. To this end, onboard devices can be fitted to record this information and then mine it afterwards for driver-training purposes. There are several other added-value telematic services that can be brought in on the basis of onboard devices that send recorded information to a remote control center where it can be suitably processed. These include systems such as advanced fleet management, remote diagnosis and preventive vehicle maintenance and other pay-per-use services like road user charging. Nonetheless, not all GMV’s telematicsrelated mobility solutions are based necessarily or solely on the connectedvehicle idea. GMV has also developed efficiency-enhancing mobility and transport solutions based on smartphonetype handhelds and platforms. These systems offer several advantages: service providers no longer need to make heavy infrastructure outlays; neither do drivers need to fit additional onboard devices. Access to and use of these applications requires only their simple installation in smartphone-type handhelds and then you are ready to go. One of the best examples is the successful DriveOn TEXpress project developed by GMV for CINTRA USA, involving a cell-phone app for obtaining discounts on high-occupancy (express) toll-road lanes of Dallas. The new high-occupancy lanes of the NTE and LBJ toll-roads of Dallas (Texas-USA) are express lanes guaranteeing users a minimum speed at any time of day. Use of these lanes is now being run on the basis of a cell-phone app and web app called “DriveOn TEXpress”, offering eligible cars (on the basis of occupancy and other factors) substantial toll discounts. Achieving these discounts could hardly be easier for users of these express toll lanes: first of all they click the register button to download the app onto any of the commonest handhelds; then they provide some basic contact info and the app is ready for use. The idea of this scheme is to encourage ridesharing, especially during rush hours, in return for which drivers are offered express lane toll discounts of up to 50%. DriveOn TEXpress enables these and other discounts and promotions to be claimed by simply clicking an application button. The app also gives additional contact information plus information on Dallas’s LBJ and NTE toll roads. More express toll-road lanes will be coming online in the near future, run by CINTRA USA, by the state of Texas itself or other concessionaires. The DriveOn TEXpress system has been designed, developed and rolled out wholly by Spanish firms working in the USA. The system is owned by CINTRA USA (belonging to the Ferrovial group), which directed the design and implementation CONDUCCIÓN ENERGÉTICAMENTE EFICIENTE El consumo medio de combustible y el nivel de emisiones de CO2 de cada vehículo se obtienen a partir de una metodología estandarizada basada en el marco legislativo; sin embargo, los datos reales de emisiones de CO2 por parte de los vehículos no están disponibles actualmente. Gracias a la incorporación de equipamiento a bordo del vehículo será posible calcular los perfiles de emisiones reales de los vehículos en contraste con el etiquetado energético de los vehículos que fija la legislación. Los perfiles de emisión tienen una relación directa con el comportamiento del conductor al volante y su perfil de conducción, y pueden ser, por tanto, una potente herramienta de gestión para los propios conductores, gestores de flotas, proveedores de servicio y autoridades / gobiernos a la hora de facilitar, comparar e intercambiar datos reales de emisiones de CO2 por parte de los vehículos. La conducción energéticamente eficiente (Ecodriving) es una manera de conducir que reduce el consumo de combustible, las emisiones que contribuyen al efecto invernadero y las tasas de accidentes. Se trata de un estilo de conducción adaptado a la tecnología de los motores modernos: técnicas de conducción inteligente, suave y segura que conducen a ahorros medios de combustible en torno a un 5-10%, ofreciendo beneficios a los conductores como ahorro económico y menos accidentes, así como reducción en los niveles de emisiones y ruido. Varios países europeos han implementado exitosos programas de conducción energéticamente eficiente. Cursos de formación en Ecodriving a los conductores pueden ayudar a los mismos a reducir el consumo de combustible entre un 5 y un 20%. Para poder desplegar este tipo de aplicación se requiere de una serie de tecnologías que permitan obtener información del vehículo, y procesarla convenientemente para proporcionarla al usuario (conductores, gestores de flotas, administración pública etc) de manera que ésta sea utilizada para realimentar el estilo de conducción llevado a cabo, facilitando el alcance del objetivo de eficiencia energética que se haya definido. Para ello, es posible utilizar dispositivos embarcados que registren esta información para su posterior uso en la formación del conductor. Existen otros diferentes servicios telemáticos de valor añadido que pueden desplegarse a partir de la utilización de un dispositivo embarcado en un vehículo que envía la información registrada a una central remota, donde esta se procesa convenientemente. Entre ellos se podrían mencionar algunos tales como la gestión avanzada de flotas, diagnosis remota y mantenimiento preventivo del vehículo u otros servicios relativos al pago por el uso de la infraestructura (peaje electrónico, Road User Charging). Sin embargo, no todas las soluciones pensadas para la movilidad que se ofrecen en GMV como parte de su oferta en telemática se basan necesaria o exclusivamente en el paradigma del vehículo conectado. De manera complementaria, GMV ha sabido explotar sus capacidades para el desarrollo de soluciones para favorecer una movilidad y transporte más eficientes basados en la utilización de dispositivos y plataformas tipo Smartphone. Esto conlleva diferentes ventajas, pues permite a los proveedores de servicios evitar inversiones GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 17 ARTICLE / ARTÍCULO through its subsidiary firm CTS. The contract for both software and hardware development of the project was awarded to GMV. Both companies, working together, have managed to carry out this trailblazing system successfully and on schedule. Other smartphone-based systems are now are being developed as groundbreaking solutions for pay-per-use toll-road schemes, often working alongside other pre-existing technology. Drivers download an app into their smartphone and register in the scheme, after which they can pay their toll fees without needing to install any additional onboard equipment. Drivers can accept and acknowledge the fee payment by means of a simple gesture or by speaking, to avoid any movement that might impair driving safety. These are only some of the new options opened up by value-added telematic services. GMV’s wealth of knowledge of the various enabling technologies means we can offer products and alternatives to meet users’ continually more demanding needs. significativas en infraestructura y evita a los conductores la necesidad de incorporar nuevos dispositivos adicionales a bordo de sus vehículos, de manera que el acceso y utilización de estas aplicaciones se consigue mediante la sencilla instalación de las mismas en los terminales tipo Smartphone y la utilización de dichas aplicaciones. Como ejemplo cabe mencionar el exitoso proyecto DriveOn TEXpress, desarrollado por GMV para CINTRA USA, consistente en una aplicación móvil para descuentos en las autopistas urbanas de Dallas. Las nuevas calzadas de peaje de las autopistas NTE y LBJ de Dallas (Texas-EE.UU), por las que los vehículos usuarios tienen garantizada una velocidad mínima en cualquier momento del día, ya utilizan como aliado tecnológico una aplicación móvil (APP) y aplicación web (WebAPP) llamada “DriveOn TEXpress” por la que consiguen descuentos sustanciales al peaje, por alta ocupación y otros conceptos. La consecución de los descuentos resulta muy fácil para el usuario de los carriles segregados de estas autopistas: mediante un registro inicial en la aplicación, que se descarga gratuitamente en los terminales móviles más comunes, en la que hay que introducir algunos datos del vehículo, la APP está lista para ser utilizada. Con esta aplicación, se pretende fomentar el uso compartido del vehículo en particular en las horas punta, ofreciendo rebajas en el precio nominal de estos tramos, que pueden llegar hasta el 50%. DriveOn TEXpress permite solicitar este y otros descuentos y promociones con pulsar un botón de la aplicación. Además, la aplicación proporciona información adicional de contacto y de las autopistas LBJ y NTE de Dallas. La aplicación se podría extender, en un futuro, sin requerir más que una parametrización, a otros tramos de calzadas segregadas gestionados por CINTRA EE.UU, por el propio Estado de Texas o por otros concesionarios. El sistema DriveOn TEXpress ha sido diseñado, desarrollado e implantado íntegramente por empresas españolas trabajando en EE.UU. El sistema es propiedad de CINTRA EE.UU. (perteneciente al grupo Ferrovial), que dirigió el diseño e implantación a través de su empresa filial CTS. El desarrollo del proyecto, tanto en el hardware como en el software, fue contratado a GMV. Ambas organizaciones han conseguido llevar a cabo con éxito y en el plazo previsto la implantación de este sistema pionero. Otras soluciones basadas en Smartphone se están desarrollando para proporcionar una opción adecuada e innovadora para el Pago por Uso en autopistas de peaje, que puede coexistir con otras tecnologías existentes. Los conductores se instalan una aplicación en sus terminales Smartphone y se dan de alta en una plataforma, pudiendo pagar sus tránsitos sin necesidad de instalar ningún equipo embarcado adicional en el vehículo. La aceptación del pago puede realizarse de forma automática mientras se conduce, mediante un gesto sencillo o a través de voz, evitando de este modo cualquier movimiento que pueda afectar a la seguridad en la conducción. Son muchas las opciones que se abren en este universo de servicios telemáticos de valor añadido. El amplio conocimiento de GMV en las diferentes tecnologías que los hacen posible nos permite ofrecer productos y alternativas a la altura de lo que esperan los cada vez más exigentes usuarios. pág. 18 I GMV NEWS nº60 Septiembre 2015 AERONAUTICS / AERONÁUTICA GMV STUDIES THE VIABILITY OF UNMANNED AIRCRAFT IN THE MARITIME ENVIRONMENT GMV ESTUDIA LA VIABILIDAD DE AVIONES NO TRIPULADOS EN EL ÁMBITO MARÍTIMO In September the European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA) has awarded GMV a study to identify the user benefits of Remotely Piloted Aircraft Systems (RPAS) in the maritime domain. The European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA) was established to contribute to the enhancement of European maritime safety, maritime security, and prevention of and response to pollution by ships. One of the assigned tasks is to develop and operate key maritime information services to the maritime community. This task is accomplished through the creation and maintenance of a complete maritime picture through the use of different resources among which satellites, AIS networks, LRIT information, and information passed by member nations and European agencies occupy an important place. In order to enhance this existing maritime picture, EMSA is always looking to incorporate any new resource that could provide more and better information on existing systems, such as RPASs. RPASs are aircraft of fixed or rotary wings with no pilot or crew aboard. RPASs are under control of a remote pilot-in-command for the entire flight under normal conditions and movements on the ground. However, onboard automation can trigger maneuvers in the absence of pilot command, in specific non-normal failure conditions: loss of command and control (C2) link and imminent risk of mid-air collision with another aircraft. RPASs belong to the wider family of Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS), which also comprises ‘autonomous’ RPASs (i.e. no human action is necessary after take-off). Successfully developing operational services using RPAS data is dependent on accurately identifying the needs of end users. As the use of RPAS for civil maritime surveillance is relatively new and throughout this 7-month study, GMV will support EMSA in acquiring a better understanding of maritime user requirements regarding RPAS services, in order to evaluate the feasibility of supporting RPAS services for EMSA Member States in the future. En septiembre la Agencia Europea de Seguridad Marítima (EMSA) ha adjudicado a GMV la realización de un estudio para identificar los beneficios para el usuario de sistemas aéreos no tripulados (RPAS) en el ámbito marítimo. La EMSA se creó para contribuir a la mejora de la seguridad y la protección marítima europea y para ayudar a prevenir y luchar contra la contaminación causada por los barcos. Una de las tareas asignadas es el desarrollo y la prestación de servicios de información marítima clave a la comunidad del mar. Esta tarea se cumple mediante la creación y el mantenimiento de una imagen marítima completa por medio del uso de diferentes recursos, entre los cuales los satélites, las redes AIS, la información de identificación y seguimiento de largo alcance (LRIT) y la información transmitida por las naciones integrantes y las agencias europeas ocupan un lugar destacado. Con el fin de mejorar esta imagen marítima, la EMSA tiene mucho interés en incorporar cualquier nuevo recurso que pueda proporcionar más y mejor información sobre sistemas existentes, como los RPAS. Los RPAS son aeronaves de alas fijas o rotatorias sin piloto o tripulación a bordo, que son controlados mediante un mando a distancia durante todo el vuelo en condiciones normales y movimientos en el suelo. Sin embargo, los sistemas automáticos embarcados que incorporan pueden poner en marcha maniobras en ausencia de una orden en condiciones concretas de fallo no ordinario: pérdida del enlace de mando y control (C2) y riesgo inminente de colisión en el aire con otra aeronave. Los RPAS pertenecen a la familia de los sistemas aéreos no tripulados UAS, que también comprende RPAS “autónomos” (es decir, sin necesidad de intervención humana después del despegue). El desarrollo con éxito de servicios operacionales que utilicen datos de RPAS depende de la identificación precisa de las necesidades de los usuarios finales. A lo largo de este estudio, GMV ayudará a la EMSA a adquirir un mayor conocimiento de las necesidades del usuario marítimo con respecto a los servicios RPAS a fin de evaluar la viabilidad del empleo de los servicios RPAS para los Estados Miembros en el futuro. GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 19 SPACE / ESPACIO THE USE OF NETS TO MITIGATE THE SPACE DEBRIS PROBLEM EL USO DE REDES PARA PALIAR EL PROBLEMA DE LA BASURA ESPACIAL Space is becoming a highly saturated environment, especially in certain zones. A considerable halo of space debris is now building up in earth orbit. Over 17,000 objects larger than a coffee cup have been recorded, any one of which might hit operational satellites with catastrophic consequences. Within space-debris capture techniques, GMV has been studying nets as one of the most promising non-rigid methods. This is being done above all through the PATENDER mission, an ESA-funded activity within the Clean Space program, which is driving the development of space-debris reduction projects, using custom-built technology to capture decommissioned satellites still orbiting the earth. The project is based on the development of a software simulator that recreates the net deployment dynamic and contact with the target satellite. This simulator has been vetted by means of a real parabolicflight experiment, and it has been filmed with high speed cameras to provide a 3D reconstruction of the trajectories of the net itself and each of its nodes/knots. This GMV-led multidisciplinary activity is being carried out within a consortium formed by the Polytechnic University of Milan, in charge of mathematical net models and 3-D reconstruction, and the Asturian Foundation PRODINTEC, responsible for manufacturing the pneumatic-electric net-launching system. GMV’s remit is to develop the software and coordinate all project phases, from acceptance and commissioning to validation of the final results. The system, developed over one year, was taken in early June to the site of Novespace, in Bordeaux-Mérignac airport (France) to conduct low-gravity tests by means of a parabolic flight aboard an Airbus A-310. Net launch trials were carried out using a mock-up of ESA’s earth-observation satellite, ENVISAT. After completion of the experiment ESA declared its satisfaction with the results, in the sure knowledge that they will help to mature non-rigid, net-based space-debris capture technology. El espacio se está convirtiendo en un entorno muy saturado, especialmente en determinadas zonas. En la actualidad, un halo considerable de basura espacial empieza a rodear a la Tierra y se han podido registrar más de 17.000 objetos más grandes que una taza de café que podrían impactar con satélites operativos y cuyas consecuencias podrían ser catastróficas. Dentro de las tecnologías de captura de basura espacial, GMV ha estado investigando el uso de redes como uno de los métodos de captura no-rígida más prometedores a través del proyecto PATENDER, actividad financiada por la ESA dentro del marco del programa “Espacio Limpio” (Clean Space), cuyo objetivo es fomentar el desarrollo de proyectos dedicados a paliar el problema de los residuos espaciales mediante tecnologías que permitan la captura de satélites fuera de su vida útil y que todavía permanecen en órbita alrededor de la Tierra El proyecto se basa en el desarrollo de un simulador software que recrea la dinámica de despliegue de una red y el contacto con el satélite objetivo. Dicho simulador se ha validado mediante un experimento real en un vuelo parabólico, y se ha filmado con cámaras de alta velocidad que permiten la reconstrucción 3D de las trayectorias realizadas por las redes y por cada uno de sus nodos/nudos. Esta actividad multidisciplinar liderada por GMV, se desarrolla en el marco de un consorcio formado por la Universidad Politécnica de Milán, encargada de los modelos matemáticos de la red y la reconstrucción tridimensional, y la Fundación Asturiana PRODINTEC, responsable de la fabricación del sistema neumático-eléctrico que permite el lanzamiento de la red. GMV ha sido el encargado de desarrollar el software y ha coordinado todas las fases del proyecto, desde la aceptación y puesta en marcha del experimento hasta la validación de los resultados obtenidos. El sistema, que se ha desarrollado a lo largo de un año, se trasladó a principios de junio a las instalaciones de Novespace, en el aeropuerto de Bordeaux-Mérignac (Francia) para llevar a cabo los ensayos en gravedad reducida mediante un vuelo parabólico a bordo de un Airbus A-310. Los ensayos de lanzamiento de la red se hicieron usando una maqueta del satélite de la ESA de observación de la Tierra, ENVISAT. Tras la ejecución del experimento con éxito, la ESA mostró su satisfacción con los resultados obtenidos, asegurando que ayudarán a incrementar la madurez tecnológica de la captura no-rígida de basura espacial mediante redes. pág. 20 I GMV NEWS nº60 Septiembre 2015 KEY GMV TECHNOLOGY IN ESA’S MISSION TO MARS TECNOLOGÍA DE GMV CLAVE EN LA MISIÓN A MARTE DE LA ESA GMV has recently won three contracts within the flagship mission ExoMars, currently being carried out by the European Space Agency (ESA) in cooperation with the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos). The aim of the mission is to send two missions to the Red Planet, one in 2016 and another in 2018. These three contracts, all relating to the second ExoMars mission due for launch in 2018, are the following: firstly, development of the application software of the main onboard computer (Application SW); secondly, development of the software verification facility (SVF) and finally development of the onboard computer simulator (OBC1). GMV has already been working for three years on the first ExoMars mission, scheduled for launch in March 2016. This mission comprises two spacecraft: the trace gas orbiter (TGO) satellite that will orbit Mars to analyze the gases of the Martian atmosphere; and the entry, descent and landing demonstrator module (EDM), which will separate off from the TGO once it has gone into Martian orbit. GMV’s input to this first mission is to develop the OBSW of the guidance, navigation and control system of the EDM capsule. Beginning in autumn 2016, the TGO will be orbiting the red planet for five years to check for atmospheric gases that could be a sign of possible biological or geological activity. Three days before reaching Mars, the EDM will separate from the TGO and cross the Martian atmosphere at an initial speed of 21,000 k.p.h. After an aerobraking maneuver and parachute descent the module will then use a liquid fuel propulsion system to land on the planet’s surface. This whole process will be controlled by GMV-developed software. If successfully carried through, the 2016 mission will be a red-letter event as the first Mars touchdown by a European spacecraft. The second mission, to be launched in 2018, comprises a carrier module (CM) and a descent module (DM) with a Martian rover inside. GMV’s participation involves not only guidance, navigation and control of the descent module (as in 2016) but also other subsystems (thermal system, remotecommand system, guidance and control of the carrier module as well as the descent module, power system), apart from the aforementioned SVF and onboard computer models, which will be used in testing. The second mission will end with the launch of the ExoMars exploration vehicle, the first Martian Rover to be deployed on the planet’s surface by Europe. Recientemente GMV ha resultado adjudicataria de tres contratos en el marco de la emblemática misión ExoMars, desarrollada por la Agencia Espacial Europea (ESA) en cooperación con la Agencia Espacial Federal Rusa (Roscosmos) para enviar dos misiones al Planeta Rojo en 2016 y 2018. Estos tres contratos se refieren a la segunda misión de ExoMars prevista para ser lanzada en 2018 y abarcan en primer lugar el desarrollo del software de aplicación completo de la misión 2018 (Application SW), en segundo lugar el desarrollo del Software Verification Facility (SVF) utilizado para la validación de dicho SW, y finalmente el desarrollo del simulador del computador de a bordo (OBC1). GMV ya venía trabajando desde hace tres años en la primera misión del programa ExoMars cuyo lanzamiento se realizará en Marzo de 2016 y que consta de dos naves: un satélite que se quedará orbitando en Marte con un instrumento dedicado al análisis de los gases de la atmosfera marciana (TGO); y el módulo demostrador de Entrada, Descenso y aterrizaje (EDM) que se desacoplará del orbitador una vez este haya llegado a la órbita marciana. La contribución de GMV en esta primera misión es el desarrollo del OBSW del sistema de guiado, navegación y control de la cápsula del EDM. A partir de otoño de 2016, el vehículo orbitador (TGO) permanecerá en órbita alrededor del planeta rojo durante cinco años para analizar los gases atmosféricos que podrían indicar la presencia de procesos biológicos o geológicos activos. Tres días antes de llegar a Marte, el módulo EDM se separará del TGO y atravesará la atmósfera marciana a una velocidad inicial de 21.000 km/h. Tras realizar una maniobra de frenado aerodinámico y un descenso en paracaídas, el módulo utilizará un sistema de propulsión de combustible líquido para realizar el aterrizaje sobre la superficie del planeta. Todo este proceso estará controlado por el software desarrollado por GMV. Cabe destacar que, si la misión del 2016 culmina con éxito, será la primera vez en la historia que una nave europea consigue aterrizar en Marte con éxito. La segunda misión a ser lanzada en 2018 consta de un módulo portador (CM) y un módulo de descenso (DM) con un Rover Marciano en su interior. La participación de GMV no solamente cubrirá el guiado, navegación y control del módulo de descenso (como en 2016), sino que se extiende a otros subsistemas (sistema térmico, sistema de telecomandos, guiado y control del módulo portador además del módulo de descenso, sistema de potencia), aparte de los ya mencionados SVF y modelos del computador de a bordo, que servirán para las pruebas. La segunda misión finalizará con el lanzamiento del vehículo de exploración ExoMars, primer Rover marciano que Europa consiga poner en Marte. Image courtesy of ESA GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 21 SPACE / ESPACIO AN EXCEPTIONAL LABORATORY FOR VALIDATION OF GNC SPACE SYSTEMS UN LABORATORIO EXCEPCIONAL PARA LA VALIDACIÓN DE SISTEMAS ESPACIALES DE GNC In October 2013 GMV inaugurated platform-art©, a robotic testbed for pre-launch ground testing of space operations and systems. Since its inauguration this testbed has enhanced GMV’s capacity of developing and validating complete guidance, navigation and control (GNC) systems of space vehicles. GMV has also offered the testbed to other sector companies inside and outside Spain as a flexible validation facility for a wide range of space missions: space debris capture missions, formation flying missions, missions for exploring the surface of other planets and moon descent missions, among others. The testbed was also recently used to validate a complete guidance, navigation and control (GNC) system for descent and landing (D&L) operations on small bodies. The objective of this activity (NEOGNC2-CCN2) is to extend the test campaign of the NEOGNC2 project to incorporate HW representative of a true navigation camera (i.e. NPAL breadboard navigation camera). This improves testing realism/ fidelity and gives further insights into the use of optical navigation in future ESA missions. The selected scenario for this validation is the European Space Agency’s Asteroid Impact Mission (AIM). Targeted at the Dydimos asteroid, the mission’s aim is to explore and demonstrate technologies for future asteroid missions. For this purpose ESA furnished a low resolution Didymos model, to which GMV then added details and colors to make it more realistic. The NEOGNC2 system has been successfully tested with the NPAL navigation camera in both the Optical Laboratory and the robotic testbed (platform-art©) on GMV’s site. This validation activity has enabled verification of the functions and performance of the GNC system (implemented in flight representative processors) with an electric model of a flight navigation camera, thus enhancing its maturity level. En octubre de 2013 GMV inauguró platform-art©, un laboratorio robotizado para la realización de pruebas en tierra antes de su lanzamiento de Sistemas y Operaciones Espaciales. Desde su inauguración este Laboratorio ha permitido a GMV afrontar en mejores condiciones el desarrollo y validación de sistemas completos de Guiado, Navegación y Control (GNC) de vehículos espaciales. Adicionalmente, GMV ha ofrecido el Laboratorio a otras empresas del sector dentro y fuera de España para su uso como entorno de validación flexible para un amplio espectro de misiones espaciales: misiones de captura de basura espacial, misiones de vuelo en formación, misiones de exploración de la superficie de otros planetas y descenso sobre la Luna, entre otras. Recientemente el Laboratorio ha servido para validar un sistema completo de guiado, navegación y control (GNC) para las operaciones de descenso y aterrizaje (D&L) sobre cuerpos pequeños. El objetivo de esta actividad (NEOGNC2-CCN2) ha sido ampliar la campaña de ensayos del proyecto NEOGNC2 para incorporar equipos representativos de una verdadera cámara de navegación (es decir, el breadboard de la cámara de navegación NPAL). De esta forma, se ha conseguido mejorar tanto el realismo y la fidelidad de las pruebas como aprender nuevos detalles sobre la navegación óptica para futuras misiones de la ESA. El escenario seleccionado para esta validación ha sido el de la misión AIM (Asteroid Impact Mission) de la Agencia Espacial Europea que tiene como destino el asteroide Dydimos y cuyo objetivo es explorar y demostrar tecnologías para futuras misiones hacia asteroides. Para ello, la Agencia facilitó un modelo de de Didymos de baja resolución, al que GMV añadió detalles y color para conseguir un mayor realismo. El sistema NEOGNC2 ha sido probado con éxito con la cámara de navegación NPAL tanto en laboratorio óptico como en laboratorio robótico (platform-art©) situados en las instalaciones de GMV. Esta actividad de validación ha permitido verificar las funciones y prestaciones del sistema GNC (implementado en procesadores representativos de vuelo) con un modelo eléctrico de una cámara de navegación HW de vuelo y así aumentar su nivel de madurez. pág. 22 I GMV NEWS nº60 Septiembre 2015 GMV IN THE ASTEROID IMPACT MISSION GMV EN LA MISIÓN ASTEROID IMPACT The last asteroid to pass close to the Earth was baptized as 2011 MD. This asteroid “buzzed” the Earth at a distance of 12,000 kilometers. It is estimated that asteroids over 1 km in diameter, capable of causing global catastrophes or mass extinctions, pass close to the Earth every few hundred thousand years. The European Space Agency has launched the Asteroid Impact Mission (AIM), targeted on the Dydimos asteroid with the objective of exploring and demonstrating technologies to pre-empt any devastating asteroid Earth impact. GMV is playing a key part in AIM, with responsibility for mission analysis, the guidance, navigation and control (GNC) subsystem and an important part of operations design, in one of the two ESA studies currently underway. At the same time GMV’s Romanian subsidiary is developing the Hazard Avoidance and Fault Detection Isolation and Recovery (FDIR) function for the same mission. Last but not least GMV is leading one of the five concept studies for additional AIM science experiments with two CubeSats. AIM is an active part of the Asteroid Impact and Deflection Assessment (AIDA) project of ESA, DLR (Germany), the Observatoire de la Côte d´Azur (France), NASA, and Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (JHU/APL), designed to assess the potential of the kinetic impactor concept for deflecting nearby asteroids. The second component of this mission is the DART satellite (Double Asteroid Redirection Test), which is American. AIM’s 200-million-euro budget places it among low-cost missions. The fate of the AIM mission is to be decided in the upcoming Ministerial Conference scheduled for late 2016. If approved, AIM would be launched in 2020 towards the Didymos asteroid. Arriving 18 months later, it would then begin its analysis of Didymoon while the binary asteroid system is passing about 11 million kilometers from Earth (30 times the Earth-Moon distance). Once at the asteroid, AIM will study the secondary body Didymoon by means of two radars, the infrared camera TIRI (Thermal Imager) and the VIS camera (Visual Imaging System), which will build up a 1-meter resolution map. At the same time AIM will release two mini satellites for scientific research purposes and also the Lander MASCOT-2 of Germany’s Aerospace Center, DLR. One of the new features of this mission is use of the Optel-D laser communications system to send recorded information back to Earth, specifically to ESA’s Optical Ground Station (OGS) in Tenerife. Finally, in 2022, AIM and DART will work jointly to determine the energy transfer resulting from DART’s impact against Didymoon. El último asteroide que pasó cerca de la Tierra fue bautizado como el asteroide 2011 MD. Este asteroide “rozó” la superficie de la Tierra a una distancia de 12.000 kilómetros. Se estima que cada varios cientos de miles de años asteroides de más un 1Km de diámetro, capaces de producir catástrofes globales o grandes extinciones, pasan próximos a la Tierra. La Agencia Espacial Europea ha puesto en marcha la misión AIM (Asteroid Impact Mission) que tiene como destino el asteroide binario Dydimos y cuyo objetivo es explorar y demostrar tecnologías que permitan evitar el impacto de asteroides sobre la Tierra y las devastadoras consecuencias que ello puede tener. Dentro de la misión AIM, GMV tiene un papel relevante ya que es responsable del análisis de misión, del subsistema GNC (Guiado, Navegación y Control) y de una parte importante del diseño de las operaciones, en uno de los dos estudios en marcha de la Agencia Espacial Europea. El mismo tiempo GMV está desarrollando desde su filial rumana la función de Hazard Avoidance y FDIR (identificación de fallos y recuperación de los mismos) para la misma misión. Y por último Ultimo pero no menos importante GMV está liderando un de los cinco estudios de concepto para hacer ciencia o experimentos adicional con AIM con dos CubeSats. AIM es parte activa del proyecto AIDA (Asteroid Impact and Deflection Assessment) de la ESA del DLR (Alemania), del Observatoire de la Côte d´Azur (Francia), NASA, y Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (JHU/APL), destinado a evaluar el potencial de la técnica del proyectil cinético para desviar asteroides cercanos. El segundo elemento de esta misión es el satélite DART (Double Asteroid Redirection Test), que es americano. El coste previsto de AIM, misión considerada de bajo coste, es de 200 millones de euros. El destino de la misión AIM se decidirá en la próxima Conferencia Ministerial prevista para finales de 2016. De ser aprobada la misión, AIM sería lanzada en 2020 rumbo al asteroide Didymos, al cual llegaría 18 meses más tarde y comenzaría entonces el análisis de Didymoon, cuando el sistema binario pase a aproximadamente 11 millones de kilómetros de la Tierra (30 veces la distancia de la Luna). AIM se dirigirá hacia Didymoon y lo estudiará empleando dos radares, la cámara infrarroja TIRI (Thermal Imager) y la cámara VIS (Visual Imaging System), que creará un mapa con una resolución de un metro. Al mismo tiempo, AIM volará dos mini satélites para dedicarlos a la ciencia y también el Lander MASCOT-2 del Centro de Investigación Aeronáutica y Espacial de Alemania, DRL. Una de las novedades de la misión es que la sonda empleará el sistema de comunicaciones Optel-D mediante láser para enviar la información recogida a la Tierra, concretamente a la estación terrestre OGS (Optical Ground Station) de la ESA en Tenerife. Finalmente, en 2022, AIM y DART trabajarán conjuntamente con el fin de determinar la transferencia de energía que resulta del choque de DART contra Didymoon. Image courtesy of ESA GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 23 SPACE / ESPACIO ACCEPTANCE OF THE SENTINEL-3 MISSION PLANNING SYSTEM ACEPTACIÓN DE SISTEMA DE PLANIFICACIÓN DE MISIÓN DE SENTINEL-3 In August EUMETSAT’s Darmstadt site in Germany hosted the acceptance of the mission planning system (MPF) of the Copernicus Sentinel-3 system. This event represented EUMETSAT’s official acceptance of the GMV-developed system as ready for the launch of the first satellite (S3A) of the two to be launched in the Sentinel-3 constellation; this first launch is scheduled for the first weeks of December. In this first phase the GMV-developed mission planning system (MPF) will generate the operational plans of the 4 instruments of the first of the two satellites, the data downloading plan and ground station network’s instrument-data acquisition plans. Later, when the second of the constellation’s satellites is launched (scheduled for 2017) the MPF will generate the plans for both satellites and reach its full operational capacity. The MPF is based on the Eumetsat Polar System (EPS, Metop) planning system, also operated by EUMETSAT. EPS MPF has been up and running since the launch of Eumetsat’s first satellite 9 years ago and has proven to be a robust and flexible system that meets mission needs at all moments. The Sentinel-3 MPF represents a considerable advance on its forerunner, responding to the technological demands posed by the new satellites, such as position-based commands or onboard autonomy, slashing ground operation costs. GMV is rounding out this activity with the onsite support service. This has involved posting a GMV engineer to EUMETSAT’s German HQ to prepare the system for operations and give support to the S3A launch. Durante el mes de agosto tuvo lugar en las instalaciones de EUMETSAT en Darmstadt (Alemania) la aceptación del Sistema de planificación de misión (MPF) del sistema Copernicus Sentinel-3. Con este hito EUMETSAT considera el sistema desarrollado por GMV listo para el lanzamiento del primero de los dos satélites (S3A) de la constelación Sentinel-3, que tendrá lugar en las primeras semanas de diciembre. En esta primera fase el Sistema de Planificación de Misión (MPF) desarrollado por GMV generará los planes operacionales de los 4 instrumentos del primero de los dos satélites, el plan de descargas de datos pág. 24 I GMV NEWS nº60 Septiembre 2015 así como los planes de adquisición de la red de estaciones de Tierra de los datos generados por los instrumentos. Más adelante, cuando se lance el segundo de los satélites de la constelación (previsto para 2017) el MPF generará los planes para ambos satélites y alcanzará su plena capacidad de funcionamiento. El MPF está basado en el sistema de planificación del Eumetsat Polar System (EPS, Metop), sistema también operado por EUMETSAT. El EPS MPF es un sistema que lleva operando exitosamente la misión desde el lanzamiento de su primer satélite hace 9 años y ha demostrado ser un sistema robusto y flexible, atendiendo las necesidades de la misión en todo momento. El MPF de Sentinel-3 supone un avance considerable en funcionalidad con respecto a su predecesor, respondiendo a las demandas tecnológicas que presentan los nuevos satélites como por ejemplo el comandado basado en posición o la autonomía a bordo, que reducen drásticamente los costes de operación en Tierra. GMV complementa esta actividad con el servicio de soporte “in situ” mediante un ingeniero de GMV desplazado en la sede central de EUMETSAT en Alemania, preparando el sistema para operaciones y dando soporte al lanzamiento del S3A. SATELLITE OBSERVATION APPLICATIONS FOR THE OIL AND GAS SECTOR APLICACIONES DE OBSERVACIÓN POR SATÉLITE PARA EL SECTOR PETROLERO Y GASÍSTICO GMV has recently finished an urban change detection analysis for Shell Global Solutions International over Iraq, using Very High Resolution satellite images to ascertain land use and land-coverage (LULC) changes from 2008 to 2015. The mapping standard set by the Multinational Geospatial Co-production Program (MGCP) for 1:50,000 scale maps was adapted in this project to more demanding spatial analysis requirements. Images obtained from the QuickBird satellite for 2008 and the Pleiades satellite for 2015 were then used to build up a GeoDatabase (GDB) for comparing the state of spatial elements from one date to another, the statistical analysis of LULC changes and cartographic representation. The resulting GDB helps Shell International keep up its Corporate Social Responsibility commitments with local communities in 8 major areas: agriculture, industry, dwellings, leisure urban facilities, road upkeep and care of water resources. This project has enabled GMV, as an expert in remote-detection and earth observation, to spread the use of VHR satellite applications into the oil and gas industry and demonstrate the usefulness of these images for projects with a tangible social benefit. Recientemente GMV ha concluido un proyecto de análisis de detección de cambio urbano para Shell Global Solutions sobre Iraq, en el que se han utilizado imágenes por satélite de muy alta resolución para ver los cambios producidos en la zona en los usos del suelo y la cobertura vegetal (LULC) entre 2008 y 2015. En el proyecto se ha adaptado el estándar cartográfico establecido por el Multinational Geospatial Co-production Program (MGCP) para mapas con una escala 1:50.000 a unas necesidades de análisis espacial más exigente. A través de las imágenes obtenidas de los satéltites QuickBird para 2008 y Pleiades para 2015 se ha creado una Base de Geodatos (GDB) que permite la comparación del estado de los elementos espaciales entre fechas, el análisis estadístico de los cambios LULC y la representación cartográfica. La base de Geodatos resultante ayuda a Shell International a mantener sus compromisos de responsabilidad social corporativa con las comunidades locales en 8 áreas principales: agricultura, industria, vivienda, instalaciones urbanas recreativas, estado de la red viaria y cuidado de los recursos hídricos. Para GMV, experta en teledetección y observación de la Tierra, este proyecto permite difundir el uso de aplicaciones de satélite de muy alta resolución en el sector del petróleo y el gas así como demostrar el uso de las imágenes en proyectos con un beneficio social tangible. UK SPACE CONFERENCE GMV was present at the “UK Space Conference 2015: Space-enabled Futures”, held from 13 to 15 July 2015 in Liverpool’s Arena & Convention Centre (ACC) in the UK. Held every two years, the UK Space Conference is the unmissable gathering for the entire UK space community; bringing together the space industry, users of space-based services, entrepreneurs, academia and government. GMV also took part in the exhibition area, giving demonstrations of its complete range of products for the space sector. GMV estuvo presente en el evento ‘UK Space Conference 2015: Space-enabled Futures’ (Conferencia espacial del Reino Unido 2015: El Futuro que hace posible el espacio) que tuvo lugar durante los días 13 al 15 julio de 2015, en el Arena & Convention Centre (ACC) de Liverpool, Reino Unido. Celebrada cada dos años, esta conferencia es reunión ineludible para toda la comunidad espacial del país, que reúne a la industria espacial, los usuarios de los servicios basados en el espacio, los empresarios, la universidad y el gobierno. GMV participó en la zona de exposición donde se llevarán a cabo diferentes demostraciones de su línea completa de productos para el sector espacial. GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 25 SPACE / ESPACIO SUCCESSFUL LAUNCH OF SKY MUSTER SKY MUSTER LANZADO CON ÉXITO Right on schedule, on 30 September, the Sky Muster communications satellite of the Australian operator NBN Co successfully blasted off atop an Ariane 5 ECA rocket from Kourou Spaceport in French Guiana. GMV has been responsible for the real time telemetry and command processing system based on its hifly® product plus three other ground subsystems: the flight dynamics system based on focusSuite, the ground segment control and monitoring system based on magnet and the payload management system based on smart rings. These systems, installed in five of NBN Co’s operation stations in Australia, provide a complete packet of software and functions for controlling NBN Co’s satellites in an efficient, safe and automatic manner. They have been successfully integrated and deployed in a modern virtual and ecological environment using blade and vSphere servers. As well as the software, GMV is also seeing to training, support and maintenance arrangements for the system’s end users. Sky Muster, also called NBN Co N1A, will be phased into the nbn™ network, giving fast broadband access to the remotest corners of Australia’s vast territory. NBN Co 1A forms part of a program including 2 satellites built by SSL, the second of which, NBN Co 1B, is scheduled for launch next year. Tal y como estaba previsto, el día 30 de septiembre el satélite de comunicaciones Sky Muster del australiano NBN Co. despegó con éxito a bordo de un lanzador Ariane 5 ECA desde el Centro espacial de Kouru, en la Guayana Francesa. GMV ha sido responsable del sistema de procesamiento en tiempo real de telemetría y comando basado en su producto hifly®, así como otros tres subsistemas terrenos: el sistema de dinámica de vuelo basado en focusSuite, el sistema de monitorización y control de segmento terreno basado en magnet y el sistema de gestión de la carga de pago, basado en smart rings. Estos sistemas, instalados en cinco estaciones de operaciones de NBN en Australia, proporcionan un paquete completo de software y funcionalidades para el control de los satélites NBN de una manera eficiente, segura y automática. Han sido integrados y desplegados con éxito en un entorno virtual moderno y ecológico que utiliza servidores blade y vSphere. Además del software, GMV proporciona también formación, soporte y mantenimiento para los usuarios finales del sistema. Sky Muster, también denominado NBN Co N1A, estará integrado en la red nbn™ dando acceso a la banda ancha rápida hasta en los rincones más alejados del territorio australiano. NBN Co 1A forma parte de un programa que incluye 2 satélites construidos por SSL, el segundo de los cuales, NBN Co 1B, está previsto lanzarlo el próximo año. GMV DISPLAYS ITS SPACE PRODUCTS AND SERVICES TO THE ASIAN MARKET GMV PRESENTA SUS PRODUCTOS Y SERVICIOS DEL SECTOR ESPACIAL AL MERCADO ASIÁTICO GMV has taken part in APSCC 2015 (AsiaPacific Satellite Communications Council), the benchmark space event in the AsiaPacific region, held this year in Seoul, South Korea, from 22 to 24 September. Under the watchword “Stay Connected” APSCC 2015 brought together over 500 professionals and leaders of the space industry and helped to identify new business lines while also serving as a forum for swapping notes in a constantly evolving market. As well as running a stand, GMV was again invited to take part as speaker, this year in the session dealing with New Developments in Ground Systems and Equipment. This involved a review of the roadmap of GMV’s products, dealing in particular with the following aspects: compatibility with new satellite platforms, the management of constellations, planning and automation of operations and, last but not least, payload optimization. In general the review highlighted the technological advantages recently phased in and the evolutions scheduled for upcoming years. GMV ha participado en la Conferencia y Exhibición de la APSCC (Asia-Pacific Satellite Communications Council), evento espacial de referencia de la región Asia Pacífico, celebrado en Seúl, Corea del Sur, durante los días 22 al 24 de septiembre. Bajo el lema “Mantente Conectado” (Stay Connected), la conferencia APSCC 2015 ha reunido a más de 500 profesionales y líderes de la industria espacial y ha servido para identificar nuevas líneas de negocio, así como para compartir conocimientos de un mercado en constante evolución. Además de disponer de un stand, GMV fue nuevamente invitada a participar como ponente en el panel dedicado a “Nuevos Desarrollos en Sistemas en Tierra”, donde tuvo lugar una revisión del mapa de ruta de los productos de GMV, en particular la compatibilidad con nuevas plataformas de satélites, la gestión de constelaciones, la planificación y automatización de operaciones y, por último, la gestión y la optimización de la carga de pago, destacando las ventajas tecnológicas incorporadas recientemente, así como las evoluciones previstas para los próximos años. pág. 26 I GMV NEWS nº60 Septiembre 2015 ACTIVE GMV PARTICIPATION IN EGS-CC, THE ESA’S NEW GROUND INFRASTRUCTURE ACTIVA PARTICIPACIÓN DE GMV EN LA NUEVA INFRAESTRUCTURA EGS-CC DE LA ESA The European Ground Systems – Common Core (EGS-CC) is a European initiative to develop a new ground software infrastructure for the Monitoring and Control (M&C) of space systems. The initiative was initiated in 2009 by ESA and is currently supported by the European System Integrators, including AIRBUS Defence and Space, Thales Alenia Space and OHB System and also by the French, German and UK national space agencies, CNES, DLR and UKSA. The EGS-CC is intended to be used in the spacecraft Assembly, Integration and Testing environment, as well as in actual flight operations. The system will therefore allow for a smooth transition between both environments in terms of databases and procedures, which in turn will reduce risks and costs. It is thus envisaged that the wide variety of systems currently used for AIT and operations will be reduced to systems based on a common kernel used throughout phases by subsystemists, integrators, and operations teams. The EGS-CC is a “Core”; this means that it will provide the basis for the actual M&C development adapted by extension to user needs and the mission itself. The EGS-CC will however remain as a core that provides the level of commonality that ensures the aforementioned synergies and advantages. The EGS-CC C/D phase is funded under the ESA GSTP program with contributions from a large number of countries, among them Spain with a very significant contribution. EGS-CC is currently at the beginning of its more than 4-year C/D Phase and is being developed by a multinational consortium of around 20 companies. GMV is playing an important role with an active participation in system-level activities and two engineers in the System Architects and Integration and Validation teams, as well as being responsible for the implementation of three important components. The EGSCC is based on a layered architecture and makes use of state-of-the-art technologies. In addition to GMV’s participation in the EGS-CC development itself, the GMV branch in Portugal is also starting a GSTP study to analyze the impact of the new EGS-CC in the existing ESTEC Avionics Test Bench used for space systems testing. La European Ground Systems – Common Core (EGS-CC) es una iniciativa europea cuya finalidad es desarrollar una nueva infraestructura de software terreno para la monitorización y el control de sistemas espaciales. La iniciativa fue puesta en marcha en 2009 por la Agencia Espacial Europea (ESA) y en ella participan actualmente integradores de satélites europeos como AIRBUS Defence and Space, Thales Alenia Space y OHB System, así como las agencias espaciales nacionales francesa, alemana y británica CNES, DLR y UKSA. El sistema EGS-CC se utilizará no solo en el entorno de montaje, integración y ensayos de la nave espacial, sino también en las operaciones reales de vuelo. El sistema, por tanto, facilitará la transición entre ambos entornos en lo que se refiere a bases de datos y procedimientos, lo que, a su vez, reducirá riesgos y gastos. Está así previsto que la amplia variedad de sistemas que actualmente se utilizan para AIT y operaciones se reduzca a sistemas basados en un núcleo común que utilizarán integradores, responsables de subsistemas y equipos de operaciones en todas sus fases. La EGS-CC es una infraestructura básica, es decir, que a partir de ella se podrán desarrollar los sistemas finales de monitorización y control especialmente adaptados a las necesidades del usuario y a la misión concreta. La EGS-CC, sin embargo, seguirá siendo una plataforma básica con un nivel de funcionalidad común que garantice las sinergias y ventajas antes mencionadas. La fase EGS-CC C/D recibe financiación dentro del programa GSTP de la ESA, con aportaciones de un gran número de países, entre ellos España, con una contribución muy significativa. La EGS-CC se encuentra actualmente en el inicio de su fase C/D, que tendrá una duración de más de cuatro años, desarrollada por un consorcio multinacional de cerca de 20 países. GMV desempeña una función importante con su activa participación en actividades relacionadas con los sistemas y dos ingenieros en los equipos de arquitectura de sistemas y de integración y validación, y es además responsable de la implantación de tres componentes importantes. La EGSCC se basa en una arquitectura en capas y utiliza las más modernas tecnologías. Además de la participación de GMV en el propio desarrollo de la EGS-CC, la filial de GMV en Portugal está también comenzando un estudio financiado a través del Programa General de Apoyo Tecnológico (GSTP) de la ESA para analizar el impacto de la nueva EGS-CC en el banco de pruebas para aviónica del ESTEC, que ya se utiliza para la verificación y validación de sistemas espaciales. GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 27 SPACE / ESPACIO 40TH ANNIVERSARY CELEBRATION OF ESA’S EUROPEAN TRACKING NETWORK 40 ANIVERSARIO DE LA RED EUROPEA DE SEGUIMIENTO DE LA ESA At the end of September the European Space Agency (ESA) celebrated the fortieth anniversary of its tracking station network, ESTRACK, a vital space-mission ally that allows scientists and experts to track satellites with great precisión. The ceremony was held in the deep-space ground station of Cebreros (Ávila), to coincide with the tenth anniversary of its own inauguration. Key participants were Thomas Reiter ESA’s Director of Human Spaceflight and Operations; Álvaro Giménez, Director of Science and Robotic Exploration; Valeriano Claros-Guerra, the former Director of Villafranca Ground Station; and Alaudin Bhanji, NASA’s Deep Space Network Project manager. GMV’s President, Mónica Martínez Walter, was also keen not to miss this red-letter event. ESA’s European tracking network was born in 1975 in Spain. Four decades later it now runs ground stations in three continents, all operated remotely from the European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) in Darmstadt, Germany. It is now catering for over a dozen earth-observation and science missions, including the Swarm and Sentinel satellites and the Rosetta, Gaia and Mars Express missions. During the ceremony Thomas Reiter highlighted the constant evolution of the network to meet operational requirements of future missions, a process backed up, he explained, by the solid and ongoing support of the whole European industry. La Agencia Espacial Europea (ESA) celebró a finales del mes de septiembre el 40 aniversario de su red de estaciones de seguimiento, ESTRACK, como elemento indispensable para las misiones espaciales, que permite a científicos y expertos determinar con gran precisión la posición de los satélites. La ceremonia de celebración tuvo lugar en la estación de espacio profundo de Cebreros (Ávila), coincidiendo con los diez años desde su inauguración, y contó con la presencia del director de vuelos tripulados de la ESA, Thomas Reiter; el director de Ciencia y Exploración Robótica, Álvaro Giménez; el ex director de la estación de Villafranca, Valeriano Claros-Guerra; y el jefe de la Red de Espacio Profundo de la NASA, Alaudin Bhanji. Una celebración a la que no quiso faltar la presidenta de GMV, Mónica Martínez. La Red Europea de Seguimiento de la ESA nació en 1975 en España y, tras cuatro décadas, cuenta con estaciones en tres continentes, todas ellas operadas de forma remota desde el Centro Europeo de Operaciones Espaciales (ESOC) en Darmstadt, Alemania. En la actualidad atiende a más de una docena de misiones de Ciencia y Observación de la Tierra, incluyendo los satélites Swarm y los Sentinel y las misiones Rosetta, Gaia y Mars Express. Durante el evento, Thomas Reiter destacó la continua evolución de la red para atender a los requisitos operacionales de las futuras misiones, algo para lo que, según afirmó, cuentan con el apoyo sólido y continuado de la industria europea. pág. 28 I GMV NEWS nº60 Septiembre 2015 TWO NEW GALILEO SATELLITES IN ORBIT DOS NUEVOS SATÉLITES GALILEO EN ÓRBITA As scheduled, on 11 September, two new Galileo satellites (9 and 10) successfully lifted off from the European Spaceport in French Guiana onboard a Soyuz rocket. Both satellites follow in the wake of the six satellites launched two by two in October 2011, October 2012, August 2014 and March 2015. GMV has played a key part in the GALILEO program right from the word go. It has supplied several key elements for the system’s ground segment such as the Orbit & Synchronisation Processing Facility (OSPF), the Integrity Processing Facility (IPF), the Service Product Facility (SPF), the Flight Dynamics Facility (FDF) and the MDDN Network equipment (MNE). GMV is also currently the main contractor for providing Galileo’s essential Timing and Geodetic Validation Facility (TGVF) services; it is co-leading development of the European Union’s GNSS Service Centre (GSC) and is leading the development of Galileo’s commercial service (CS) demonstrator. Europe’s GALILEO satellite navigation system, being jointly developed by the European Commission and the European Space Agency (ESA), is due to begin providing navigation services by late 2015 with full system capability in place by 2020. Two other satellites will be launched by the end of 2015. The total Galileo constellation will consist of 30 satellites in three orbital planes, with their corresponding ground infrastructure. It will provide high-precision global geo-positioning services that are interoperable with the US GPS system and Russia’s GLONASS system, considerably boosting Europe’s technological independence. Tal y como estaba previsto el día 11 de septiembre dos nuevos satélites Galileo (9 y 10) despegaron con éxito desde el Puerto Espacial Europeo en la Guayana Francesa a bordo de un lanzador Soyuz. Ambos satélites seguirán los pasos de los seis satélites lanzados de dos en dos en octubre de 2011, octubre de 2012, agosto de 2014 y marzo de 2015. GMV ha tenido una participación relevante en el Programa GALILEO desde sus fases iniciales. GMV ha suministrado varios elementos clave del segmento terreno del sistema, tales como el OSPF (Orbit & Synchronisation Processing Facility), IPF (Integrity Processing Facility), SPF (Service Product Facility), FDF (Flight Dynamics Facility) y MNE (MDDN Network equipment). Actualmente, GMV es el contratista principal para la provisión de los servicios de geodesia y sincronización precisa de tiempo (TGVF) que precisa el sistema Galileo para su funcionamiento; colidera el desarrollo del Centro Europeo de Servicios de Navegación por Satélite (GSC) de la Unión Europea y lidera el contrato para el desarrollo del Demostrador del Servicio Comercial (CS) de Galileo. Está previsto que el sistema de navegación por satélite europeo GALILEO, desarrollado por la Comisión Europea en colaboración con la Agencia Espacial Europea (ESA), empiece a prestar servicios a finales de 2015 y esté completamente operativo en 2020. Antes de finalizar 2015 se lanzarán otros dos satélites. En total Galileo contará de una constelación de treinta satélites situados en tres planos orbitales, con su correspondiente infraestructura en tierra, y facilitará servicios de geolocalización global de gran precisión e interoperables con el GPS americano y el GLONASS ruso, incrementando considerablemente la independencia tecnológica europea. ION 2015 For yet another year GMV took part in ION GNSS+ 2015, one of the world’s most important satellite navigation events, held from 14 to 18 September 2015 at the Tampa Convention Center in Tampa, Florida. GMV played a key role in this meeting, in keeping with its leadership position in the satellite navigation market. In this year’s conference GMV presented several articles. The company also ran a stand showcasing the family of magicGNSS products, developed by GMV, plus other applications and developments in the field of satellite navigation. Un año más GMV estuvo presente en ION GNSS+ 2015, uno de los eventos más importantes en el campo de la navegación por satélite, que tuvo lugar durante los días 14 al 18 de septiembre de 2015 en el Centro de Convenciones Tampa en Tampa, Florida. En línea con la posición de liderazgo de GMV en el mercado de la navegación por satélite, la presencia de GMV fue muy relevante. En esta edición GMV presentó diversos artículos. Asimismo, GMV contó con un stand en el que presento la familia de productos magicGNSS, desarrollada por GMV, así como otras aplicaciones y desarrollos en el campo de la navegación por satélite. GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 29 ROBOTICS / ROBÓTICA FOXIRIS ROBOT GETS READY FOR THE 2ND ARGOS CHALLENGE OF THE OIL AND GAS COMPANY TOTAL EL ROBOT FOXIRIS SE PREPARA PARA LA 2ª COMPETICIÓN ARGOS DE LA PETROLERA TOTAL The first ARGOS challenge competition of June 2015 was a challenging experience for all participating teams that are taking part in this competition sponsored and brokered by the oil and gas company TOTAL with the support of the French National Research Agency (ANR). Many lessons learned have been compiled and analyzed by the FOXIRIS team led by GMV together with IDMind, Polytechnic University of Madrid (UPM) and University of Malaga (UMA). A major conclusion was the need of practicing and completing the proposed autonomous missions before starting on any modifications of the current robot version. For that purpose our engineers have been continuously exercising the robot this summer both over the virtual UMAD simulator and our outdoor industrial mock-up area until successfully fulfilling the missions of the first competition. At the same time the Foxiris team has been working on an improved design of the robot’s capabilities in view of the comments and feedback from the ARGOS Jury. At present, the FOXIRIS consortiumis working very hard on the detail design and manufacture of a new robot body with better traction abilities and integrated sensors. Minor modifications will be performed depending on the final version of the incoming rules for the Second Competition. All hardware upgrades are expected to be performed during this autumn 2015 allowing us to start an intensive testing period by next January 2016: climbing of stairs, validation of new perception and manipulation capabilities, increase of robot safety, inclusion of a versatile Control Centre, etc. Following this roadmap the FOXIRIS robot will be ready for the second ARGOS Challenge competition and prepared to play a major role among all participating teams. La primera competición del desafío ARGOS, celebrada en junio de 2015, fue un verdadero reto para todos los equipos que participan en esta competición patrocinada y gestionada por la compañía petrolera y gasística TOTAL, con el apoyo de la Agencia Nacional francesa de Investigación (ANR). El equipo FOXIRIS, encabezado por GMV y del que también forman parte IDMind, la Universidad Politécnica de Madrid (UPM) y la Universidad de Málaga (UMA), ha recopilado y analizado muchas de las lecciones que allí se aprendieron y una de las principales conclusiones extraídas ha sido la necesidad de poner en práctica y completar las misiones autónomas propuestas antes de comenzar a hacer cualquier modificación de la versión actual del robot. Para ello, nuestros ingenieros han estado ejercitando este verano de forma continuada el robot en el simulador virtual UMAD y en nuestra área industrial de ensayos al aire libre hasta el cumplimiento con éxito de las misiones de la primera competición. Al mismo tiempo, el equipo FOXIRIS ha estado trabajando en un diseño mejorado de las capacidades del robot teniendo en cuenta los comentarios y la información recibidos del jurado de ARGOS. En la actualidad, el consorcio FOXIRISestá concentrando todos sus esfuerzos en el diseño de detalle y la fabricación del cuerpo principal de un nuevo robot, con mejor capacidad de tracción y sensores integrados. Se realizarán modificaciones menores dependiendo de la versión final de las bases de participación en la segunda competición. Está previsto que todas las mejoras en los equipos estén finalizadas durante este otoño 2015, lo que nos permitiría el inicio de un periodo intensivo de pruebas el próximo mes de enero de 2016: subida de escalones, validación de nuevas capacidades de percepción y manipulación, mejora de la seguridad del robot o inclusión de un Centro de Control versátil, entre otras. Siguiendo esta hoja de ruta, el robot FOXIRIS estará listo para la segunda competición ARGOS y preparado para quedar en buen lugar entre todos los equipos participantes. NIGHT OF ROBOTS On 22 May GMV ran a stand in the 3rd Night of Robots, a science event organized by the Industrial Research Institute for Automation and Measurements (PIAP) in Warsaw. Night of Robots is Poland’s biggest and most popular science-education event for robotics fans. Its aim is to promote technological innovation and to showcase the activity and scope of Polish firms, research centers and university organizations in the robotics area. GMV’s stand, one of the most popular, displayed videos on the company’s space activities and solutions. Several simulations were also set up to give younger visitors a chance to try out their skills at eliminating space debris or placing a satellite in orbit. El día 22 de mayo GMV participó con un stand en la 3ª edición de “Night of Robots”, evento científico organizado por el Industrial Research Institute for Automation and Measurements (PIAP) en Varsovia. Night of Robots es el mayor y el más popular evento científico-educativo de Polonia dedicado a los aficionados de la robótica. Su objetivo es la promoción de innovaciones tecnológicas, así como la presentación de la actividad y el alcance de los centros de investigación, organizaciones universitarias y empresas polacas en el área de la robótica. En el stand de GMV, que gozó de una enorme popularidad, se presentaron vídeos sobre las soluciones y la actividad de la empresa en el sector espacial. Asimismo, se montaron varias simulaciones para que los más pequeños pudiesen probar sus dotes a la hora de eliminar la basura espacial o colocar un satélite en órbita. pág. 30 I GMV NEWS nº60 Septiembre 2015 LABORATORY WITH A RESISTOJET-DRIVEN ROBOTIC ARM LABORATORIO CON BRAZO ROBÓTICO Y PROPULSIÓN CON “RESISTOJET” Image courtesy of CBK PAN GMV is currently involved in a project that aims to develop and validate the laboratory model of an orbital system consisting of a resistojet-driven spacecraft and robotic arm. The project is funded by Poland’s National Centre for Research and Development (NCBiR) and is being carried out by a consortium of Polish companies and academic institutions led by CBK PAN (Space Research Centre of the Polish Academy of Sciences). Within this project GMV’s Poland subsidiary is responsible for the work package dealing with the definition of scenarios and requirements. The particular work carried out by GMV in this project has included the definition of possible use cases, including Active Debris Removal (ADR) and servicing missions, their trade-off, a brief mission analysis and definition of system requirements. The project is currently in the detailed design phase; the recently conducted Preliminary Design Result (PDR) was deemed successful. GMV has also taken part in detailed design and testing, where the aim of the baseline scenario is to deorbit the Kosmos rocket stage from low earth orbit (LEO) into a neutral free-fall orbit, in line with the ESA’s Clean Space program activity. Actualmente GMV se encuentra inmersa en un proyecto que tiene como objeto el desarrollo y validación de un modelo de laboratorio de un sistema orbital consistente en una nave con propulsor resistivo (resistojet) y un brazo robótico. El proyecto está financiado por el Centro Nacional de I+D de Polonia (NCBiR) y su ejecución está a cargo de un consorcio compuesto por empresas e instituciones universitarias polacas encabezado por CBK PAN (Centro de Investigación Espacial de la Academia Polaca de las Ciencias). Dentro del proyecto, la filial de GMV en Polonia es responsable del paquete de trabajo dedicado a la definición de escenarios y de requerimientos. En concreto la labor de GMV en el proyecto ha incluido la definición de usos posibles (como las misiones de retirada de basura espacial y de servicios), sus ventajas e inconvenientes, así como un análisis de la misión y definición de los requerimientos del sistema. Actualmente el proyecto se encuentra en la fase de diseño detallado una vez que el resultado del diseño preliminar (PDR), realizado recientemente, resultó satisfactorio. Para la fase de diseño detallado y de ensayos, en los que también participa GMV, se ha designado como escenario básico de referencia maniobrar el cohete portador del Kosmos de la órbita terrestre de baja altura (LEO) para situarlo en una órbita neutral de caída, de acuerdo con la actividad del programa Clean Space de la ESA. INNOVASPAIN BRUNCH “ME, THE ROBOT” BRUNCH DE INNOVASPAIN ´YO ROBOT´ On 16 June GMV took part in the Innovaspain Brunch “Me, the robot”, organized for analyzing and debating the robotics and artificial intelligence industry in Spain. Artificial Intelligence and Robotics have now made such unexpected headway that they are now closing in on the realms of science fiction or even surpassing it. Driven by this revolution, classic robotics will soon be left far behind by groundbreaking developments taken up in such aspects of our daily lives as education, health and leisure. In this new Innovaspain Brunch, to be held in the Real Academia de Ingeniería (Royal Engineering Academy), Alberto Medina Andrés, head of GMV’s robotics section, will be taking part with other experts in the debate about the present and future of this ongoing revolution. El día 16 de junio, GMV participó en el Brunch de Innovaspain, ´Yo, robot´, encuentro organizado para analizar y debatir en torno a la industria de la robótica y de la Inteligencia Artificial en España. La Inteligencia Artificial y la Robótica han traspasado los horizontes previstos, acercándose, y en muchos casos superando, lo que eran hipótesis que podían definirse como ciencia-ficción. Se trata de una revolución donde la robótica clásica queda superada por una serie de realidades y expectativas próximas que la acercan a lo cotidiano como lo puede ser la educación, la salud o el ocio. Esta nueva cita del ´Brunch de Innovaspain´, que tuvo lugar en la Real Academia de Ingeniería, contó con Alberto Medina, jefe de sección robótica de GMV que junto a otros expertos, participó en el debate-coloquio para reflexionar sobre el presente y futuro de esta revolución. GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 31 ROBOTICS / ROBÓTICA ROBOTIC ADVANCES IN SPACE REFUELING SYSTEMS AVANCES EN ROBÓTICA PARA SISTEMAS DE REPOSTAJE ESPACIALES There is no doubt that space exploitation could clearly benefit from the latest robotics breakthroughs. The provision of services in space is a clear candidate for application of autonomous approach and docking mechanisms. This provision of services in space is an increasingly important factor in space exploitation and in maintaining the required space infrastructure. On-Orbit Servicing (OOS) operations help to slash operating costs for unmanned space assets such as navigation and geostationary communication satellites. The servicing of satellites in orbit includes many aspects of component assembly and equipment maintenance (both corrective and preventive), the replenishment of consumables and upgrade and repair. The European Space Agency (ESA) considers that grasping and refueling operations are promising near-mid-term capabilities that could be performed by servicing spacecraft. In this line of research ESA has awarded the ASSIST project to a GMV-led consortium. The aim of this project is to tackle the analysis, design and validation of internal provisions (such as modifications to fuel, gas, electrical and data architecture to allow servicing) and external provisions (such as integrated berthing fixtures with peripheral electrical-, gas- and liquid-connectors, leak check systems and corresponding optical and radio markers for cooperative rendezvous and docking). As well as the overall coordination of activities GMV has also led the requirements specification phase and the development of a dynamic simulator for designing the electromagnetic berthing system and subsequent refueling procedure. This detailed design will then serve as the basis for a prototype of the electromechanical system, which will be tested both in a thermal vacuum chamber and on an airbearing granite table testbed to simulate two-dimensional zero-gravity conditions. The ultimate aim of this project is to design and promote standard refueling systems to be installed in Europe’s current and future fleet of commercial geostationary satellites (GEO) and on scientific space missions. This refueling approach is being developed in common with the European industry (OHB, Thales Alenia Space) and is expected to be consolidated with European commercial operators as a first step towards its conversion into an international standard; this approach is also being studied for OOS spacecraft like Airbus DS’s SpaceTug. No hay duda de que la explotación del espacio puede beneficiarse claramente de los últimos avances en robótica. La prestación de servicios en órbita es un claro candidato para la aplicación de mecanismos autónomos de aproximación y acoplamiento. Esta prestación de servicios en el espacio es un factor cada vez más importante en la explotación del espacio, así como en el mantenimiento de la infraestructura espacial requerida. Las operaciones OOS (On-Orbit Servicing) permiten una reducción considerable de los costes operativos asociados a los vehículos espaciales no tripulados, como los satélites de navegación y de comunicaciones. La prestación de servicios por satélites en órbita incluye muchos aspectos de montaje de componentes y mantenimiento de equipos (tanto de corrección como preventivo), la reposición de consumibles y la actualización y reparación. La Agencia Espacial Europea (ESA) considera que las operaciones de captura y repostaje tienen un prometedor potencial a corto y medio plazo como funciones realizables por naves espaciales de servicio. En esta línea de investigación, la Agencia Espacial Europea (ESA) ha adjudicado a un consorcio liderado por GMV el proyecto ASSIST, que tiene como objetivo abordar el análisis, el diseño y la validación de elementos internos (como, por ejemplo, modificaciones a las arquitecturas de combustible, gas, electricidad y datos para permitir la prestación de servicios) y elementos externos (tales como accesorios integrados de atraque con conectores periféricos eléctricos, de gas y líquido, sistemas de comprobación de fugas y los correspondientes marcadores ópticos y de radio para operaciones cooperativas de aproximación y acoplamiento). Además de la coordinación de las actividades, GMV ha liderado la fase de toma de requisitos y el desarrollo de un simulador dinámico que permite diseñar de forma eficiente el sistema electromecánico de atraque y posterior reposición de combustible. A partir del diseño detallado se fabricará un primer prototipo del sistema electromecánico que se probará tanto en una cámara térmica de vacío como en una mesa de granito con un colchón de aire que permite condiciones de ingravidez en dos dimensiones. El objetivo final de este proyecto es diseñar y promover sistemas estándar de repostaje que puedan instalarse en las plataformas comerciales europeas presentes y futuras de satélites geoestacionarios (GEO) y en misiones espaciales científicas. Este enfoque para el repostaje se está desarrollando en común con la industria europea (OHB, Thales Alenia Space) y se espera su consolidación con los operadores comerciales europeos como un primer paso hacia su conversión en estándar internacional; también se está estudiando este enfoque para naves espaciales de servicio en órbita, como el SpaceTug, de Airbus DS. Image courtesy of MOOG pág. 32 I GMV NEWS nº60 Septiembre 2015 DEFENSE & SECURITY / DEFENSA Y SEGURIDAD ENHANCEMENT OF THE SURVEILLANCE CAPACITY OF EU’S MARITIME BORDERS MEJORA DE LA CAPACIDAD DE VIGILANCIA DE FRONTERAS MARÍTIMAS DE LA UE As part of the CLOSEYE project dissemination strategy, the Guardia Civil of Madrid hosted on 30 September the first “CLOSEYE VIP Day”. CLOSEYE is an FP7 European Commission project that aims to provide an operational and technical framework that increases situational awareness and improves the reaction capability of authorities surveying the external borders of the EU. To that end CLOSEYE has been structured into three phases to last 38 months in all. The first phase identified user needs, available solutions and the validation strategy. This phase ended in July 2014 with the selection, via competitive call, of the companies to provide the solutions to be tested; GMV was chosen as supplier of one of them. GMV’s solution comprises an integrated command, control and coordination system rolled out in different centers and Como parte de la estrategia de difusión del proyecto CLOSEYE, el día 30 de septiembre la dirección de la Guardia Civil de Madrid acogió el primer ´CLOSEYE VIP Day´. CLOSEYE es un proyecto financiado por el VII Programa Marco de Investigación y Desarrollo de la Comisión Europea que persigue proporcionar un marco técnico y operativo para incrementar la conciencia situacional y mejorar la capacidad de reacción de las autoridades de vigilancia de las fronteras exteriores de la Unión Europea. Para ello, CLOSEYE se ha estructurado en tres fases a lo largo de 38 meses de duración. En la primera fase se identificaron las necesidades de los usuarios y las soluciones disponibles así como la estrategia de validación. Esta fase finalizó en julio de 2014 con la selección de resources both of the Spanish Guardia Civil and the Portuguese Guardia Nacional Republicana. This system incorporates various pre-existing information sources plus a series of groundbreaking sensors, providing the capacity of distributing information between the various nodes in different countries and agencies as well as coordination of their resources. The second phase, now underway, will validate the initially designed solutions in real operational scenarios during joint operations run by Frontex. Once these validations have been completed, the project will move on to the third and last, results-assessment phase, establishing the type approval of services and systems of similar characteristics for their supply to the rest of Europe’s security corps and forces. The event included diverse presentations by representatives of the European Commission and project partners and contractors plus an exhibition area showcasing the main developments carried out in CLOSEYE. The event agenda included diverse presentations from European Commission representatives and project partners and contractors, while the exhibition area showcased the main developments carried out in CLOSEYE. GMV was thus able to explain and display the benefits of its solution during the presentations and in the exhibition area.The event was formally opened by the General Director of the Guardia Civil, Arsenio Fernández de Mesa, and closed by the Spanish Minister of Interior, Jorge Fernández Díaz. Other key participants were representatives of the European Commission, several border surveillance authorities from different member states and representatives of various organizations and European security corps and forces. las compañías que proporcionarían las soluciones a ser evaluadas y en la que GMV fue seleccionada como suministrador de una de ellas. La solución de GMV consiste en un sistema Integrado de Mando, Control y Coordinación desplegado en distintos centros y medios de la Guardia Civil y la Guardia Nacional Republicana portuguesa. Este sistema incorpora distintas fuentes de información ya existentes así como una serie de sensores innovadores, proporcionando la capacidad de distribución de información entre distintos nodos de distintos países y agencias así como la coordinación de sus medios. En una segunda fase, actualmente en curso, se validarán sobre el terreno en operaciones conjuntas dirigidas por Frontex, las soluciones inicialmente diseñadas. Una vez finalizadas estas validaciones se pasará a la tercera y última fase de evaluación de los resultados, donde se establecerá la homologación de servicios y sistemas de similares características para su suministro al resto de Fuerzas y Cuerpos de Seguridad europeos. La agenda del evento incluyó diversas presentaciones de representantes de la Comisión Europea, de partners y contratistas del proyecto así como un área de exposición en la que se mostraron los principales desarrollos llevados a cabos dentro de CLOSEYE. La agenda del evento incluyó diversas presentaciones de representantes de la Comisión Europea, de partners y contratistas del proyecto así como un área de exposición en la que se mostraron los principales desarrollos llevados a cabo dentro de CLOSEYE. GMV tuvo oportunidad de explicar a todos los asistentes los beneficios de su solución tanto durante las presentaciones como en el área de exposición. El evento, inaugurado por el Director General de la Guardia Civil, Arsenio Fernández de Mesa, y clausurado por el ministro del Interior, Jorge Fernández Díaz, contó con representantes de la Comisión Europea, autoridades de vigilancia de fronteras de diferentes estados miembros así como representantes de distintos organismos, Cuerpos y Fuerzas de Seguridad europea. GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 33 DEFENSE & SECURITY / DEFENSA Y SEGURIDAD PLATFORM FOR SENSING AND MONITORING ILLEGAL SUBSTANCES PLATAFORMA PARA LA DETECCIÓN Y VIGILANCIA DE SUSTANCIAS ILEGALES GMV forms part of the consortium carrying out the NOSY project (New Operative Sensing sYstem), which aims to set up a tamper-proof platform for sensing and monitoring illegal or suspicious chemical substances to support the fight against organized crime. Miniaturized and highly sensitive devices will be integrated into law enforcement agencies’ field equipment, enabling data exchange with remote stations and handheld devices through cryptographically secure channels. NOSY field devices will combine stateof-the-art micro- and nano-technologies with advanced smart sensing materials, providing essential help in tackling illegal drug trafficking and the development of homemade bombs. The platform’s tamper resistance, and its compliance with all legal, integrity and chain-of-custody requirements associated with evidence gathering protocols (identified by law enforcement and forensic agencies involved in the project), will ensure that all data obtained through the NOSY platform is admissible in a Court of Justice. NOSY, coordinated by Aero Sekur, forms part of the European Union’s Horizon 2020 (H2020) program. GMV forma parte del consorcio que llevará a cabo el proyecto NOSY (New Operative Sensing sYstem), que tiene como objetico el desarrollo de una plataforma no manipulable para la detección y vigilancia de sustancias químicas ilegales o sospechosas como ayuda en la lucha contra el crimen organizado. Dicha plataforma integrará dispositivos miniaturizados y de alta sensibilidad en los equipos de campo de los cuerpos de policía, que permitirán el intercambio de datos con estaciones remotas y dispositivos manuales a través de canales protegidos mediante encriptación. Los dispositivos de campo NOSY combinarán las más modernas micro y nano tecnologías con avanzados materiales inteligentes de detección, proporcionando una ayuda esencial en la lucha contra el tráfico de sustancias estupefacientes y la fabricación de bombas caseras. La resistencia a la manipulación de la plataforma y su cumplimiento de todos los requisitos legales, de integridad y de cadena de custodia asociados a los protocolos de recogida de pruebas (identificados por los cuerpos y fuerzas de seguridad y de investigación judicial participantes en el proyecto), garantizarán que todos los datos obtenidos mediante la plataforma NOSY sean admisibles en un tribunal de justicia. NOSY forma parte del programa marco de la Unión Europea Horizon 2020 (H2020) y está coordinado por Aero Sekur. GMV PARTICIPATION IN MSPO 2015 / PARTICIPACIÓN DE GMV EN MSPO 2015 GMV participated as an exhibitor in the 23rd International Defence Industry Exhibition MSPO 2015, held from 1 to 4 September 2015 in Kielce, Poland. As a tried-and-trusted supplier of international defense organizations and armed forces, GMV exhibited its solutions of system-engineering, -design, -development, -integration and -maintenance. Pride of place on GMV’s stand went to the eForce Fire C4ISTAR system, a project for the planning, management and execution of all fire support. Another standout exhibit was the Landing Craft Command and Control System (eForce SCE). Within the JISR (Joint Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance) area, as part of Spain’s participation in NATO’s MAJIIC project, GMV highlighted its inhouse Mobile ISTAR Operating system (called SEISMO after its Spanish initials: Sistema de Explotación ISTAR Móvil), the Coalition Shared Database (CSD) and Atenea (IRM&CM Tool). GMV also showcased its latest developments in avionics systems, such as its participation in the ATLANTE program. This involves the development of an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) for ISTAR operations; GMV is responsible for the Flight Control Computer (FCC), one of the project’s most critical pieces of equipment. GMV participó como expositor en la nueva edición de la Feria International de la industria de Defensa (23nd International Defence Industry Exhibition) MSPO 2015, que tuvo lugar durante los días 1 al 4 de septiembre de 2015 en Kielce, Polonia. Como proveedor de confianza consolidado de las Fuerzas Armadas y organismos internacionales de Defensa, GMV ha presentado sus soluciones de ingeniería, diseño, desarrollo, integración y mantenimiento de sistemas. Así, en el stand de GMV destacó el sistema C4ISTAR eForce Fire, un proyecto para el planeamiento, conducción y ejecución de todos los apoyos de fuego; además de los sistemas de Mando y Control para embarcaciones de desembarco (eForce SCE), En el área JISR (Inteligencia, Vigilancia y Reconocimiento), y dentro de la participación española en el proyecto MAJIIC de la OTAN, GMV destacó los sistemas SEISMO (Sistema de explotación de Inteligencia), CSD (Coalition Shared Database) y Atenea (IRM&CM Tool). GMV mostró asimismo sus últimos desarrollos en sistemas de aviónica, como su participación en el programa ATLANTE (desarrollo de un avión no tripulado –UAV- para operaciones ISTAR) en el que GMV es responsable del FCC (Flight Control Computer), uno de los equipos más críticos del proyecto. pág. 34 I GMV NEWS nº60 Septiembre 2015 GMV FURNISHES NATO WITH A NEW INTELLIGENCE SYSTEM GMV PONE A DISPOSICIÓN DE LA OTAN UN NUEVO SISTEMA DE INTELIGENCIA The High-Readiness Land Headquarters (Cuartel General Terrestre de Alta Disponibilidad: CGTAD), made over to NATO as its Rapid Deployment Headquarters, is implementing a set of management and operation tools of Joint, Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance (JISR) systems. This set of tools, called SAPIIEM, is the result of a project driven by the Directorate General of Armaments and Material (Dirección General de Armamento y Material) of the Spanish MoD and being carried out by GMV. Its purpose is to ensure interoperability of ISR resources, thus maximizing the military usefulness of this information in a coalition. The SAPIIEM project will also address integration with other C4ISR systems (Command, Control, Communications and Computers Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance) currently available in the armed forces. The idea is to obtain additional tools to increase interoperability of the JISR cycle in support of operations and intelligence. These systems work on the basis of a Service Oriented Architecture (SOA). The advantage of this architecture is that it avoids the need for one-to-one connections between systems and enables data interchange rather than particular solutions for integrating each specific system. It is based on the use of common services that facilitate the sharing of data (and processes) in an efficient, dynamic, flexible and near-realtime way for decision taking, supported by the exchange of data rather than files. Another of its advantages is its use of standards for sharing products and information, thus ensuring complete interoperability of the systems developed by different nations and maximizing use of generally scarce ISR resources. SAPIIEM has been successfully put through its paces in both national and international exercises (EXCIVIR, MAJIIC, Unified Vision, Steadfast Cobalt, etc.) and it is currently taking part successfully in the Trident Juncture Exercise 2015 (TRJE15) in which the Spanish SAPIIEM systems provide JISR-capacity support for the various command levels. Trident Juncture will serve for certification of the command posts of NATO’s rapid deployment forces (NRF16 – NATO Response Force 2016) and also for validation of Initial Operational Capability (IOC) in JISR. El Cuartel General Terrestre de Alta Disponibilidad (CGTAD), puesto a disposición de la OTAN como Cuartel General de Despliegue Rápido, está implementando un conjunto de herramientas de gestión y explotación de sistemas de inteligencia, reconocimiento y vigilancia conjunta (JISR-Joint, Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance). Este conjunto de herramientas, denominada SAPIIEM, es el resultado de un proyecto impulsado por la Dirección General de Armamento y Material del Ministerio de Defensa y está siendo desarrollado por GMV. Su finalidad es asegurar la interoperabilidad de los medios ISR, y por tanto, maximizar la utilidad militar de esta información en una coalición. Adicionalmente, el proyecto SAPIIEM abordará la integración con otros sistemas C4ISR (Command, Control, Communications and Computers Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance) disponibles en las Fuerzas Armadas (FAS) actualmente, por lo que se prevé obtener herramientas adicionales que permitan aumentar la interoperabilidad del ciclo JISR en soporte a operaciones e inteligencia. El funcionamiento de estos sistemas se basa en una arquitectura cliente-servidor orientada a servicios (SOA – Service Oriented Architecture), una arquitectura que tiene como ventaja que se evitan conexiones uno a uno entre los sistemas y se permite el intercambio de datos, evitando soluciones particulares para integrar cada sistema concreto. Se basa en el uso de unos servicios comunes que permiten compartir los datos (y los procesos) de una forma eficiente, dinámica, flexible y en tiempo cercano al real necesario para la toma de decisiones, soportado por el intercambio de datos en lugar de ficheros. Otra de las ventajas es que se hace uso de estándares para la compartición de los productos y la información, asegurando así la completa interoperabilidad de los sistemas desarrollados por distintas naciones y maximizando así el uso de los recursos ISR generalmente escasos. SAPIIEM ya ha sido probado con éxito tanto en ejercicios nacionales como internacionales (EXCIVIR, MAJIIC, Unified Vision, Steadfast Cobalt, etc.) y actualmente está participando con éxito en el ejercicio Trident Junture, 2015 (TRJE15) en el que los sistemas españoles SAPIIEM proporcionan soporte a los distintos escalones de mando en la capacidad JISR. Trident Junture, servirá para la certificación de los Puestos de Mando de las Fuerzas de Despliegue Rápido de OTAN (NRF16 – NATO Response Force 2016), así como validar la Capacidad Operativa Inicial (IOC – Initial Operational Capability) en JISR. GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 35 DEFENSE & SECURITY / DEFENSA Y SEGURIDAD GMV SUPPLIES THE GUARDIA CIVIL POLICE WITH A MARITIME SURVEILLANCE SYSTEM GMV PROPORCIONA A LA GUARDIA CIVIL UNA PLATAFORMA DE VIGILANCIA MARÍTIMA GMV has recently won a contract for developing a system with satelliteenabled surveillance capabilities for the Guardia Civil. This new contract award is fruit of the wealth of satellite-monitoring experience built up by GMV in the last 10 years, especially in the maritime area using RADAR sensors, and also in the development of technological security and defense solutions. This new system merges earth-observation technology with active monitoring by means of transmission equipment fitted on the ships. GMV is now spearheading the trailblazing scientific data-processing techniques that underpin the whole system. GMV’s solution is based on tried and tested products like the GMV-developed maritime monitoring service called SIMONS and Socrates CO, which helps to cut down the project’s costs and development risks. It also includes a map-based dynamic data viewer, allowing users to interpret the system’s information layers quickly and correctly. The resulting processing chain has been put through its paces by various users in different scenarios. Performance has been verified in terms of quantifiable quality parameters (response time, detection probability, probability of false alarm, etc) with more than satisfactory results. The chain is therefore now ready for integration in the operational processes of the tactical missions of both civil and military users. The Guardia Civil has been actively involved in this whole process, participating in diverse Europe-wide research projects funded by both the European-Commission (EC) and the European Space Agency (ESA). These performance frameworks have provided the ideal scenario for forging even closer professional bonds between the Guardia Civil and GMV. This has enabled GMV to enhance its knowledge of Guardia Civil procedures and also of the hardware-, software- and operationalrequirements. GMV is also inputting its experience acquired during development and implementation of the EUROSUR network. Recientemente GMV ha resultado adjudicataria de un contrato para desarrollar una plataforma para vigilancia marítima con capacidades de satélite para la Guardia Civil. Esta adjudicación es fruto de la amplia experiencia que GMV ha acumulado en los últimos 10 años en el área de la monitorización por satélite, especialmente en el área marítima haciendo uso de sensores RADAR, así como en el desarrollo de soluciones tecnológicas para seguridad y defensa. El uso que se hace de la tecnología de observación de la Tierra fusionado con la monitorización activa mediante equipos de transmisión instalados dentro de los buques se basa en técnicas avanzadas de procesamiento de datos que son pioneras en el ámbito científico internacional y que GMV domina ampliamente. La plataforma planteada por GMV se basa en productos existentes y probados como SIMONS (servicio de monitorización marítima desarrollado por GMV) y Socrates CO, lo que permite abordar el proyecto minimizando los costes y riesgos de desarrollo. Asimismo, incluye un visor de datos dinámicos sobre una base de mapas cartográficos que permitirá al usuario interpretar de forma adecuada, puntual y rápida las capas de información publicadas por el sistema. La cadena de procesado resultante ha sido testeada por diferentes usuarios en diferentes escenarios. Las prestaciones se han verificado en términos de parámetros de calidad cuantificables (tiempo de respuesta, probabilidad de detección, probabilidad de falsa alarma…) y los resultados han sido más que satisfactorios. Con ello, la cadena está potencialmente lista para ser integrada en los procesos operacionales de misiones tácticas tanto de usuarios civiles como militares. Durante todo este proceso, Guardia Civil ha estado activamente implicada mediante la participación en diversos proyectos de investigación de ámbito europeo financiados tanto por la Comisión Europea (EC) como por la Agencia Espacial Europea (ESA). Dichos marcos de actuación han proporcionado el entorno idóneo para fortalecer las relaciones Guardia Civil-GMV y permitir una colaboración estrecha en el ámbito profesional, lo que ha permitido a GMV incrementar el conocimiento acerca de los procedimientos de este Cuerpo así como de los requisitos tanto del sistema (HW, SW) como operacionales. Adicionalmente, GMV aporta su experiencia en el desarrollo e integración con la red EUROSUR. pág. 36 I GMV NEWS nº60 Septiembre 2015 CYBERSECURITY / CIBERSEGURIDAD GMV COLLABORATION WITH EUROPOL IN ITS ATM CYBERATTACK GUIDE COLABORACIÓN DE GMV CON EUROPOL EN SU GUÍA FRENTE A CIBERATAQUES A CAJEROS Since 2013 the rate of ATM cyberattacks has soared, causing considerable damage to the financial industry and stunting its development. Society is now aware of this growing threat, which is becoming a worldwide problem. In many cases, however, logical attacks of this type could have been avoided by implementation of suitable countermeasures. The European Police Office (Europol), a law enforcement agency to combat organized crime, acknowledges the seriousness of the threat posed by these cyberattacks and has drawn up a guide called “Guidance and Recommendations regarding Logical attacks on ATMs”. To create this guide and confront this problem Europol has cooperated closely with representatives of the European ATM Security Team (EAST), a group of which GMV is a member. The guide taps into the knowledge, experience and consultancy of the cybersecurity experts of GMV and the other EAST members, establishing a series of countermeasures and a set of indicators to detect when a cyberattack might have occurred. The guide is made up by three chapters, the first describing the modus operandi (offline & online attacks), the second explaining how to mitigate ATM cyberattack risk and install lines of defense, and the last how to identify and respond to these attacks. The document will also be periodically updated as cyberattacks evolve to make sure it keeps pace with ongoing events. GMV has been providing companies and institutions with technological cybersecurity solutions and services since 1993, building up a wealth of knowledge and experience along the way and developing inhouse products like checker ATM Security. As of today checker is the market-leading ATM security product, now protecting nearly 100,000 ATMs in over 15 countries around the world. Major finance and insurance companies therefore turn to GMV to ensure such a critical aspect as the cybersecurity of their systems and information networks. Desde 2013, los ciberataques en cajeros automáticos se han incrementado de manera significativa, lo que provoca un daño económico considerable en el desarrollo de la industria financiera. Actualmente la sociedad es consciente del crecimiento de esta amenaza, llegando a ser un problema a nivel mundial y en muchos casos este tipo de ataques podrían haberse evitado mediante la aplicación de contramedidas adecuadas. La Oficina Europea de Policía (Europol), organismo centrado en la lucha contra la delincuencia organizada, reconoce la gravedad de la amenaza producida por estos ciberataques, y ha elaborado una guía con el objetivo de concienciar y hacer una serie de recomendaciones respecto a este tipo de ciberamenazas a las que se enfrenta el sector financiero. Para la creación de esta guía, Europol ha cooperado activamente con los representantes del Equipo de Seguridad Europeo de ATM (EAST), grupo del que GMV es miembro, para hacer frente a dicho problema. La guía está compuesta por el conocimiento, experiencia y asesoramiento de los expertos en ciberseguridad de GMV y del resto de miembros del EAST, estableciendo una serie de contramedidas y un conjunto de indicadores que pueden ser utilizados para detectar cuándo pudo haber ocurrido un ciberataque. La guía se compone de tres capítulos a través de los cuales se aborda la descripción del modus operandi (offline & online attacks), cómo mitigar el riesgo de ciberataques a cajeros automáticos y la instalación de líneas de defensa, y una identificación y respuesta a los ciberataques. Además, para asegurar la eficacia y eficiencia de los resultados, el documento se actualizará periódicamente a medida que los ciberataques van evolucionando. El conocimiento y experiencia de GMV proporcionando servicios y soluciones tecnológicas para la ciberseguridad de organismos y empresas desde 1993, se ha materializado en el desarrollo de productos especializados como checker ATM Security. A día de hoy, checker es el producto de seguridad para sistemas de autoservicio financiero líder del mercado, protegiendo cerca de 100.000 cajeros en más de 15 países de todo el mundo. Por ese motivo, grandes entidades financieras y compañías de seguros confían en la experiencia de GMV a la hora de abordar un aspecto tan crítico como es la ciberseguridad de sus sistemas y redes de información. GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 37 CYBERSECURITY / CIBERSEGURIDAD GMV INCLUDED IN INCIBE’S CATALOGUE OF COLLABORATING FIRMS GMV EN EL CATÁLOGO DE EMPRESAS COLABORADORAS DEL INCIBE GMV now forms part of the network of collaborators of the National Cybersecurity Institute (Instituto Nacional de Ciberseguridad: INCIBE) following an agreement under which both entities cooperate with the common objective of contributing to the fostering and development of the information society and, in particular, ensuring that their collaboration relationships fall within the framework of the Security Demonstration Centre for SMEs (Centro Demostrador de Seguridad para la Pyme). INCIBE, which depends on the Ministry of Industry, Energy and Tourism (MINETUR) through the Secretariat of State for Telecommunications and for the Information Society (Secretaría de Estado de Telecomunicaciones y para la Sociedad de la Información: SETSI), is the benchmark entity for the development of cybersecurity and the digital confidence of the public at large, the Spanish academic and research network (RedIRIS) and companies, particularly those in strategic sectors. As a center of excellence, INCIBE is a government instrument for developing cybersecurity as a vehicle for social change and an opportunity for innovation. GMV forma parte de la red de colaboradores de Instituto Nacional de Ciberseguridad (INCIBE) en virtud de un acuerdo por el que ambas entidades cooperan con el objetivo común de contribuir al fomento y desarrollo de la sociedad de la información, y en particular, sus relaciones de colaboración se circunscriben al marco del Centro Demostrador de Seguridad para la Pyme. El INCIBE, dependiente del Ministerio de Industria, Energía y Turismo (MINETUR) a través de la Secretaría de Estado de Telecomunicaciones y para la Sociedad de la Información (SETSI), es la entidad de referencia para el desarrollo de la ciberseguridad y de la confianza digital de los ciudadanos, la red académica y de investigación española (RedIRIS) y las empresas, especialmente para sectores estratégicos. Como centro de excelencia, INCIBE es un instrumento del Gobierno para desarrollar la ciberseguridad como motor de transformación social y oportunidad para la innovación. GMV PRESENTS THE NEW SECURITY AWARENESS-RAISING STRATEGY GMV PRESENTA LA NUEVA ESTRATEGIA DE CONCIENCIACIÓN DE SEGURIDAD Ante un foro de CISOs, responsables de seguridad del sector público y privado y periodistas especializados, Mariano J. Benito, CISO de GMV Secure e-Solutions presentó la nueva Estrategia de Concienciación de Seguridad, en el evento “La concienciación como base de la Seguridad de la Información”, organizado por AUTELSI (Asociación Española de Usuarios de Telecomunicaciones y de la Sociedad de la Información). pág. 38 I GMV NEWS nº60 Septiembre 2015 In a forum of CISOs, security heads of the public and private sector and specialist journalists, Mariano J. Benito, CISO of GMV Secure e-Solutions, presented the new security awareness-raising strategy in the event organized by the Spanish Association of Information-Society and Telecommunications Users (Asociación Española de Usuarios de Telecomunicaciones y de la Sociedad de la Información: AUTELSI) under the title “Awareness-raising as the bedrock of information security”. People-centeredness, gamification, identification of the Hero figure as change driver, adaptation of the language to suit each particular group and the use of the new communication channels were the key features of his speech. The experience built up in terms of boosting our clients’ security awareness “has led to a rethink of GMV’s own security awareness-raising strategy”, he explained. The aim, at the end of the day, “is to get across the idea that security is important not only for security professionals but also at personal level, approaching change as a fun event, like a game, employing tools like gamification. Because the best way of teaching children is by playing, and we can’t deny that we all retain something of the child within us. The game is the exception for bringing in change not the norm”, he concluded. Centrarse en las personas, la gamificación, la identificación de la figura del Héroe como modelo impulsor de la gestión del cambio, la adecuación del lenguaje según grupos y la utilización de nuevos canales de comunicación fueron los cimientos de su exposición. La experiencia obtenida a la hora de ayudar a mejorar la concienciación en materia de seguridad en clientes “ha dado lugar al replanteamiento de la estrategia de Concienciación en Seguridad en GMV”, compartió. A fin de cuentas, “se trata de entender que la Seguridad es interesante no solo para el profesional, sino también para la persona, planteando el cambio como algo divertido, como un juego, empleando herramientas como la gamificación. Porque, la mejor manera de enseñar a los niños es jugando y no podemos negar que todos guardamos algo del niño que fuimos. El juego es la excepción para llegar al cambio, no la norma”, concluyó. GMV AGAINST CYBERCRIME GMV CONTRA EL CIBERCRIMEN According to the figures of the Antiphishing Working Group (APWG), 2014 was a record year in phishing attempts, where criminals feign to be a bank to take over the user’s identity and withdraw cash from his or her bank account. One such attack occurs every two minutes, adding up to 250,000 around the whole world in a single year. The same figures point to a 7% growth in the number of web domains set up for identity theft, while 549 corporations around the world suffered some sort of phishing attack. GMV belongs to this new European alliance against cybercrime, which aims to bring together all the stakeholders in the fight against this new form of online crime. The eCrime 2015 Symposium on Electronic Crime Research, organized by APWG, brought together worldwide experts who are working towards increased efficiency in combatting this type of crime. Participants included the FBI, Interpol, the Spanish National Police and the Catalan Policeforce, Mossos Escuadra, as well as executives of financial institutions, international researchers and major internet- and telecommunication-related companies, GMV to the fore. José María Legido, GMV’s Director of the Northwest Region Secure e-Solutions, believes that “today’s internet and telecommunications threats come from all over the world; a local response is no longer enough”. Según el Antiphishing Working Group (APWG), 2014 fue un año de récord en cuanto a intentos de “phishing”, aquellos casos en que el delincuente se hace pasar por el banco para usurpar los datos del usuario y sacar dinero. Se produjeron uno cada dos minutos, es decir, 250.000 en todo el mundo. También, según estos datos, crecieron un 7% el número de dominios dedicados al robo de credenciales y 549 corporaciones de todo el mundo sufrieron ataques de “phishing”. GMV pertenece a esta nueva alianza europea contra el cibercrimen, que pretende reunir a todos los actores directamente relacionados en la lucha contra esta nueva forma de delincuencia a través de la red. Durante el Congreso Mundial contra el cibercrimen, organizado por la APWG, se reunieron expertos de todo el mundo que trabajan por ser más eficientes contra este tipo de delincuencia. Participaron el FBI, la Interpol, la Policía Nacional y los Mossos, así como directivos de entidades financieras, investigadores internacionales y grandes empresas relacionadas con el mundo de Internet y las telecomunicaciones, como es el caso de GMV. José María Legido, Director Regional Noreste de GMV Secure e-Solutions, considera que “hoy en día las amenazas que tenemos en el mundo de Internet y las telecomunicaciones vienen de todas partes del mundo, son globales, y una respuesta local es insuficiente”. GMV COLLABORATES IN ATMIA’S ATM SOFTWARE SECURITY BEST PRACTICES GUIDE GMV PARTICIPA EN EL MANUAL DE BUENAS PRÁCTICAS DE SEGURIDAD ATM GMV, as a member of the Security Council of the ATM Industry Association (ATMIA), has input its wealth of cybersecurity experience for drawing up a Best Practices Guide to improve ATM security from cyberattacks. Juan Jesús León, Director of Products and New Developments GMV Secure e-Solutions, has guided the research work in the various working sessions called by ATMIA. The ATM Software Security Best Practices Guide gives a blow-by-blow account of 16 particular attacks around the world, analyzing exactly what happened in each case. The conclusion drawn from this is that these attacks did not, as has normally been claimed, stem from lack of system updates or support of the Windows operating systems. It explains how an ATM was completely cleared out of cash by using malware specifically designed for that purpose. With this guide GMV and the other ATMIA members are helping to shed light on logical ATM attacks, explaining how they actually occur and helping cybersecurity officers to mitigate their risks. GMV, como miembro del Consejo de Seguridad de la Asociación de la Industria de Cajeros Automáticos (ATMIA), ha aportado su amplia experiencia en el campo de la Ciberseguridad para la elaboración de un Manual de Buenas Prácticas que mejore la seguridad de los cajeros automáticos ante ciberataques. Juan Jesús León, Director de Productos y Nuevos Desarrollos de GMV Secure e-Solutions ha pilotado la investigación en las distintas sesiones de trabajo que ha convocado la Asociación. El Manual de Buenas Prácticas para mejorar la seguridad en cajeros automáticos describe con detalle 16 ataques concretos en todo el mundo y analiza la realidad de los mismos, extrayéndose como conclusión que los orígenes de éstos no tienen que ver, como habitualmente se aduce, con la falta de actualizaciones o de soporte de los sistemas operativos Windows, y explica cómo se consigue en realidad vaciar completamente de efectivo un cajero utilizando software malicioso, diseñado ex profeso para este propósito. Con esta guía, GMV y los demás miembros de ATMIA, contribuyen a arrojar luz sobre la realidad de los ataques lógicos a redes de cajeros, informar y concienciar a los responsables de la Ciberseguridad de estas redes, así como mitigar sus riesgos. GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 39 CYBERSECURITY / CIBERSEGURIDAD RON KNODE SERVICE INTERNATIONAL AWARD OF THE CLOUD SECURITY ALLIANCE PREMIO INTERNACIONAL DE LA CLOUD SECURITY ALLIANCE The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) of GMV Secure e-Solutions, Mariano J. Benito, has been awarded by the Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) with the “Ron Knode Service Award”, because he has been considered a key player in the development and application of models and controls for a Secure Cloud. CSA is the world’s leading organization dedicated to defining and raising awareness of best practices to help ensure a Secure Cloud computing environment. From the Spanish chapter of CSA, Mariano J. Benito has boosted the Spanish translations of the CSA Guide, Cloud Control Matrix and the Study of State of the Art about Cloud Computing in Spain for the years 2013, 2014 and 2015, among other initiatives. In addition, he is the author of the first security analysis in Spain regarding Could Security (2009) and is the coordinator of the Spanish Chapter of CSA since 2012. El Director de Seguridad/CISO de GMV Secure e-Solutions, Mariano J. Benito, ha sido galardonado por la Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) con el premio “Ron Knode Service”, por ser considerado una pieza clave en el desarrollo y aplicación de los modelos y controles para una Nube Segura. CSA es la principal organización del mundo dedicada a definir y dar a conocer las mejores prácticas para ayudar a garantizar un entorno de cloud computing seguro. Desde el capítulo español de CSA Mariano J. Benito ha impulsado las traducciones al Español de la CSA Guide, Cloud Control Matrix y de los Estudios de Estado del Arte en Cloud Computing en España de los años 2013, 2014 y 2015, entre otros trabajos realizados por el capítulo. Además, es el autor del primer análisis español sobre seguridad en Cloud que vio la luz en 2009 y es coordinador del Capítulo Español de CSA desde 2012. EVENTOS / EVENTS GMV participates in SEG2 (11/06/2015 Madrid) For yet another year GMV showed its support for SEG2, the 7th Integral Security Encounter, jointly organized by the two trade reviews Red Seguridad and Seguritecnia. GMV is spearheading the national campaign against fraud and has been working for some years on the fight against Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs). EAST FCS Forum 2015 (11-12/06/2015 The Hague – Holland) For yet another year GMV was one of the sponsors of the EAST Financial Crime and Security FCS Forum 2015, put on this year in The Hague (Holland). ISACA Lecture Cycle at Universidad Carlos III (28/09/2015 Madrid) GMV was invited to take part in the ISACA Madrid Lectures, held in Universidad Carlos III. Javier Osuna, Head of the Division of Security and Consultancy and Security Processes, gave a lecture on Resilience in Critical and Industrial Environments. Rooted Satellite Valencia (11-12/09/2015 Valencia) GMV sponsored Rooted Satellite Valencia, a congress held with the aim of promoting information technology security. During this two-day event two RootedLabs and top level speakers analyzed the current state of the sector, giving their particular points of view and presenting specialized technical contents. GMV participa en el SEG2 (11/06/2015 Madrid) Un año más GMV mostró su apoyo a SEG2, el VII Encuentro de Seguridad Integral, organizado por la revista Red Seguridad y Seguritecnia. GMV es una de las empresas nacionales más implicadas en la gestión del fraude, trabajando desde hace años en la lucha contra ataques APTs (Advanced Persistent Threat). EAST FCS Forum 2015 (11-12/06/2015 La Haya – Holanda) Un año más GMV fue uno de los patrocinadores del EAST Financial Crime and Security FCS Forum 2015, organizado este año en La Haya (Holanda). Conferencias ISACA en la Universidad Carlos III (28/09/2015 Madrid) GMV fue invitada a participar en las Conferencias ISACA Madrid en la Universidad Carlos III. Javier Osuna, Jefe de la División de Seguridad y Procesos de Consultoría y Seguridad impartió una ponencia sobre la “Resiliencia en Entornos Críticos e Industriales”. Rooted Satellite Valencia (11-12/09/2015 Valencia) GMV patrocinó el Rooted Satellite Valencia, como apoyo al fomento de la seguridad de las Tecnologías de la Información. Durante dos días se expuso la situación actual del sector a través de dos RootedLabs, y la participación de ponentes de primer nivel aportando su punto de vista con contenidos técnicos especializados. pág. 40 I GMV NEWS nº60 Septiembre 2015 HEALTHCARE / SANIDAD BIG DATA TECHNOLOGY IN THE GALICIAN HEALTH SERVICE TECNOLOGÍA BIG DATA EN EL SERVICIO GALLEGO DE SALUD Big Data has a vast potential for improving healthcare procedures. The sheer amount of information generated by this sector is staggering. All the traditional information sources (doctor’s notes, prescriptions, diagnostic tests, integral healthcare plans, monitoring and follow-up) are still with us today but they have now been swelled by others arising from the Internet of Things, such as chips or sensors for sending and receiving patient data during treatment follow-up phases. Until the advent of Big Data technology, the traditional informationprocessing and -storage systems were unable to turn all this new information to good account. Big Data projects are able to convert data of all sorts into valuable information. This capability offers huge possibilities for improving healthcare and hence boosting public welfare. A fine example of this is HEXIN, the clinical and epidemiological data mining system being set up by the Galician Health Service (Servicio Gallego de Salud: SERGAS) with GMV technology. HEXIN obtains clinical data for epidemiological surveillance, clinical assistance, management and research. Its computing capability and reusability features keep the cost down. It can also digest unstructured information and automatically turn it into records that have until now been inaccessible. HEXIN’s plethora of possible applications includes characterization of the population in terms of specific parameters (illness, study case, zone...), finding out the total number of people showing given symptoms or the incidence and prevalence of illnesses, suspected adverse effects and risk factors. It could also be used to weigh up treatment efficiency by comparing similar patients or measuring comorbidity (presence of one or more disorders or illnesses apart from the primary illness or disorder). It can likewise back up diagnoses and therapies with comparable clinical evidence, creating real test banks as research support. Last but not least the platform also has the capability of adapting healthcare protocols for chronic patients. Big Data abre un amplio espectro de posibilidades para la mejora de la salud. La cantidad de información que genera este sector es colosal. En la actualidad, a las fuentes tradicionales de información (notas del médico, recetas, pruebas diagnósticas, planes de asistencia integral, seguimiento) se suman otras que resultan del Internet de las Cosas, como chips o sensores que facilitan la recepción y transmisión de los datos de los pacientes en fases de monitorización y seguimiento en tratamientos. Hasta la llegada de la tecnología Big Data, los sistemas tradicionales de almacenaje y tratamiento de información no eran capaces de extraerles “jugo”, y así conocimiento, a los datos que se originaban. El trabajo de transformación de todo tipo de datos en información, que permiten hacer las herramientas que componen todo un proyecto Big Data, impacta directamente en la mejora de la atención sanitaria y por tanto en el bienestar del ciudadano. HEXIN, la plataforma de explotación de datos clínicos y epidemiológicos que el Servicio Gallego de Salud (Sergas) está implantando con la tecnología de GMV es un ejemplo de ello. HEXIN logra obtener datos clínicos para la vigilancia epidemiológica, la asistencia clínica, la gestión y la investigación, con un bajo coste tanto por su capacidad de cómputo como de reutilización en diferentes casos de uso. Además, es capaz de ingerir información no estructurada y obtener registros de ella, no accesibles hasta el momento, de forma automática. Entre algunas de las posibles aplicaciones que ofrece HEXIN cabe mencionar la caracterización de la población a través de la definición de ámbitos específicos (enfermedad, caso de estudio, zona...), conocer el número total de personas que presentan determinados síntomas o la incidencia y prevalencia de enfermedades, sospechas de efectos adversos y factores de riesgo. Así como, valorar la eficacia y eficiencia en tratamientos a través de la comparación de pacientes similares o poder medir la comorbilidad (presencia de uno o más trastornos o enfermedades además de la enfermedad o trastorno primario). A la vez, da apoyo a los diagnósticos y tratamientos con evidencia clínica comparable y permite crear bancos reales de pruebas como soporte a la investigación. Estas son, junto con la capacidad de adecuar protocolos de asistencia en enfermos crónicos, diferentes prestaciones que ofrece la plataforma. GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 41 HEALTHCARE / SANIDAD CLEVELAND CLINIC USES GMV TECHNOLOGY IN ITS INTRAOPERATIVE RADIATION THERAPY CLEVELAND CLINIC USA TECNOLOGÍA GMV EN RADIOTERAPIA INTRAOPERATORIA Cleveland Clinic, the world-renowned medical research center, will now be able to benefit from GMV technology in the form of its inhouse intraoperative radiation therapy (IORT) planner: radiance. The clinic has a long and solid track record in IORT research, using the most groundbreaking technology to get the best possible oncology results. radiance improves IORT security by means of a simulated display of the treatment result. The surgeon can adjust parameters beforehand to achieve the result in view without having to decide under pressure in the operating theater. radiance has obtained EC certification, authorizing its marketing in all EU member states, and also FDA certification for marketing in the US. Cleveland Clinic is a nonprofit, multispecialty academic medical center combining patient care with research and education activities. It is recognized as one of the ten best hospitals of the USA, coming third in this ranking in 2015. La “Cleveland Clinic” podrá beneficiarse de la tecnología de GMV a través de radiance, su planificador de Radioterapia Intraoperatoria (RIO). En el ámbito de la radioterapia intraoperatoria, el centro cuenta con un sólido programa de investigación donde utiliza las tecnologías más innovadoras, para obtener mejores resultados en los tratamientos oncológicos. radiance mejora la seguridad de RIO al permitir la visualización simulada del resultado del tratamiento. El especialista puede ajustar los parámetros para conseguir el resultado previsto sin tener que decidir bajo presión durante la operación. radiance cuenta con la certificación de Marca CE, que autoriza su comercialización en todos los estados miembros de la Unión Europea, y con la autorización de la Agencia de Alimentos y Medicamentos de EE.UU. La Cleveland Clínic es un centro médico académico multiespecialidad sin ánimo de lucro que comparte su actividad asistencial con la educativa e investigadora. Es reconocido como unos de los diez mejores hospitales de EE.UU., ocupando el tercer puesto en 2015. GMV PRESENTS HEALTHCARE SOLUTIONS TO IMPROVE THE QUALITY OF LIFE OF THE ELDERLY GMV, SOLUCIONES DE SALUD PARA MEJORAR LA CALIDAD DE VIDA DE LOS MAYORES GMV’s healthcare development consultant, Víctor Ferrero, took part in the Valladolid conference of the association Groundbreaking Solutions for Independent Living (Soluciones Innovadoras para la Vida Independiente: SIVI), shortened to Cluster SIVI. GMV showcased the company’s groundbreaking solutions for improving the quality of life of the elderly. In particular it dealt with patient-care solutions while also presenting success stories on which GMV has worked together with its partner EverSalud. Based in the region of Castilla y León, Cluster SIVI pools a large number of public and private organizations, healthcare service providers, technology firms, university research groups, technology centers and tertiary sector organizations, with experience in the design, development and application of groundbreaking technological solutions in the fields of healthy and active ageing, mental health and independent living. GMV is a member of this association; other active participants are the Family Regional Ministry (Consejería de Familia) and the Development Agency (Agencia de Desarrollo) of the Regional Council (Junta) of Castilla y León. GMV participó en la jornada organizada por el Clúster SIVI (Soluciones Innovadoras para la Vida Independiente), organizado en Valladolid, con la intervención de Víctor Ferrero, consultor de desarrollo GMV en el área de salud. GMV presentó las soluciones innovadoras de la compañía para la mejora en la calidad de vida de los mayores. En concreto se profundizó en aquellas relacionadas con el cuidado y asistencia al paciente/usuario. De la misma forma, se presentó uno de los casos de éxito en los que GMV ha trabajado con su socio EverSalud. Con sede en Castilla y León, SIVI agrupa a un importante número de organizaciones públicas y privadas, prestadores de servicios socio-asistenciales, empresas de carácter tecnológico, grupos de investigación de universidades, centros tecnológicos y tercer sector, con experiencia en el diseño, desarrollo y aplicación de soluciones tecnológicas innovadoras en los campos de envejecimiento activo y saludable, la salud mental y la vida independiente. GMV es miembro de esta asociación, en la que participan activamente la Consejería de Familia y la Agencia de Desarrollo de la Junta de Castilla y León. pág. 42 I GMV NEWS nº60 Septiembre 2015 CARL ZEISS WILL MARKET GMV’S INTRAOPERATIVE RADIOTHERAPY PLANNER CARL ZEISS COMERCIALIZA EL PLANIFICADOR DE RADIOTERAPIA INTRAOPERATORIA DE GMV GMV and Carl Zeiss Meditec have signed a worldwide agreement for the distribution of radiance in its version adapted to Intrabeam®. radiance, the world’s first ever and unique Intraoperative radiotherapy simulation system, is the specialists’ “precise” ally, providing the exact radiotherapy application parameters. GMV’s simulation system allows surgical decisions and the patient’s radiotherapy effects to be preplanned before any radiation dose is actually given. The agreement signed between GMV and Zeiss Meditec AG, the IORT market leader, represents further endorsement for GMV’s radiotherapy planner. This alliance is the reward for and recognition of 8 years of groundbreaking R&D in GMV’s own research labs and in the oncology and experimental medicine and surgery departments of the Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañón. The work of a multidisciplinary team made up by engineers and researchers has boosted the precision and efficiency of the operation radiation dose. This is good news for patients, cutting down the operation time and improving their quality of life, and also for surgeons and oncologists, who can enter the operating theater with many of the decisions already vetted and agreed. GMV y Carl Zeiss Meditec han firmado un acuerdo para la distribución en todo el mundo de radiance en su versión adaptada para Intrabeam®. radiance, el primer y único software de simulación de radioterapia intraoperatoria en el mundo, es el aliado “preciso” del especialista en la intervención, ya que le proporciona los parámetros exactos para la aplicación de la radioterapia. El sistema de simulación de GMV permite preplanificar las decisiones de una intervención quirúrgica y los efectos de la radioterapia aplicada al paciente en una operación, antes de que éste reciba ninguna dosis de radiación. El convenio suscrito entre GMV y Zeiss Meditec AG, la empresa líder en el mercado de la radioterapia intraoperatoria, supone un aval al planificador de radioterapia de GMV. Esta alianza conlleva el reconocimiento al trabajo realizado durante 8 años de investigación en los laboratorios de I+D+i de GMV y en los departamentos de Oncología, y Medicina y Cirugía Experimental del Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañón. El trabajo de un equipo multidisciplinar constituido por ingenieros e investigadores ha contribuido a aumentar la precisión y eficiencia de la irradiación en una operación, lo que aporta ventajas sustanciales tanto a pacientes reduciendo la duración de las intervenciones y mejorando su calidad de vida como a cirujanos y oncólogos, pudiendo entrar al quirófano con muchas de las decisiones previamente evaluadas y consensuadas. EVENTOS / EVENTS 3RD ESTRO FORUM (24-28/04/2015 Barcelona) GMV attended the third congress organized by the European Society for Radiotherapy & Oncology to showcase radiance, its intraoperative radiotherapy solution. 9th ZEISS INTRABEAM USER MEETING (9-10/07/2015 Germany) Two of the programmed sessions at this conference, organized by Zeiss, dealt with the advantages of GMV’s intraoperative radiotherapy planner, radiance. 57th AAPM 2015 (12-16/07/2015 California) GMV travelled to California together with Carl Zeiss to showcase its intraoperative radiotherapy planner, radiance. Healthcare Journalism Congress (18/07/2015 Buenos Aires – Argentina) Carlos Royo, Business Development Manager of the e-Health area at GMV was invited to participate in the Healthcare Journalism Congress, with the presentation about “Telemedicine and its relationship with the media” 3RD ESTRO FORUM (24-28/04/2015 Barcelona) GMV asistió a la tercera edición del Congreso organizado por la European Society for Radiotherapy & Oncology, para presentar su solución radiance sobre radioterapia intraoperatoria. 9th ZEISS INTRABEAM USER MEETING (9-10/07/2015 Alemania) Los asistentes a la Conferencia organizada por Zeiss pudieron conocer las ventajas que ofrece radiance, el planificador de radioterapia intraoperatoria de GMV, a través de dos ponencias. 57th AAPM 2015 (12-16/07/2015 California) GMV acude junto a Carl Zeiss al Califoria para presentar la plataforma radiance, sobre radioterapia intraoperatoria. Congreso de Periodismo Sanitario (18/07/2015 Buenos Aires – Argentina) Carlos Royo, Director de Desarrollo de Negocio de Sanidad en GMV fue invitado a participar en el Congreso Internacional de Periodismo Sanitario con la ponencia “Telemedicina y su relación con los medios de comunicación”. GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 43 TRANSPORTATION / TRANSPORTE HIGH-PROFILE PRESENCE AT THE MAIN PUBLIC-TRANSPORT MEETINGS DESTACADA PRESENCIA EN LOS PRINCIPALES ENCUENTROS DE TRANSPORTE PÚBLICO During the second quarter of 2015 GMV attended three of the main public-transport events held in Europe, showcasing its wide range of solutions and products for the transport sector. From 8 to 10 June GMV was present at the 61st International Association of Public Transport (UITP) World Congress and Mobility & City Transport Exhibition, held this year under the watchword “Smile in the City”. GMV’s 75m2 stand was the biggest exhibition space it has ever run at any event, displaying its various network-planning and servicescheduling systems plus its transporton-demand systems to improve the efficiency and profitability of public transport in country areas. From 22 to 25 September GMV took part as exhibitor in the eleventh International Railway Fair TRAKO, the largest rail industry meeting in Poland and in the whole of Eastern Europe. On this occasion GMV’s stand showcased its inhouse railway fleet- pág. 44 I GMV NEWS nº60 Septiembre 2015 management system (SAE-R®) for the allin management and operation of railway transport plus its passenger-information system and video-surveillance systems especially designed by GMV for the railway market. Last but not least, at the end of September, GMV took part in the 2015 Rencontres Nationales du transport public, France’s flagship public-transport event held this year in Lyon. This gave it the chance to present to the French market its advanced fleet-management and public-information systems for urban public transport, its transport-ondemand solutions for rural areas and also its electronic fare collection systems. The turnout at these transport events is growing year after year. They have now become unmissable forums for displaying the most groundbreaking products and unveiling the latest ideas within a blossoming sector that is bound to play a decisive role in the economic upturn and future growth. Durante este segundo trimestre de 2015 GMV ha asistido a tres de los principales eventos de transporte público que se celebran en Europa con el objetivo de promocionar su extensa gama de soluciones y productos para el sector transporte. Del 8 al 10 de junio, GMV estuvo presente en la edición número 61 del Congreso UITP 2015 (61st UITP World Congress and Mobility & City Transport Exhibition), que este año se presentaba bajo el lema el lema “Smile in the City”. En el stand de GMV con una dimensión de 75 m2, el espacio de exposición de mayor superficie en el que ha participado hasta ahora la empresa, se presentaron diferentes sistemas que permiten planificar la red de transporte y optimizar la programación del tránsito, además de soluciones que permiten gestionar la modalidad de transporte a la demanda del viajero para mejorar la eficacia y la rentabilidad del transporte público en el medio rural. Del 22 al 25 de septiembre, GMV acudió como expositor a la undécima edición de la Feria Internacional de Transporte ferroviario TRAKO, el mayor evento, relacionado con este sector ferroviario tanto en Polonia, como en Europa del Este. En esta ocasión en el stand de GMV se presentó SAE-R®, el sistema integral desarrollado por GMV para la planificación, gestión y explotación del transporte ferroviario así como los sistemas de información al pasajero y los sistemas de video vigilancia de GMV especialmente diseñados para el mercado ferroviario. Por último, a finales de septiembre, GMV tuvo la oportunidad de presentar al mercado francés sus sistemas SAE para el transporte público urbano, sus soluciones de transporte a la demanda para zonas rurales así como sus equipos y soluciones de billetaje con su participación en la edición 2015 de ´Rencontres Natinales du transport public´, evento de referencia en Francia y que este año tuvo lugar en Lyon (Francia) Año tras año el número de participantes en los eventos de transporte crece con respecto a ediciones anteriores al ser oportunidades únicas para aportar nuevas ideas y concretar los más innovadores proyectos, dentro de un sector cuyas soluciones son cada vez más demandadas y cuyo papel puede ser decisivo en la recuperación económica y el crecimiento. GMV CONSOLIDATES ITS BUSINESS IN NORTH AFRICA GMV CONSOLIDA SU PRESENCIA EN EL NORTE DE ÁFRICA A few years ago now the Moroccan government set itself the task of turning its country into a top-ranking international logistics center. In fact it spent nearly 60 percent of its annual budget on creating an infrastructure network to improve both its internal and international connectivity, with an additional input from multilateral funds for international tenders and bid invitations. GMV has been carrying out projects for Morocco’s transport sector for some years now to meet the country’s burgeoning need for new transport equipment and systems. Over the last year, together with the Moroccan multinational CityBus and the Spanish bus operator ALSA, GMV has won two new projects that give it an even firmer footing in North Africa. The Moroccan multinational CityBus is running an expanding business in the country, winning new publictransport concessions in the cities of Kenitra, Tetouan and El Jadida. GMV is collaborating closely with the company as technological partner, supplying an advanced fleet-management and passenger-information system to be incorporated into its multi-fleet management platform already up and running in the cities of Fez and Meknes. The system supplied by GMV is rounded out with an onboard electronic farecollection system made up by ETC-500 ticket-vending machines. GMV’s is also a longstanding collaborator of Alsa in Morocco, with up-and-running projects in the cities of Marrakech and Agadir. This collaboration agreement has recently been topped up with a new project in which GMV will supply an electronic fare-collection system comprising 40 machines in the publictransport buses of the city of Khouribga in the center of Morocco, 100 Kms from Casablanca. Hace ya unos cuantos años que el gobierno marroquí estableció el objetivo de convertir a su país en un centro logístico internacional de primer orden. De hecho, cerca del 60 por ciento de su presupuesto anual va destinado a la creación de una red de infraestructuras que mejore tanto su conectividad interna como internacional, a lo que se suma las aportaciones de los fondos multilaterales para la licitación de obras y servicios internacionales. GMV lleva ya unos años desarrollando proyectos en el sector transporte de Marruecos, con oportunidades crecientes por estas necesidades de desarrollo. En el último año, junto a la multinacional marroquí CityBus y la española ALSA, GMV ha logrado consolidar su implantación en el Norte de África con la adjudicación de dos nuevos proyectos. Como partner tecnológico de la multinacional marroquí CityBus, GMV colabora estrechamente en su expansión operativa en Marruecos con las nuevas concesiones de Transporte Publico en las ciudades de Kenitra, Tetuán y El Jadida. GMV suministrará a la multinacional marroquí un Sistema de Ayuda a la Explotación (SAE) que se integrará dentro de su plataforma de Gestión Multiflota que ya opera los sistemas de las ciudades de FEZ y Meknes. El sistema proporcionado por GMV se complementa con el suministro de un sistema de Validación y Venta embarcado formado por equipos ETC-500. Por otro lado la histórica colaboración de GMV con Alsa en Marruecos, con proyectos actualmente en marcha en las ciudades de Marrakech y Agadir, se complementa con un nuevo proyecto en el que GMV suministrará un Sistema de Validación y Venta compuesto por 40 máquinas en los autobuses de transporte Público de la ciudad de Khouribga, situada en el centro de Marruecos, a 100 Km de Casablanca. GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 45 TRANSPORTATION / TRANSPORTE GMV PROVIDES THE REGIONAL COUNCIL OF GALICIA WITH INTEGRAL MOBILITY MANAGEMENT GMV PROPORCIONA A LA XUNTA UNA GESTIÓN INTEGRAL DE LA MOVILIDAD GMV has won a contract for the development and installation of a platform for integral mobility management of public passenger transport after a bid invitation from the XUNTA de Galicia (Regional Council of Galicia) through the Agency for Technological Modernization of Galicia (Axencia para a Modernización Tecnolóxica de Galicia: AMTEGA) and the General Mobility Directorate (Dirección General de Movilidad). Under this large-scale, far-reaching project, the management of 51 firms running over 400 public-transport buses in the region of Galicia will be integrated in a single Operation and Control Center called COMGA. The project also comprises the installation of complete onboard equipment made up by a fleet-management device and an ETC-606 ticket-vending machine functionally integrated in a single system. To round things out the project also includes installation of an operation support center for the complete fleetmanagement system and an electronic fare-collection system covering the whole set of firms included in COMGA. This will be done through a CallCenter with bilingual operators to clear up any doubts of COMGA-inscribed firms during the five years of the contract term. The system will also include information from third party firms not included under the COMGA umbrella, enabling Galicia’s mobility planners to gain complete passenger transport information from the whole of Galicia. This project makes GMV a true benchmark in Spain in the supply and management of regional publictransport systems, after its participation in the regional projects of Madrid, Asturias, Castilla-León, Castilla-La Mancha, Andalucía (Andalusia), Murcia, Valencia, Balearic Islands and Catalunya (Catalonia). GMV ha resultado adjudicataria del proyecto para el desarrollo e instalación de la Plataforma para la Gestión integral de la movilidad del Transporte público de Viajeros convocado por la XUNTA de Galicia a través de AMTEGA (Axencia para a Modernización Tecnolóxica de Galicia) y la Dirección General de Movilidad. Este proyecto de gran envergadura integrará en un mismo Centro de control y Operaciones, denominado COMGA, la gestión de 51 empresas con más de 400 buses de transporte público de ámbito regional gallego. Asimismo en el proyecto está previsto la instalación equipamiento completo embarcado compuesto por un dispositivo SAE y una expendedora ETC-606 integrados funcionalmente como un sistema único. Complementariamente, el proyecto contempla la instalación de un centro de soporte a la operación del sistema completo SAE (Sistema de Ayuda a la Explotación) y SVV (Sistema de Validación y Venta) para el conjunto de empresas inscritas a COMGA a través de una plataforma CallCenter con operadores bilingües como ayuda a la resolución de dudas de las empresas de transporte adscritas, durante los cinco años de contrato del sistema. El Sistema integrará además información de terceras empresas de transporte no adscritas en COMGA, posibilitando a los responsables de movilidad de Galicia conocer información completa del transporte de viajeros de toda la comunidad gallega. Este proyecto posiciona a GMV como el referente en España en el suministro y gestión de Sistemas de Transporte Público regional después de participar en proyectos de ámbito regional en Madrid, Asturias, Castilla-León, CastillaLa Mancha, Andalucía, Murcia, Valencia, Baleares o Cataluña. pág. 46 I GMV NEWS nº60 Septiembre 2015 GMV KEY IN THE ROLL OUT OF ECALL IN EUROPE GMV CLAVE EN LA IMPLANTACIÓN DEL ECALL EN EUROPA GMV is a key partner of the “I_HeERO Portugal” sub-project, which aims to guarantee that – by October 2017 – the required infrastructure for eCall is ready in Portugal. eCall based on the European emergency number 112 is the emergency call system that automatically alerts emergency/rescue services in case of vehicle crashes. An eCall device (called “In-Vehicle System” – IVS) will have to be fitted into all new models of cars and light vans by 31 March 2018. Similarly, EU Member States must put in place by 1 October 2017 the necessary Public Safety Answering Points (PSAP) infrastructure to process eCalls. The call can be triggered manually by the vehicle occupants, or automatically when sensors detect a collision. As well as establishing a voice connection between the vehicle occupants and emergency operator, eCall sends vital data such as the current GPS location coordinates, incident time and vehicle description in the EU standardized MSD (minimum set of Data) format. It is estimated that, if the system was implemented as standard in all vehicles, 2,500 lives could be saved across Europe every year and the overall severity of injuries will be reduced by 15%. The I_HeERO project - funded through the Connected Europe Fund project (Annual Program) - is addressing the need for Member States to upgrade their PSAPs in compliance with the ITS Directive (2010/40/EU), thus enabling eCall to be correctly implemented across all EU Member States. The I_HeERO project brings together 61 partners from 12 Member States and will also undertake studies on the extension of eCall to other types of vehicles not included in the EU legislation on eCall, i.e.: powered two wheelers, trucks and dangerous goods carriers. Furthermore, it will also examine the requirement for data integration and define conformity assessment for all PSAPs as required by the legislation. GMV es uno de los principales miembros del subproyecto “I_HeERO Portugal”, cuyo propósito es garantizar que la infraestructura requerida en Portugal para el sistema eCall esté listo en octubre de 2017. El sistema de llamada de emergencias eCall, basado en el número de emergencias europeo 112, envía una alerta de forma automática a los servicios de urgencias o de rescate en caso de accidente de automóvil. A partir de marzo de 2018, todos los nuevos modelos de automóviles y vehículos comerciales ligeros deberán llevar instalado un dispositivo eCall (denominado “In-Vehicle System” – IVS). De igual modo, los Estados miembro de la UE deberán poner en marcha antes del 1 de octubre de 2017 la infraestructura necesaria de puntos de respuesta de seguridad pública (PSAP) para el procesamiento de las llamadas a través de eCall. La llamada puede ser activada manualmente por los ocupantes del vehículo o bien de forma automática cuando los sensores detectan indicios de que se ha producido un accidente. Además de establecer una conexión de voz entre los ocupantes del vehículo y el operador del PSAP, eCall envía datos vitales, como las coordenadas GPS de localización, la hora del incidente y la descripción del vehículo en el formato estándar MSD (serie mínima de datos) de la UE. Se ha calculado que, si el sistema se instalase de serie en todos los vehículos, podrían salvarse 2.500 vidas en toda Europa cada año y la gravedad de las lesiones se reduciría en un 15%. El proyecto I_HeERO – financiado a través del Connected Europe Fund (Programa Anual) – tiene como objeto dar respuesta a la necesidad de los Estados miembro de mejorar sus PSAP en cumplimiento de la Directiva 2010/40/ UE de sistemas de transporte inteligentes y permitir así la correcta implantación de eCall en todos los Estados miembro. El proyecto I_HeERO aglutina a 61 socios procedentes de 12 Estados miembro que también se encargarán de realizar estudios sobre la extensión del sistema eCall a otros tipos de vehículos no incluidos en la legislación europea sobre el eCall, es decir, vehículos de motor de dos ruedas, camiones y vehículos para transporte de mercancías peligrosas. Asimismo, examinarán el requisito para integración de datos y definirán la evaluación de conformidad para todos los PSAP que requiera la legislación. GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 47 TRANSPORTATION / TRANSPORTE GMV’S RAILWAY SOLUTIONS SET UP IN THE ARAB WORLD SOLUCIONES FERROVIARIAS IMPLANTADAS POR GMV DENTRO DEL MUNDO ÁRABE GMV continues to make headway as a supplier of railway solutions in the Arab world. GMV is playing a key role in Saudi Arabia’s projected Mecca-Medina high-speed train line, supplying the train manufacturer Talgo with four onboard systems to be fitted on the 36 trains to run on this line: the intercom and public-address system; the video-surveillance system (CCTV); a specific event-recording and networksecurity-hardening system on the train’s Ethernet backbone; and a final system providing an interface for displaying onboard diagnosis information on each car of the train. All these systems have now passed their Talgo validation tests and are currently in supply and installation phase on all trains being manufactured for Saudi Arabia. Another country where GMV is providing state-of-the-art railway technology is Morocco, where it is rolling out an advanced railway fleet-management system (SAE-R®) for the public railway transport operator ONCF (Office National des Chemins de Fer). This project, of great strategic importance for ONCF, will greatly improve its control over passenger- and freight-transport services and also over its auxiliary trackworking machinery and the service rolling stock used by ONCF’s maintenance personnel. The GMV-developed advanced fleet management system (SAE-R®) takes in 300 electric and diesel locomotives, 95 railway machines, 300 service vehicles and 200 handhelds for fieldwork teams and will also carry out centralized monitoring of all fleet operations. The contract includes tracking of the fleet of trains and rolling stock plus management of the cellularnetwork messenger and communication service between the control center and trains. The supplied system will also manage service-regulation operations to guarantee the transport service runs as scheduled. This project has successfully passed the pilot-scheme validation stage and is currently being installed in the whole Moroccan fleet. The solution developed for ONCF is based on GMV’s trademark railway and tram fleet management system, SAE-R®, which has already been supplied for clients such as Spain’s railway operator RENFE, Servicios Ferroviarios de Mallorca, the Warsaw tramline, the tram system of Zaragoza and the trams of Kaohsiung (Taiwan), among others. GMV continúa su avance como suministrador de soluciones ferroviarias en el mundo árabe con una fuerte presencia dentro del proyecto de Alta velocidad entre las ciudades de Meca y Medina, en Arabia Saudí, GMV suministra a Talgo cuatro de los sistemas a bordo que equipan los 36 trenes que forman parte del proyecto: el sistema de megafonía e intercomunicación; el sistema de videovigilancia (CCTV); un sistema específico de captura de eventos y securización de red en el backbone Ethernet del tren; y un último sistema que proporciona un interfaz para la visualización de información de diagnosis a bordo, en cada coche del tren. Todos estos sistemas han superado ya las pruebas de validación por parte de Talgo y están actualmente en fase de suministro e instalación en todos los trenes que son fabricados con destino a Arabia Saudí. Otra país donde GMV aporta tecnología en el ámbito ferroviario es Marruecos, donde se está desplegando un Sistema de Ayuda a la Explotación (SAE-R®) en la flota del operador público de transporte ferroviario ONCF (Office National des Chemins de Fer). Este proyecto, de gran importancia estratégica para ONCF, permitirá una mejora sustancial tanto en el control de los servicios de transporte de viajeros y mercancías, como en el de la maquinaria auxiliar para trabajos en vía, así como en el seguimiento de los vehículos de servicio utilizados por el personal de mantenimiento de ONCF. Con un alcance de 300 locomotoras eléctricas y diésel, 95 máquinas ferroviarias, 300 vehículos de servicio y 200 terminales móviles para equipos de trabajo en campo, el Sistema de Ayuda a la Explotación (SAE-R®) desarrollado por GMV realizará el seguimiento centralizado de toda la operación de la flota. El contrato incluye la localización de la flota de trenes y vehículos así como la gestión de mensajería y comunicaciones entre el centro de control y los trenes sobre redes celulares. También el sistema suministrado gestionará las operaciones de regulación del servicio, con objeto de garantizar el cumplimiento de la oferta de transporte. Este proyecto ha superado ya con éxito la fase de validación del sistema piloto y se encuentra actualmente instalándose en toda la flota marroquí. La solución desarrollada para ONCF se basa en SAE-R®, la plataforma de ayuda a la explotación desarrollada por GMV para los entornos ferroviario y tranviario y que ya se ha suministrado para clientes como RENFE, Servicios Ferroviarios de Mallorca, Tranvías de Varsovia, Tranvía de Zaragoza o el Tranvía de Kaohsiung (Taiwán), entre otros. pág. 48 I GMV NEWS nº60 Septiembre 2015 A SWELLING CLIENT PORTFOLIO FOR GMV’S FLEET MANAGEMENT AND TRACKING SYSTEM EL SISTEMA DE GESTIÓN DE FLOTAS DE GMV AUMENTA SU CARTERA DE CLIENTES The companies CLH, IVECO and British American Tobacco have all turned to GMV for setting up its advanced fleet management and tracking system MOVILOC® in their respective vehicle fleets. The fuel-transport firm Compañía logística de Hidrocarburos, CLH, will fit the service in a total of 400 vehicles. IVECO and British American Tobacco, for their part, will install it in their commercial fleets, a total of 70 and 160 vehicles, respectively. As well as tracking equipment for controlling the daily operation of its fleet, all the vehicles of CLH, IVECO and British American Tobacco will be fitted with a peripheral panic button, allowing the driver to trip an alarm in the event of any emergency situation. This tool allows the driver to send an alarm to the control center or an SMS to an emergency telephone, doing so without calling attention to this action thanks to the totally hidden installation of the button. Information sent will include an identification of the alarm-triggering vehicle and the incident time and place, allowing the company to act accordingly. The features that prompted these companies to choose MOVILOC® include the possibility of obtaining real-time and historical information on each worker’s driving profile, enabling the company to cut costs. All the vehicles have also been fitted with an accident alarm, allowing realtime detection of any incident, whereupon a warning is immediately sent to the fleet manager or the agent designated by each firm. In all three cases the vehicles involved have been hired from ALD Automotive, the vehicle leasing and vehicle fleet management business line of Société Générale Group, a technological partner of MOVILOC® since 2012. Las empresas CLH, IVECO y British American Tobacco, han confiado en GMV para implantar el servicio avanzado de gestión y localización de flotas MOVILOC® en su flota de vehículos. La Compañía logística de Hidrocarburos, CLH, dedicada al transporte de combustible, instalará el servicio en un total de 400 vehículos. Por su parte, IVECO y British American Tobacco lo instalarán en su flota comercial, un total de 70 vehículos y 160 vehículos respectivamente. Además de la localización para el control de la operativa diaria de los vehículos, todos los vehículos de CLH, IVECO y British American Tobacco serán equipados con un botón de pánico periférico, que permite al conductor, mediante su pulsación, activar una alarma inmediata ante una situación de emergencia que se esté produciendo. Esta herramienta permite que el conductor, de forma disimulada, gracias a su instalación totalmente oculta, emita una alarma de pánico a su Centro de Control o que se envíe un SMS al teléfono de emergencia que se determine. El aviso informará del vehículo que ha generado la alarma, la hora y el lugar en el que se produjo el incidente permitiendo a la empresa lanzar la operativa que se considere adecuada para solucionar la incidencia o problema. Entre los aspectos que han llevado a estas empresas a decantarse por MOVILOC® destacan la posibilidad de obtener, en tiempo real y a través de históricos, la información relativa al perfil de conducción de cada trabajador, lo que permite a las empresas reducir constes. Por otra parte, todos los vehículos disponen de una alarma de accidente, que permite la detención de cualquier incidencia en tiempo real, enviando un aviso inmediato al responsable de la flota o al agente designado por cada empresa. En los tres casos se trata de vehículos en renting con ALD Automotive, la compañía de renting y administración de flotas de vehículos del grupo financiero Société Générale, partner tecnológico de MOVILOC® desde 2012. GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 49 TELECOMMUNICATIONS / TELECOMUNICACIONES GMV AT THE SANTANDER CONGRESS TELECOMMUNICATIONS GMV EN EL CONGRESO DE LAS TELECOMUNICACIONES DE SANTANDER For yet another year Santander has been the cynosure of telecommunications and information technologies, attracting the main ICT stakeholders to the 29th Telecommunications and Digital Economy Encounter, organized by AMETIC (Spanish Association of ICT Companies) under the slogan “Strategies for the Single Digital Market”. The Encounter set itself the aim of presenting ICTs as the best empowerment device and driving force of the digital transformation, playing a key role in the country’s economic upturn and recovery of its social welfare. The encounter, as usual, was backed by GMV, in this case with the participation of Luis Fernando Álvarez-Gascón, General Manager of GMV Secure e-Solutions, who ran through the latest trends now setting the pace in the digital transformation such as Big Data and the Internet of Things (IoT). These are now being set up in sectors such as healthcare, the automobile industry, insurance or industry 4.0. GMV is now applying groundbreaking technologies that are driving the digital transformation in a varied range of fields such as healthcare, banking and farming. In healthcare, predictive analytical techniques are now being applied for epidemiological purposes; in the banking world, fraud is being combatted with artificial intelligence technologies while farming practices are being optimized on the strength of satellite data from earth observation systems. Part of Álvarez-Gascón’s speech dealt with the crucial importance of security as a key part of the digital transformation. He explained the pressing need for such measures as a single, coordinated, Europe-wide regulation, a bigger training effort and a public awareness-raising campaign, paying particular attention to the privacy issue as a fundamental right of human beings. He also urged companies to adopt socially responsible informationsystem governance formulas. Álvarez-Gascón wound up with the following observation: “It is obvious that new technologies are driving economic progress but it is no less obvious that our work has a knock-on effect on the quality of life of our society as a whole, and this means we have a responsibility as an industry”. pág. 50 I GMV NEWS nº60 Septiembre 2015 Un año más, Santander ha sido el epicentro de las Tecnologías de la Información y las Telecomunicaciones, donde los principales protagonistas del sector TIC se han reunido en el 29 Encuentro de las Telecomunicaciones y Economía Digital organizado por AMETIC, bajo el lema “Estrategias para el Mercado Único Digital”. El Encuentro ha tenido como objetivo otorgar a las TIC el título de mejor herramienta y motor de impulso de la transformación digital, como pieza clave para la recuperación económica y bienestar social del país. El encuentro contó con el apoyo de GMV, y la participación de Luis Fernando Álvarez-Gascón, Director General de GMV Secure e-Solutions, quien hizo un repaso por las nuevas tendencias que están marcando la transformación digital: Big Data, Internet de las cosas (IoT)…, que están siendo implantadas ya en sectores como salud, industria del automóvil, aseguradoras o industria 4.0. GMV está aplicando tecnologías innovadoras que están contribuyendo a esta transformación digital, tanto en el campo de la sanidad con técnicas de analítica predictiva para epidemiología, como en la lucha contra el fraude bancario basado en tecnologías de inteligencia artificial, o la optimización de la agricultura mediante observación de la tierra a través de datos recogidos por satélites, entre otros. Álvarez-Gascón dedicó parte de su ponencia a destacar la importancia de la seguridad como pieza clave en esta transformación digital. Se debe reclamar además de una regulación única y coordinada en Europa, un esfuerzo en la formación y la concienciación de la ciudadanía, cuidando el tema de la privacidad de los ciudadanos, como derecho fundamental del ser humano. Asimismo, abogó por que las empresas adopten fórmulas responsables de gobernanza de los sistemas de información. Para concluir su participación, ÁlvarezGascón señaló el progreso económico al que contribuyen las nuevas tecnologías, pero esta transformación digital también está definiendo la calidad de vida de nuestra sociedad, y en ese sentido la industria TIC debe tener una responsabilidad. PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION AND LARGE CORPORATIONS / AAPP Y GRAN EMPRESA GMV HELPS SPRINTER TO OPTIMIZE ITS ORDER MANAGEMENT PROCEDURES GMV AYUDA A SPRINTER A OPTIMIZAR SU GESTIÓN DE PEDIDOS Sound logistics management is essential for any firm that wishes to be competitive within its market. The increasing takeup of new technologies in this field is helping to win new space and streamline procedures, saving time and boosting the company’s productivity. Sprinter, a Spanish fashion, footwear and sports-complements firm, runs almost 100 shops throughout the whole of Spain plus an e-commerce shop to top up its sales outlets. To optimize its sales processes, Sprinter has turned to GMV’s expertise and experience, asking the company to set up a new warehouse for managing orders made in both real shops and e-commerce shops, whenever customers ask for products not actually held in stock at that time. GMV has developed a system based on two main principles: proper organization of incoming stock and order preparation following the best route within the warehouse. The quantitative challenge of this project was to cut down the necessary order-preparation time. This involved designing a system in which shop assistants, using a specially designed cart, were able to prepare several orders at once, improving time management. One of the IT department’s strategies is to bring in a technological change in the software development of its products using Java development ecosystems. The development consists of a REST service layer for logistic management of locations in incoming-stock and order-preparation procedures. These services would be consumed by an Android application used by shop assistants for barcode-reading and other relevant operations. The results have been more than satisfactory. In the first week of operation the system had increased orderpreparation speed fourfold, thus meeting Sprinter’s expectations for its new warehouse. Contar con una buena gestión logística es fundamental para toda empresa que quiera ser competitiva en su mercado, y la incursión de las nuevas tecnologías en este campo permite mejorar aspectos como el tiempo y el espacio, dando lugar a una mayor productividad de la compañía. Sprinter, empresa española dedicada a la comercialización de moda, calzado, complementos deportivos y material técnico, dispone de cerca de 100 tiendas físicas repartidas en el territorio español y una plataforma e-commerce, como canales de venta de sus productos. Para optimizar su proceso de ventas, Sprinter ha confiado en los conocimientos y experiencia de GMV para desarrollar un nuevo almacén que gestione los pedidos solicitados tanto a través de su plataforma de e-commerce como los que se realizan desde las propias tiendas, cuando el cliente solicita productos no disponibles en stock de tienda. GMV ha desarrollado un sistema que permite dos funcionalidades principales: una adecuada organización de la mercancía q entra en el almacén y una preparación de pedidos siguiendo una ruta óptima dentro del almacén. El reto cuantitativo de este proyecto era mejorar el tiempo necesario para preparar un pedido. Para ello se diseñó un sistema de forma que los operarios, llevando un carro especialmente diseñado, pudieran preparar varios pedidos a la vez de la forma más óptima. Una de las estrategias del departamento TI es realizar un cambio tecnológico en el desarrollo software de sus productos utilizando los ecosistemas de desarrollo Java. El desarrollo consistía en una capa de servicios REST para la gestión lógica de ubicaciones en los procesos de entrada y preparación de pedidos. Estos servicios serían consumidos por una aplicación Android utilizada por los operarios para la realización de lecturas y operaciones relacionadas con dichos procesos. Los beneficios obtenidos han sido muy satisfactorios, ya en la primera semana de vida, el sistema había incrementado en más de cuatro veces la velocidad de preparación de pedidos, lo que cumplía con las expectativas generadas por Sprinter para su nuevo almacén. GMV PARTICIPATES IN ASTICNET / GMV PARTICIPA EN ASTICNET GMV is sponsoring the latest ASTICNET, an event organized by Fundación ASTIC, under the slogan “25 years from the Creation of the ICT Corps: The challenge of information technologies in the public sector”. This two-day event combined a working day based on panel discussions with networking activities. It attracted a turnout of over two hundred ICT professionals and executives from the public sector. GMV apoyó con su patrocinio una nueva edición de ASTICNET, encuentro organizado por la Fundación ASTIC, bajo el lema “25 años de la Creación del Cuerpo TIC: El reto de las tecnologías de la información en el sector público”. Durante dos días se combinó jornada de trabajo a través de mesas redondas, con actividades de networking. A la cita acudieron más de doscientos directivos y profesionales TIC de las Administraciones Públicas. GMV NEWS nº60 September 2015 I p. 51 GMV EN EL MUNDO GMV IN THE WORLD ALEMANIA / GERMANY ESPAÑA / SPAIN Europaplatz 2, D-64293 Darmstadt Tel.: +49 (0)6151-3975433 Fax: +49 (0)6151-8609415 Isaac Newton 11 P.T.M. Tres Cantos - 28760 Madrid Tel.: +34 91 807 21 00 Fax: +34 91 807 21 99 COLOMBIA Juan de Herrera nº17 Boecillo - 47151 Valladolid Tel.: +34 983 54 65 54 Fax: +34 983 54 65 53 Edificio World Trade Center Bogotá Calle 100 No. 8A-49. Torre B. PH.- Bogotá Tel.: +57 (1) 6467399 Fax: +57 (1) 6461101 EE.UU / NORTH AMERICA C/ Albert Einstein, s/n 5ª Planta, Módulo 2 Edificio Insur Cartuja - 41092 Sevilla Tel.: +34 95 408 80 60 Fax.: +34 95 408 12 33 GMV Innovating Solutions Inc. -Space and ICT markets2400 Research Blvd, Ste 390 Rockville, MD 20850 Tel: +1 (240) 252-2320 Fax: +1 (240) 252-2321 Balmes 268-270 5ª Planta - 08006 Barcelona Tel.: +34 93 272 18 48 Fax: +34 93 215 61 87 Syncromatics Corp. -Intelligent Transport Systems523 W 6th St Suite 444 Los Angeles, California 90014 Tel: +1 (310) 728-6997 Fax: +1 (310) 734-6831 Av. Cortes Valencianas, Edificio Sorolla Center 58 planta 2 - 46015 Valencia Tel.: +34 96 332 39 00 Fax: +34 96 332 39 01 FRANCIA / FRANCE Fomento, 9 Edificio Residencial Costa Sur - local “J1” 38003 Santa Cruz de Tenerife Tel y Fax.: +34 922 53 56 02 17, rue Hermès 31520 Ramonville St. Agne. Toulouse Tel.: +33 (0) 534314261 Fax: +33 (0) 562067963 INDIA Rectangle One, 4th floor Saket District Centre Nueva Delhi 110017 Tel.: (+91) 11 4051 4163 Fax: (+91) 11 4051 4052 MALASIA / MALAYSIA Level 8, Pavilion KL 168, Jalan Bukit Bintang, 55100 Kuala Lumpur Tel.: (+60 3) 9205 7788 Fax: (+60 3) 9205 7788 POLONIA / POLAND Ul. Hrubieszowska 2, 01-209 Varsovia Tel.: +48 22 395 51 65 Fax: +48 22 395 51 67 PORTUGAL Avda. D. João II, Nº 43 Torre Fernão de Magalhães, 7º 1998-025 Lisboa Tel.: +351 21 382 93 66 Fax: +351 21 386 64 93 REINO UNIDO / UK Harwell Innovation Centre, Building 173, 1st floor, suite C131 & C134 Curie Avenue, Harwell Science and Innovation Campus, Didcot, Oxfordshire OX11 0QG Tlf: +44 1235 838536 Fax: +44 (0)1235 838501 RUMANIA / ROMANIA Edificio Victoria Center 9ª planta, 145 Calea Victoriei, Sector 1, 010072 Bucarest Tel.: +40.031.82.42.800 Fax: +40.031.82.42.801 www.gmv.com C/ Mas Dorca 13, Nave 5 Pol. Ind. L’Ametlla Park L’Ametlla del Vallés - 08480 Barcelona Tel: +34 93 845 79 00 - +34 93 845 79 10 Fax: + 34 93 781 16 61 Avenida José Aguado, 41 Edificio INTECO, 1ª Planta - 24005 León Tel.: +34 91 807 21 00 Fax: +34 91 807 21 99 C/ Pablo Ruiz Picasso, 61. Edificio Dinamiza 61 D planta 3ª oficina B y C - 50015 Zaragoza Tel.: +34 976 50 68 08 Fax: +34 976 74 08 09
© Copyright 2026