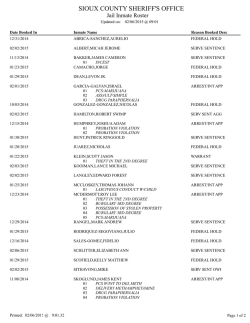
01:160:161 - Rutgers University
GENERAL CHEMISTRY 161 - SPRING 2015 All readings and assignments are in “Chemistry: Structure and Properties” by Nivaldo J. Tro, Custom edition for Rutgers University General Chemistry. Exact pace of topics and associated problems subject to change, as determined in lecture LEC # DATE READING 1 1/20, T 2 1/22, Th 3 1/27, T 4 1/29, Th 5 2/3, T 6 2/5, Th 7 2/10, T 8 2/12, Th 9 2/17, T 10 2/19, Th 11 2/24, T 12 2/26, Th 13 3/3, T 14 3/5, Th 15 3/10, T 16 3/12, Th 17 3/24, T 18 3/26, Th 19 3/31, T 20 4/2, Th 21 4/7, T 22 4/9, Th 23 4/14, T 24 4/16, Th 25 4/21, T 26 4/23, Th 27 4/28, T 28 4/30, Th TOPICS/HOME WORK Classification of matter, model of the atom, isotopes 1.1-1.10 1: 35, 41, 45, 47, 53, 59, 61, 65, 69, 73, 75, 77, 91, Math Sheet 2.1-2.7 Significant figures, accuracy and precision, units of measurement, dimensional analysis App I 2:17, 19, 23, 27, 29, 37, 65, 71, 75, 85 App II App I: 3, 7, 9, 15. App II: 1, 3, 5, 9, 11, 13 Mole concept, nature of light, photoelectric effect 2.8, 3.1-3.2 2: 49, 53, 55, 57, 59, 85, 89 3: 37, 39, 41, 43, 73, 78, 97 Bohr model, line spectra, wave-particle duality, quantum numbers, orbitals 3.3-3.6 3: 51, 53, 57, 59, 61, 69, 71, 79 Electron configurations, structure of the periodic table 4.1-4.5 4: 45, 49, 51, 53, 55, 57, 59, 61, 63, 65, 75 4.6-4.8 Periodic trends: ionization energy, atomic radius, electron affinity, metallic character 4: 71, 73, 81, 85, 87, 89, 91, 103 Ionic and covalent bonding, simple Lewis structures, polyatomic ions 5.1-5.8 5:29, 39, 41, 45, 47, 49, 51, 53, 55, 57, 59, 65, 67, 69 Molar mass, mole concept for compounds, mass-mole-molecules interconversion, chemical 5.9-5.12 composition, empirical and molecular formulas, combustion analysis, structure of hydrocarbons 5: 71, 73, 77, 79, 83, 85, 87, 95, 97, 99, 103, 105, 107, 109, 113, 121, 123, 125 CHAPTER 1.1 - 5.8 EXAM I Electronegativity, bond polarity, Lewis structures, formal charge 6.1-6.4 6: 23, 27, 29, 31, 33, 35, 37, 39 ,41, 43 Resonance, exceptions to octet rule, bond energy, bond length 6.4-6.6 6: 45, 47, 49, 51, 75, 81, 83, 85, 97 VSEPR, polarity of molecules 6.7-6.10 6: 53, 55, 57, 59, 61, 63, 65, 67, 69, 71, 73 22.1-22.5, Organic chemistry: hydrocarbons, isomerization, nomenclature, functional groups 22.8 22: 37, 39, 43, 45, 51, 53, 55, 95, 99 7.1-7.3, Hybridization, sigma and pi bonding, balancing chemical equations 8.1-8.3 7: 31, 37, 39, 41, 43, 45. 8: 15, 17, 19, 21, 25, 27, 29, 31, 33 Stoichiometry, limiting reactant, percent yield, reactivity of groups 1A, 7A, combustion reactions 8.4-8.6 8: 39, 41, 43, 45, 49, 53, 55, 59, 61, 63, 65, 67, 71 Solutions, electrolytes, molarity, dilution problems, net ionic equations, precipitation reactions 9.1-9.5 9: 21, 23, 27, 29, 31, 33, 35, 37, 39, 41, 45 CHAPTER 5.9-8.6; 22 EXAM II Acid-base reactions, redox reactions 9.5-9.9 9: 47, 51, 53, 55, 57, 59, 61, 65, 67, 69 Energy, First law of thermodynamics, calorimetry, enthalpy 10.1-10.6 10: 33, 35, 37, 41, 43, 45, 47, 49, 51, 53, 55, 59, 61, 67, 69 Calculating ΔH using Hess’s Law, bond energies 10.7-10.10 10: 71, 73, 75, 77, 79, 81, 83, 85, 89 10.11 Lattice Energies, Born Haber cycle, nature of gases, measurement of pressure, gas laws 11.1-11.3 10: 91, 93, 94, 95, 96. 11: 25, 27, 29, 31 Gas laws, ideal gas equation, molar mass, density, partial pressure 11.3-11.6 11: 33, 35, 37, 39, 41, 45, 51, 55, 57, 59, 63, 65, 67, 69, 127 Kinetic molecular theory, diffusion, effusion, real gases 11.6-11.11 11:71, 73, 75, 77, 79, 81, 83, 85, 91, 92 Liquids, nature of intermolecular forces 12.1-12.4 12: 33, 35, 37, 39, 45, 47 EXAM III CHAPTER 9.1-11.11 12.5-12.8 Vapor pressure, heating curves, phase diagrams 13.1-13.2 12: 41, 51, 53, 55, 57, 63, 65, 67. 13: 19 Solids, unit cells, crystal structures 13.3-13.7 13: 27, 29, 31, 35, 37, 39, 41, 45, 47 Final exam review 5/7, Th FINAL EXAM
© Copyright 2026
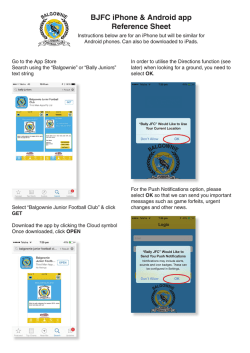






![TIME TABLE MARCH-APRIL 2015 V I III[IMP/BL]](http://s2.esdocs.com/store/data/000483508_1-7e40507e02bf7111da7196362309b7b4-250x500.png)